{tab=Clinical Review}
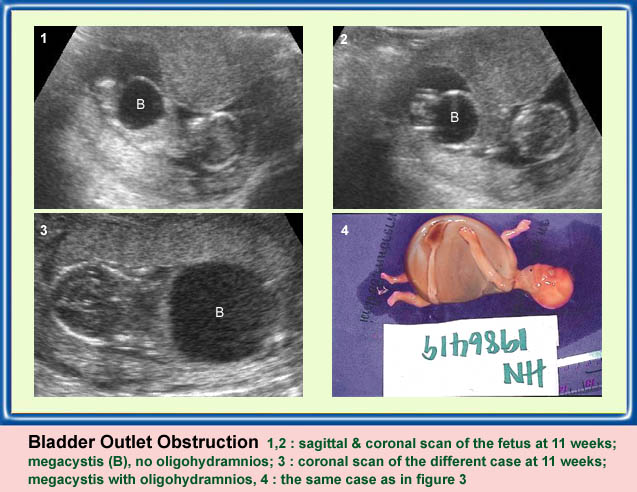
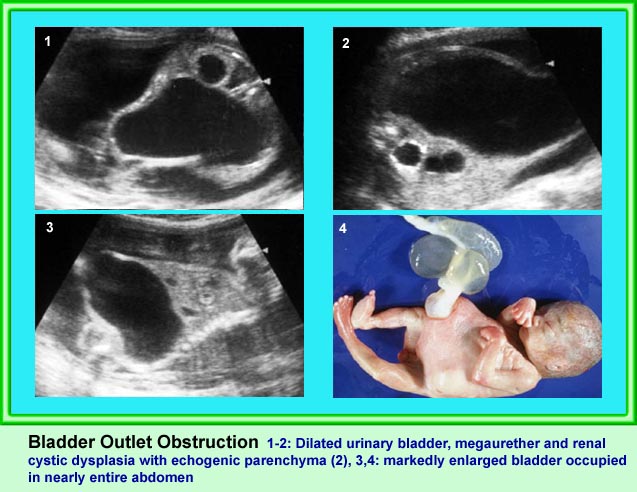
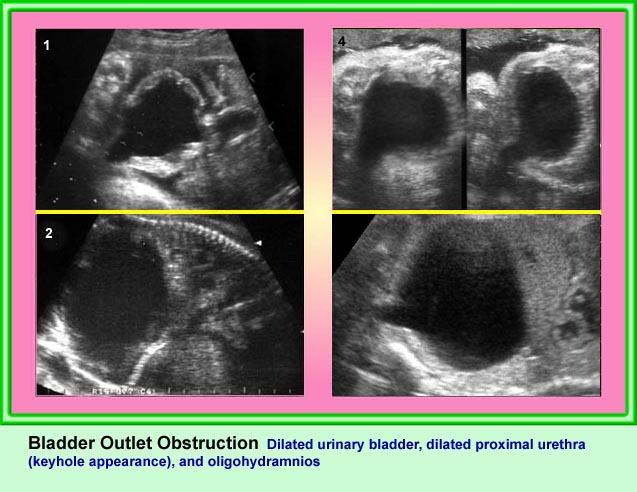
Bladder Outlet Obstruction
บทนำ
Bladder outlet obstruction ส่วนมากเกิดจาก posterior urethral valve (PUV) ซึ่งนับเป็นสาเหตุที่พบได้บ่อยที่สุด ของกระเพาะปัสสาวะโป่งขยาย มักไม่อุดตันโดยสมบูรณ์ จึงมีน้ำคร่ำในระดับใกล้เคียงปกติ แต่มีการคั่งของปัสสาวะย้อนกลับขึ้นไปส่วนบน ทำให้มีการโป่งขยายขึ้นตลอดแนว อุดตันสนิทก็จะมีน้ำคร่ำน้อยมาก กระบังลมสูง ปอดแฟบ พยากรณ์โดยทั่วไปดี
ประมาณร้อยละ 20-25 ของ PUV จะมีความผิดปกติอื่น ๆ ของระบบทางเดินปัสสาวะ-ท่อสืบพันธุ์ร่วมด้วย ซึ่งได้แก่ ท่อปัสสาวะสองอัน ท่อปัสสาวะโต อัณฑะไม่เคลื่อนลง และ hypospadias ความผิดปกติอื่น ๆ ที่พบได้ ได้แก่ patent ductus arteriosus หลอดลมเล็ก mitral stenosis รูทวารหนักไม่เปิด หลังคด
ลักษณะทางคลื่นเสียงความถี่สูง
- กระเพาะปัสสาวะและท่อปัสสาวะส่วนต้นโป่งขยายตลอดเวลา
- ผนังกระเพาะปัสสาวะหนาตัวขึ้น กระเพาะปัสสาวะมักเป็นรูปลูกแพร์
- น้ำคร่ำน้อย (ร้อยละ 50)
- กรวยไตและหลอดไตขยาย (ร้อยละ 40) ถ้าเป็นนานไตอาจฝ่อ (ขนาดเล็กลงและทึบเสียงมากขึ้น)
- ส่วนมากเป็นทารกเพศชาย
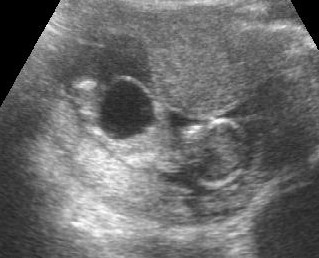
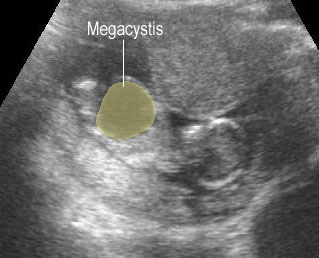
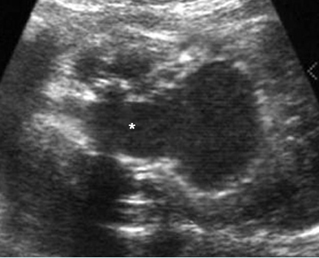
Early bladder outlet obstruction
Sagittal scan of the trunk: marked dilatation of the bladder, amniotic fluid is present
