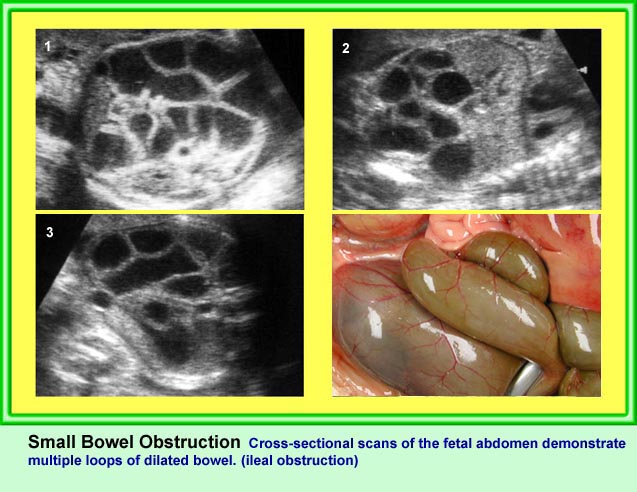
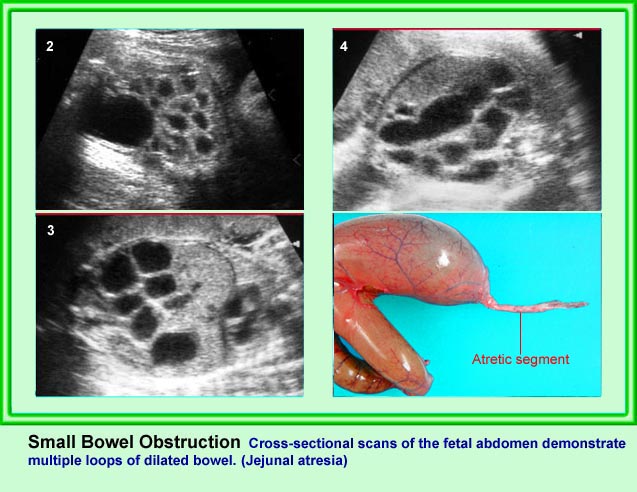
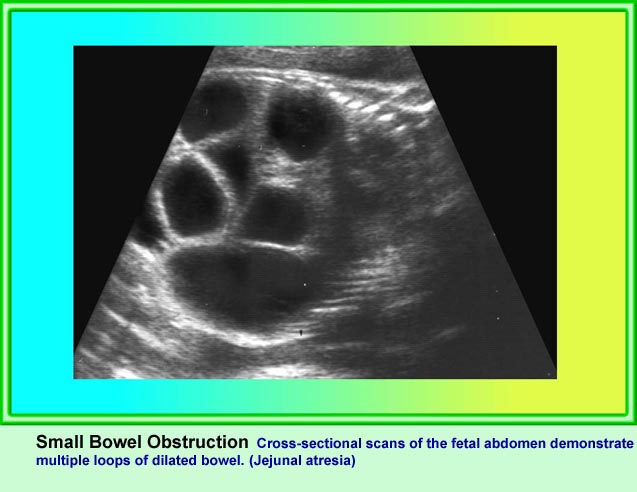
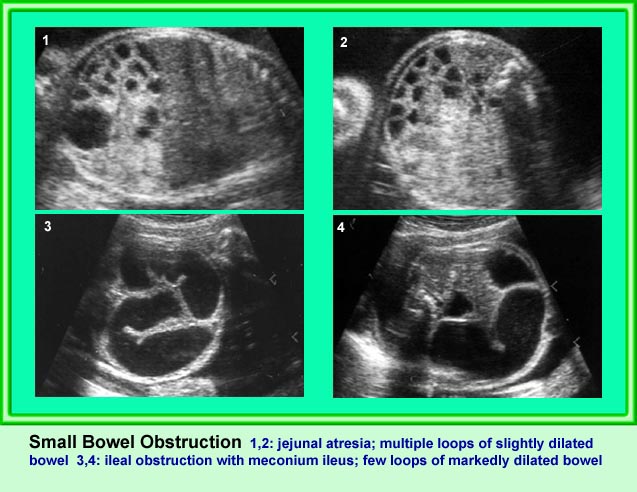
Jejunoileal Atresia
บทนำ
ลำไส้เล็กตีบตัน (นอกจากดูโอดีนั่ม) พบได้ราว 1:3,000-1:5,000 ของการคลอด ซึ่งตำแหน่งที่ตีบตันคือ เจจูนั่มส่วนต้น (ร้อยละ 31) เจจูนั่มส่วนปลาย (ร้อยละ 20) ไอเลียมส่วนต้น (ร้อยละ 13) และไอเลียมส่วนปลาย (ร้อยละ 6) ร้อยละ 33 ของลำไส้เล็กขยายจากการตีบตันเกิดจาก cystic fibrosis มีความสัมพันธ์กับความผิดปกติอื่น ๆ นอกทางเดินอาหารได้น้อย (น้อยกว่าร้อยละ 7) ไม่สัมพันธ์กับความผิดปกติทางโครโมโซม
ลักษณะทางคลื่นเสียงความถี่สูง
ลักษณะทางคลื่นเสียงของลำไส้เล็กตีบตันที่พบได้บ่อย ๆ
- ครรภ์แฝดน้ำ
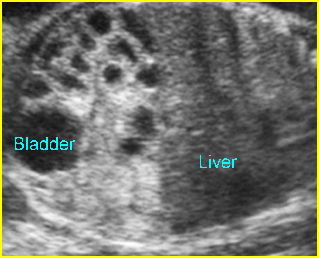
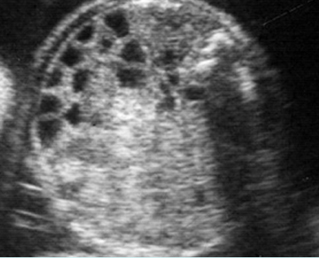
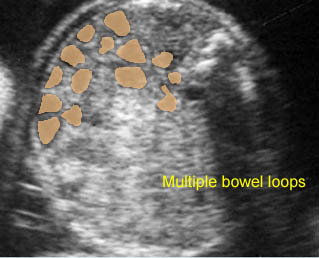
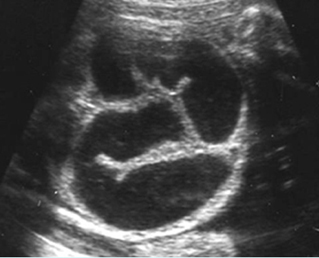
- ลำไส้เล็กหลาย ๆ ขดขยายขนาดโตขึ้น (มากกว่า 7 มม.)
