Limb-Body Wall Complex (LBWC)
LBWC or body-stalk anomaly or cyllosomas is a complex set of disruptive abnormalities consisting of failure of the anterior abdominal wall to close, short umbilical cord, disruption of the lateral body wall, distinctive scoliosis of the spine, limb defects, non-fusion of the amnion and chorion. Therefore, the amnion does not cover the cord but extends as a sheet from the margin of the cord to be continuous with the body wall and placenta.
Incidence: Sporadic, 1 in 15,000 (1:3000-42,000) births; a higher incidence was observed among mothers with a history of cigarette, alcohol and marijuana use.
Sonographic findings:
- Large body wall defect allowing abdominal contents to herniate. Fig1, Fig2
- The umbilical cord is absent or is a very short segment with a single umbilical artery. Fig3, Fig4
- The fetal abdomen is connected directly to the placenta.
- Scoliosis is evident in most cases. Fig5, Fig6
- Limb anomalies in most cases, including clubfeet, oligodactyly, arthrogryposis, absence of limbs, single forearms, split hand and feet.
- Craniofacial defects frequently seen.
- An extremely elevated level of maternal serum-alpha-fetoprotein (MSAFP) is also indicative of LBWC.
- Other associated anomalies.
- Three-dimensional ultrasound may be helpful.
- For first trimester diagnosis, the upper part of the fetal body is in the amniotic cavity, whereas the lower part is in the coelomic cavity.
- Differential diagnoses include other types of abdominal wall defects and amniotic band syndrome which may have very similar features.
- Pitfalls: Some cases have been initially misdiagnosed as omphalocele or gastroschisis, for which the prognosis is much better.
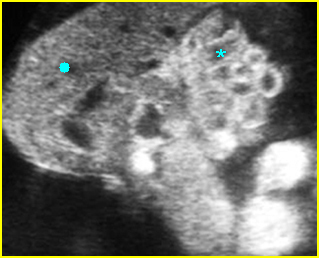
Fig 1: Limb-body wall complex Free floating complex mass containing abnormal shaped liver (solid circle) and bowel (*)
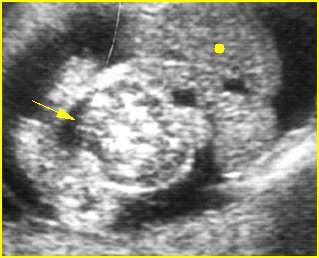
Fig 2: Limb-body wall complex Free floating complex bowel (arrow) and liver (solid circle) in the amniotic fluid
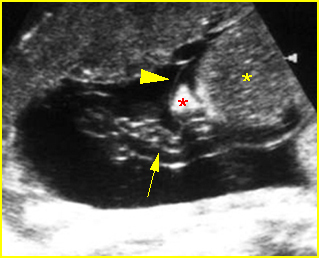
Fig 3: Limb-body wall complex Free floating complex mass containing liver (*) with covering membrane (arrowhead), short umbilical cord (arrow) originating from the placenta to the mass
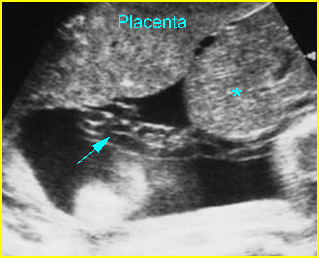
Fig 4: Limb-body wall complex Free floating complex mass containing liver (*) with short umbilical cord (arrow) originating from the placenta to the mass
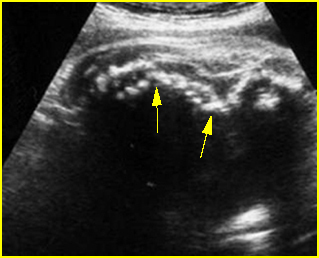
Fig 5: Kyphoscoliosis Sagittal scan of the fetal trunk: disorganized spine in association with limb-body wall complex
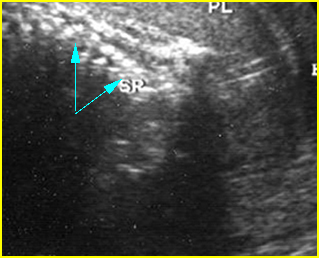
Fig 6: Disorganized spine Coronal scan of the fetal spine: disorganized spine (arrow) in association with limb-body wall complex
Video clips of limb-body wall complex (LBWC)
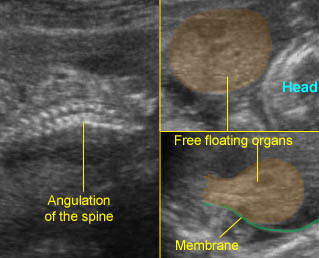
LBWC : Sagittal to cross-sectional scan of the abdomen: Extensive abdominal wall defect with free floating visceral structures Note: covering membrane and spinal angulation
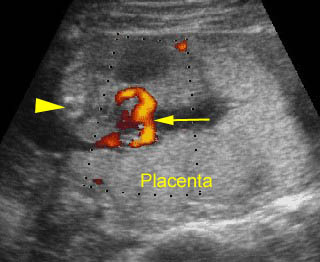
Limb-body wall complex : Cross-sectional scan of the abdomen: the total length of the cord from the fetal insertion to placental insertion (arrow) (arrow = spine)
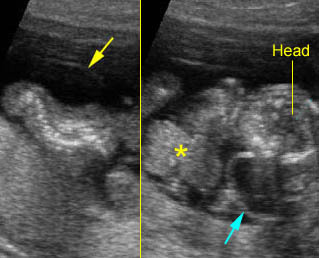
Limb-body wall complex : Coronal scan of the fetal spine: scoliosis associated with limb body wall complex
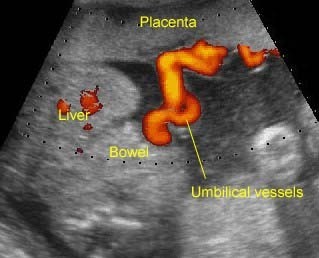
LBWC : Limb-body-wall complex: the umbilical vessels running directly from the placenta to the free floating visceral structures without true umbilical cord
Associations: Other than typical defects, other anomalies are also often seen, especially craniofacial or neural tube defects.
Management: Termination of pregnancy can be offered.
Prognosis: Uniformly fatal.
Recurrence risk: Sporadic (rare recurrence).