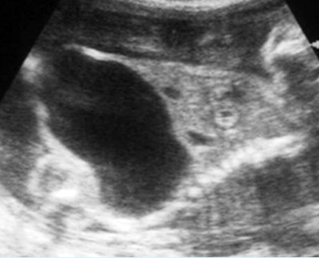
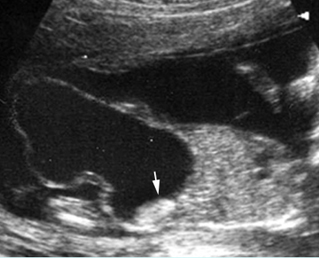
Bladder outlet obstruction
Sagittal scan of the trunk: marked dilatation of the bladder (solid circle) with protrusion of the lower abdomen (arrow = diaphragm)
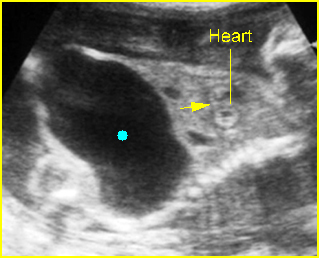
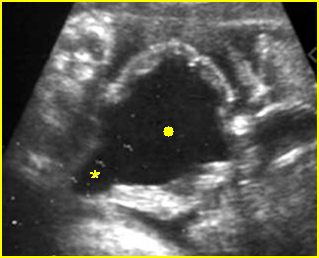
Bladder outlet obstruction
Coronal scan of the lower abdomen: dilatation of the bladder (solid circle) with thickened wall; dilatation of the proximal urethra giving the key-hole appearance (*)
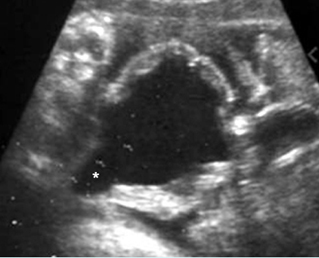
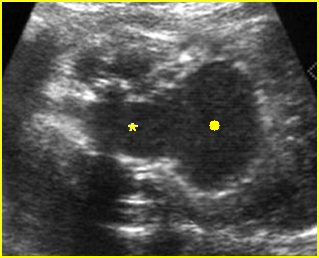
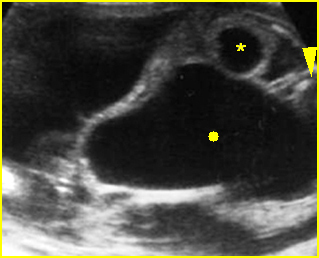
Bladder outlet obstruction
Coronal scan of the lower abdomen: dilatation of the bladder (solid circle) with marked dilatation of the proximal urethra giving the key-hole appearance (*)
Bladder outlet obstruction
Cross-sectional scan of the abdomen: marked dilatation of the bladder (solid circle) and ureter (*)with protrusion of the lower abdomen (* arrowhead = spine)
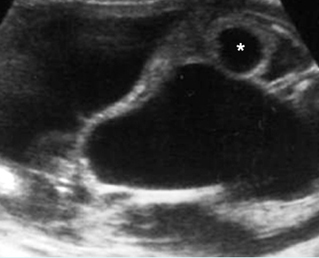
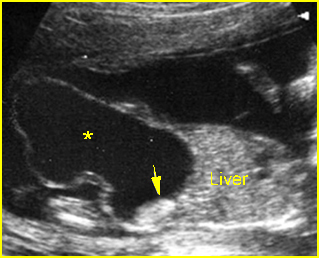
Bladder outlet obstruction
Sagittal scan of the trunk: marked dilatation of the bladder (*) with protrusion into the umbilical cord to form urachal cyst (arrow = echogenic real dysplasia)
Classic Images