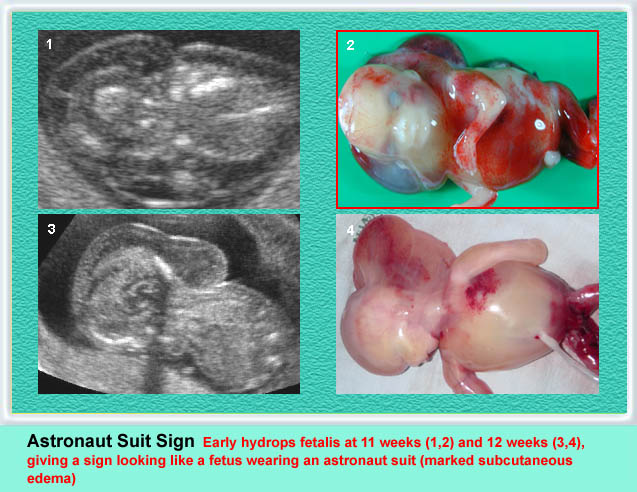
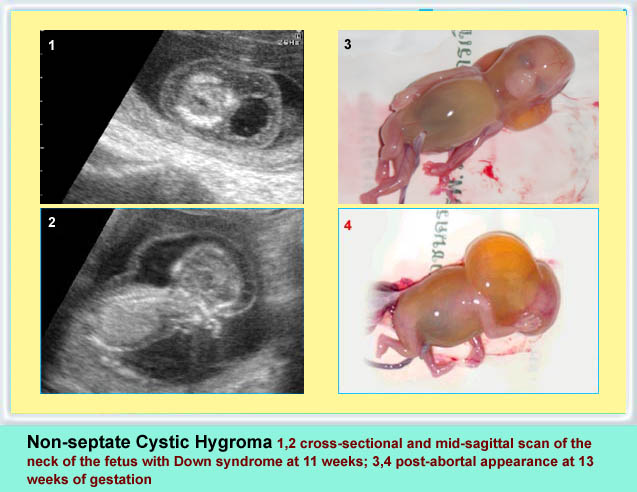
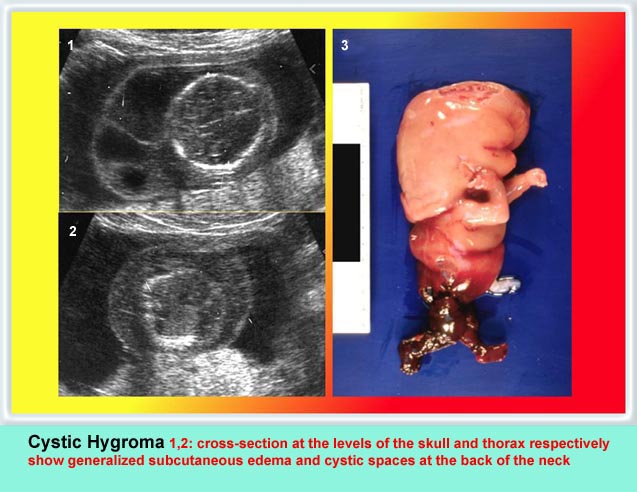
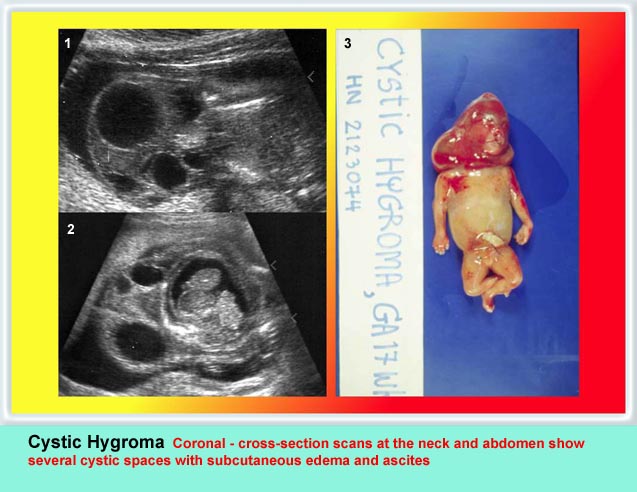
Cystic Hygroma
บทนำ
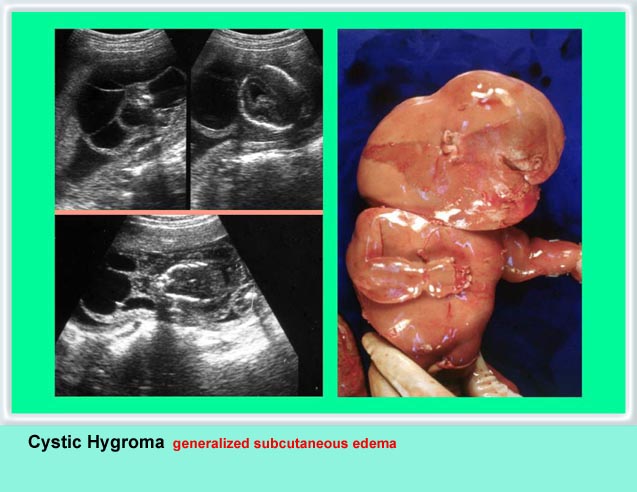
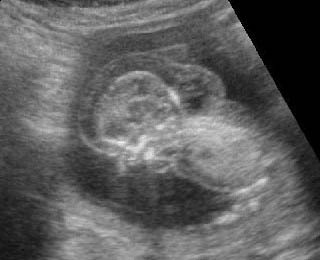
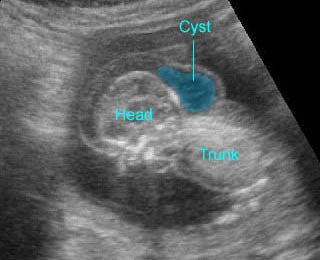
Cystic hygroma เป็นก้อนบริเวณคอทารกที่ตรวจพบได้บ่อยที่สุด คือราว 1 ต่อ 200 ของการแท้ง เกิดจากท่อน้ำเหลืองพัฒนาไม่ดี โดยปกติแล้ว การระบายน้ำเหลืองจะเทเข้าสู่สอง sac ใหญ่ที่อยู่ด้านข้างของ jugular veins ถ้าระบบท่อน้ำเหลืองไม่สามารถเชื่อมติดต่อกับหลอดเลือดดำได้ jugular lymph sac ก็จะขยายโตขึ้น และกลายเป็น cystic hygroma ที่ posterior triangle ของคอ ถุงน้ำที่โตขึ้นบริเวณคอนี้มักจะกินเนื้อที่อยู่ทางด้านข้างและด้านหลัง และมีแผ่นกั้นแยกช่องภายใน แต่กั้นแบบไม่สมบูรณ์ แผ่นกั้นแนวกลางจะค่อนข้างหนาแบ่งถุงออกเป็นสองซีก แผ่นกั้นนี้คือ nuchal ligament บ่อยครั้งที่พบว่าทารกบวมทั่ว ๆ ไปด้วย (hydrops) สัมพันธ์กับความผิดปกติของโครโมโซมร้อยละ 65 ซึ่งที่พบบ่อยที่สุดคือ Turner’s syndrome นอกจากนั้นอาจเป็น trisomy 21, 18
