Sacrococcygeal Teratoma
บทนำ
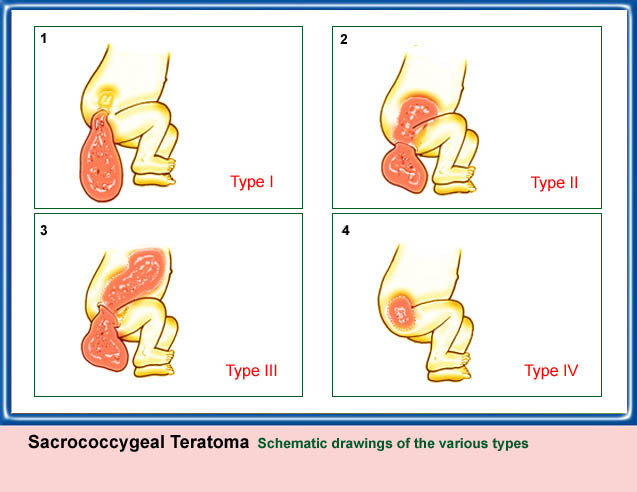
Sacrococcygeal Teratoma (SCT) เป็นเนื้องอกของเซลล์ตัวอ่อนของกระดูกก้นกบ เป็นก้อนยื่นออกไปทางข้างหลังเป็นส่วนมาก พบได้น้อย คือ 1 ต่อ 35,000 ของการคลอด แต่ก็นับว่าเป็นเนื้องอกที่พบได้บ่อยที่สุดของทารกแรกคลอด ร้อยละ 75 เป็นทารกเพศหญิง มีความผิดปกติของกระดูกและกล้ามเนื้อ ทางเดินปัสสาวะ และระบบประสาทร้อยละ 18 ภาวะทารกบวมน้ำก็พบร่วมได้บ่อย
ลักษณะทางคลื่นเสียงความถี่สูง
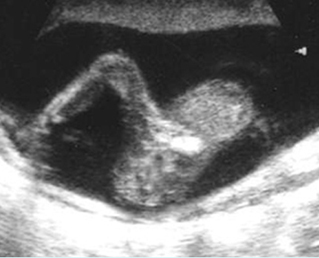
- ส่วนใหญ่พบเป็นก้อนเนื้อตัน หรือก้อนผสม ดูซับซ้อน มีประมาณร้อยละ 15 ที่เป็นถุงน้ำอย่างเดียว บริเวณที่เป็นเนื้อตันประกอบด้วยเนื้อเยื่อแตกต่างกัน ให้ความเข้มเสียงแตกต่างกัน เช่น กระดูกอ่อน ตับ อาจมีกระดูก ฟัน หรือบริเวณที่มีหินปูนจับด้วย ส่วนที่เป็นถุงน้ำมักจะมีขอบเขตไม่สม่ำเสมอ มักมีส่วนที่อยู่ในอุ้งเชิงกรานด้วย
- ครรภ์แฝดน้ำ ภาวะบวมน้ำ และรกโต พบร่วมได้บ่อย ๆ
- การวินิจฉัยแยกโรคที่สำคัญคือ myelomeningocele ซึ่งมักเป็นถุงน้ำ อาจมีส่วนเนื้อตัน อยู่ที่บริเวณ lumbosacrum
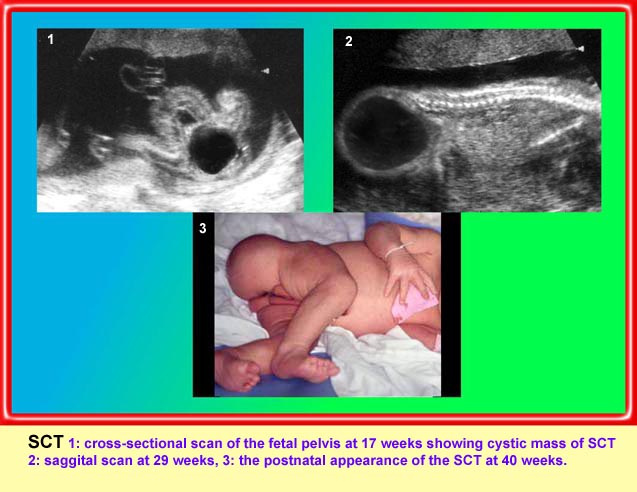
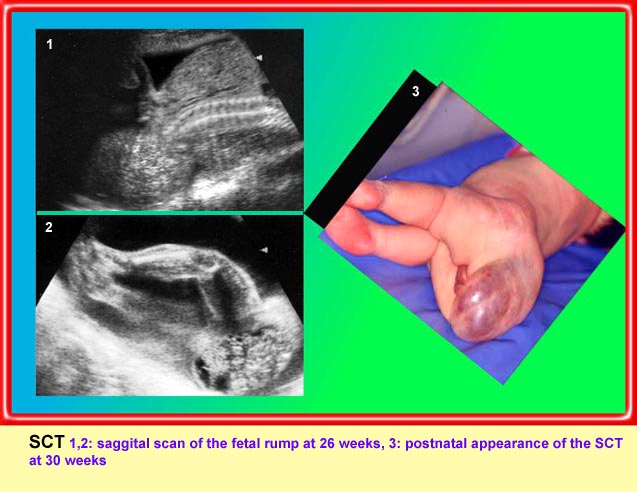