- พบการบีบตัวลำไส้เพิ่มขึ้น
การขยายของลำไส้เล็กอาจตรวจพบได้ในภาวะอื่นนอกจากลำไส้เล็กตีบตัน คือ volvulus และ meconium ileus สำหรับภาวะอื่นที่อาจสับสนกับการขยายของลำไส้ได้ ได้แก่ การขยายของหลอดไตในบางราย ถุงน้ำรังไข่ หรือ mesenteric cyst ซึ่งการตรวจอย่างรอบคอบจะช่วยแยกกันได้
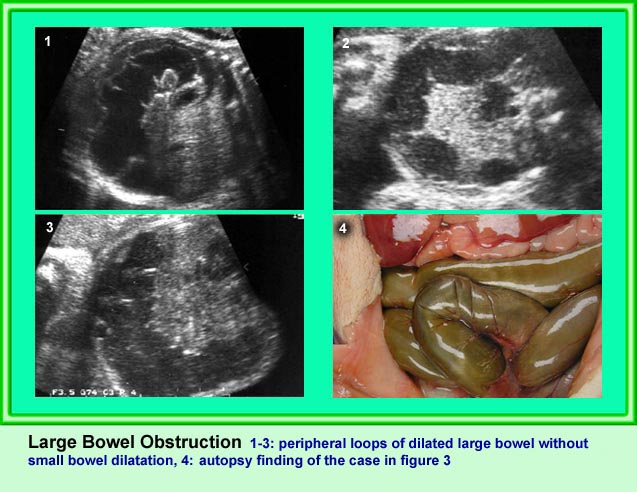
Small bowel obstruction
Coronal scan of the abdomen: Multiple loop of small bowel loops with marked dilatation (*) (arrow = diaphragm)
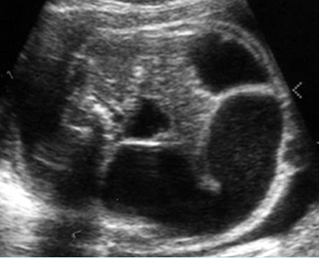
Small bowel obstruction
Coronal scan of the abdomen: Multiple dilated loops of small bowel
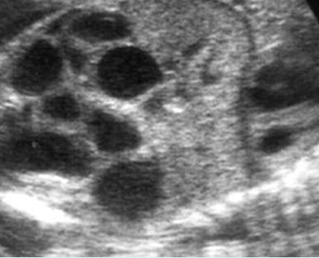
Small bowel obstruction
Cross-sectional scan of the abdomen: Multiple dilated loops of small bowel (arrowhead = spine)
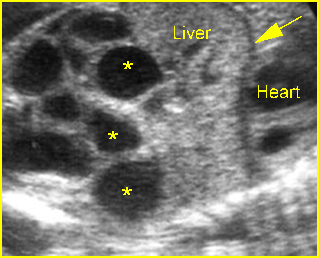
Small bowel obstruction
Cross-sectional scan of the abdomen: Multiple loops of small bowel with marked dilatation (arrowhead = spine)
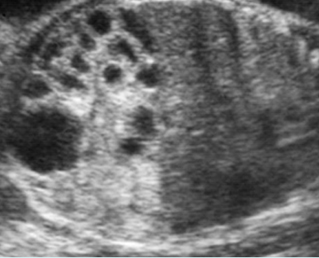
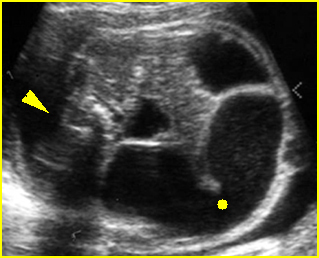
Small bowel obstruction
Cross-sectional scan of the abdomen: Markedly dilated loops of small bowel (solid circle) (arrowhead = spine)
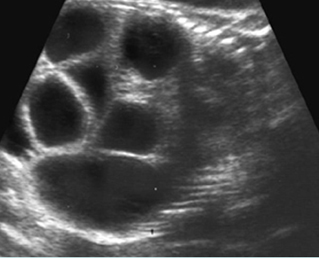
Small bowel obstruction
Coronal scan of the fetal abdomen: markedly dilated loops of the small bowels
Classic Images