รายที่โครโมโซมปกติก็จะมีโอกาสให้ผลการตั้งครรภ์ที่ปกติได้ และฝ่อหายได้เองเป็นจำนวนมาก แต่ถ้ามีภาวะบวมน้ำพยากรณ์จะแย่เสมอ กรณีที่เดี่ยว ๆ ที่ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับความผิดปกติที่อื่นเลยนั้น และไม่มีภาวะบวมน้ำสามารถผ่าตัดแก้ไขได้และมีพยากรณ์ดี
ลักษณะทางคลื่นเสียงความถี่สูง
ลักษณะทางคลื่นเสียงความถี่สูงที่ช่วยแยก cystic hygroma จากก้อนอื่น ๆ ของกระโหลกและคอ
- กระโหลกไม่มีรอยโหว่ กระดูกสันหลังไม่มีรอยแยก
- ไม่มีส่วนเนื้อตันเป็นส่วนประกอบภายใน
- ตำแหน่งโดยแบบฉบับแล้วอยู่ที่ด้านหลังและด้านข้างของคอ
- ถุงน้ำมีแผ่นกั้นแยกห้องภายใน
- แผ่นกั้นค่อนข้างหนาที่แนวกลาง (nuchal ligament)
- ไม่มีความผิดปกติในกระโหลกศีรษะ
- ลักษณะของภาวะบวมน้ำ ๆ ต่าง ๆ จะพบในรายรุนแรง ซึ่งได้แก่การมีน้ำในช่องท้อง ช่องปอด ชั้นใต้ผิวหนังบวมทั่ว ๆ ไปเป็นต้น
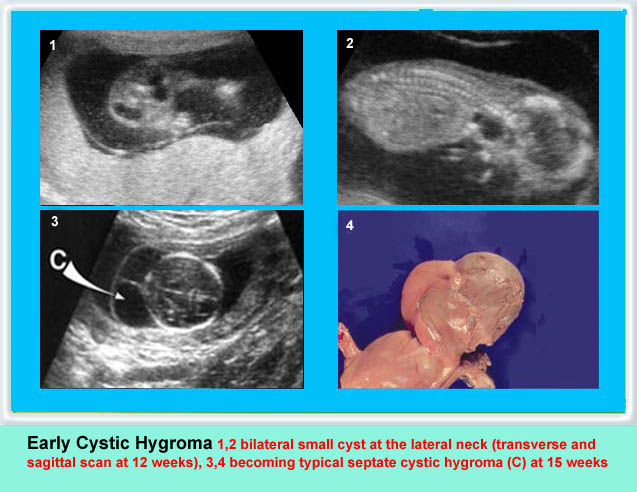
Early cystic hygroma with hydrops fetalis
Sagittal scan: cyst posterior to the fetal neck with subcutaneous edema and ascites
Early cystic hygroma with hydrops fetalis
Sagittal scan of the neck at 10 weeks: cyst posterior to the fetal neck with subcutaneous edema
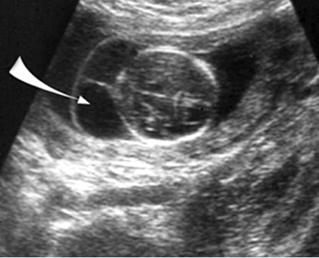
Non-septate early cystic hygroma
Cross-sectional scan of the neck at 10 weeks: non-septate cyst posterior to the fetal neck