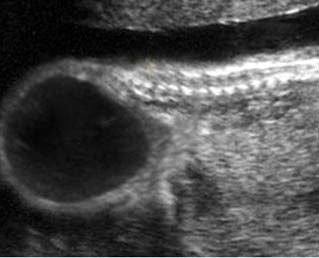
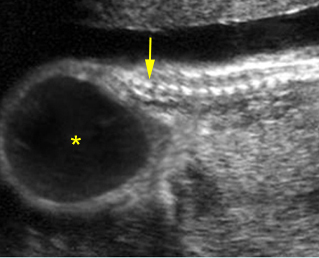
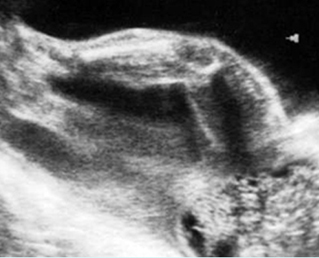
Sacrococcygeal teratoma
Sagittal scan of the lower spine (29 weeks): cystic mass (*) located at the end of sacrum (arrow)
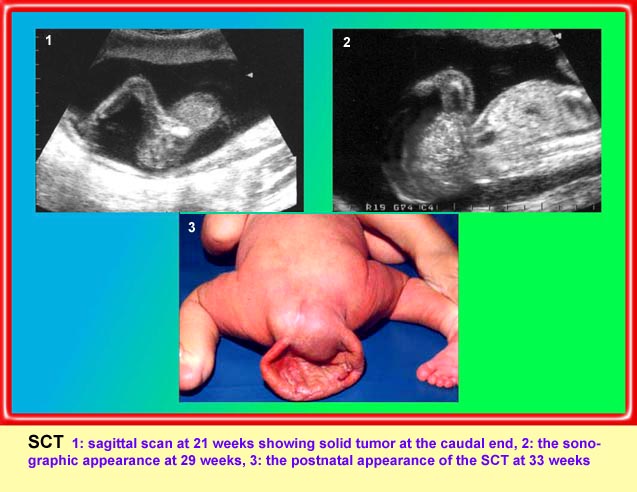
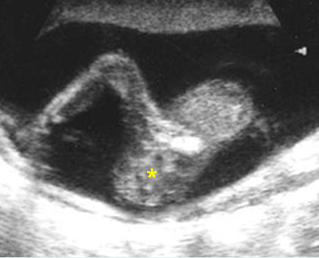
Sacrococcygeal teratoma
Sagittal scan of the spine (21 weeks): abnormal complex solid mass with heterogeneous echodensity (*) located at the end of sacrum
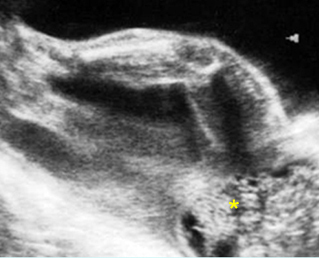
Sacrococcygeal teratoma
Sagittal scan of the spine (26 weeks): abnormal complex solid mass with heterogeneous echodensity (*) located at the end of sacrum
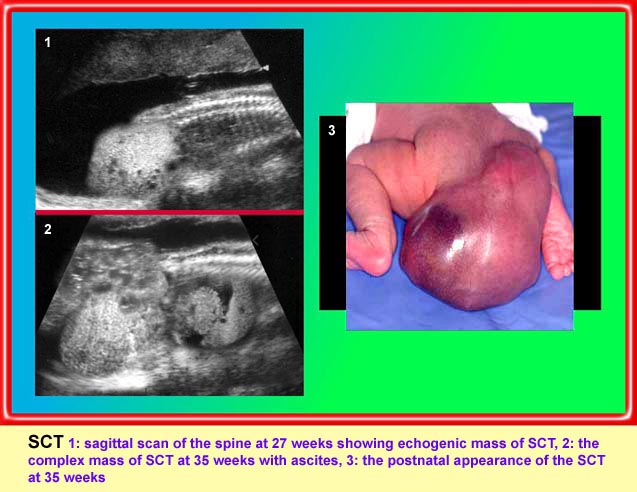
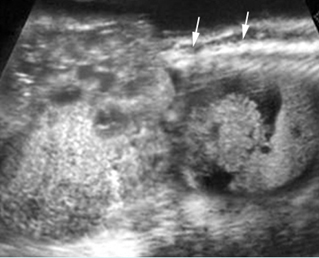
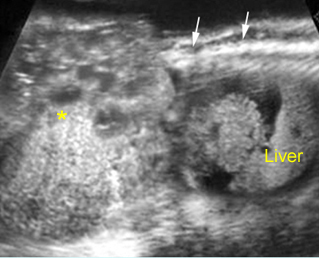
Sacrococcygeal teratoma
Sagittal scan of the spine (35 weeks): bizarre complex solid mass with heterogeneous echodensity (*) located at the end of sacrum (arrow) and complicated with ascites
Classic Images