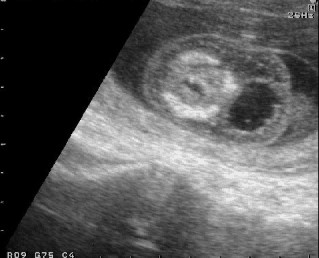
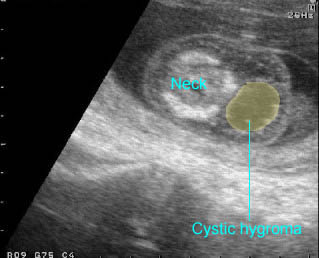
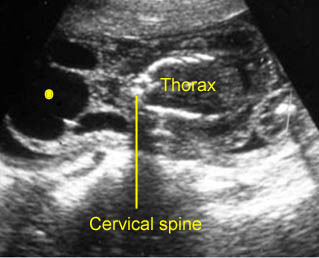
Early cystic hygroma
Cross-sectional scan of the neck at 12 weeks: bilateral cyst lateral to ther fetal neck
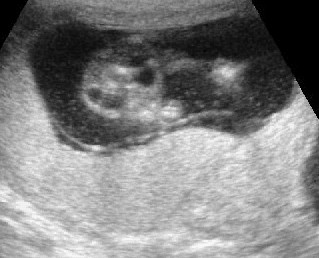
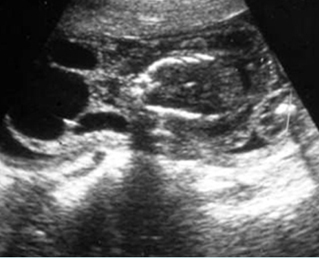
Cystic hygroma
Oblique cross-sectional scan at the level of cerebellum: anechoic cyst (arrow) with central septum
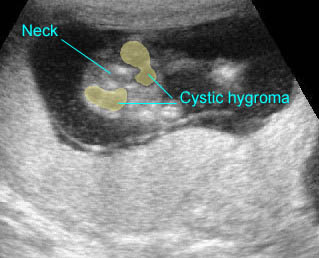
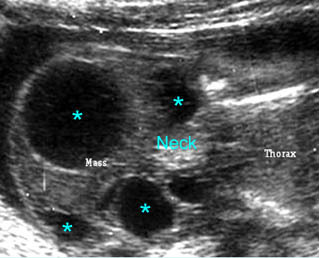
Cystic hygroma
Oblique coronal scan at the neck: multiple anechoic cysts with thickened septum at the posterior aspect of the neck
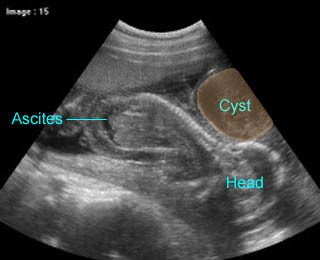
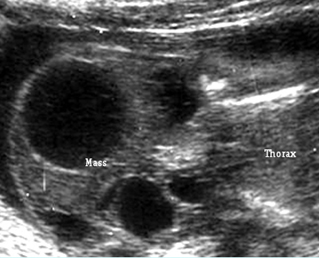
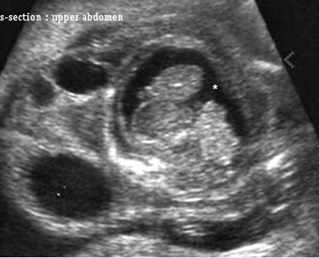
Cystic hygroma with hydropic changes
Cross-section scan of the abdomen: anechoic cysts (solid circle) in subcutaneous edema (extending from the neck area) (* = ascites)
Cystic hygroma
Oblique coronal scan at the neck: anechoic septate cyst (solid circle) at the posterior aspect of the neck
Classic Images