Renal Cysts
Sonographic differential diagnosis of common renal cystic conditions
Fig 1, Fig 2, Fig 3, Fig 4
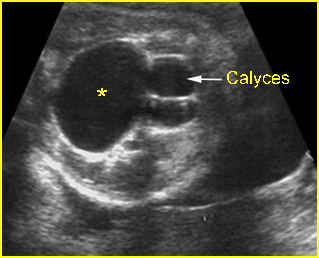
Fig 1: Hydronephrosis Cross-sectional scan of the abdomen: markedly dilated renal pelvis (*) with calyces (arrow)
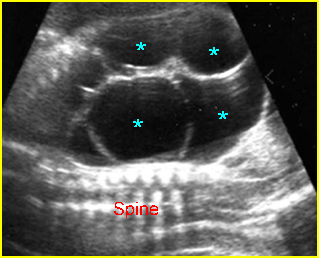
Fig 2: Multicystic kidney Sagittal scan of the abdomen: multiple cysts varying in size in the kidney
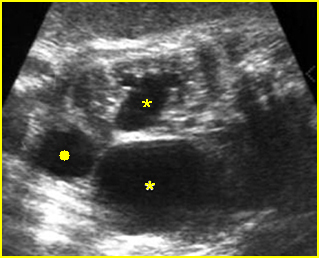
Fig 3: Hydronephrosis Coronal scan of the abdomen: bilateral dilated renal pelvis (*) (solid circle = bladder)
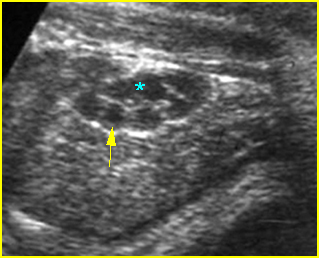
Fig 4: Normal kidney The kidneys consisting of multiple normal pyramids (arrow), looking like multicystic kidney (* = renal pelvis)
Video clips of renal cysts
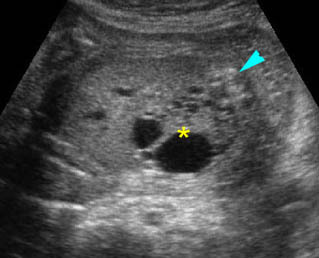
Renal cystic dysplasia: Cross-sectional scan of the abdomen: muliticystic kidney (*) with oligohydramnios and absent contralateral kidney
Severe hydronephrosis:
- visible renal parenchyma
- peripheral oval cysts communicating with each other and the renal pelvis
- often ureteral dilatation
- underlying cause in some cases such as bladder outlet obstruction
- abnormalities in the contralateral kidney (10-40%)
Autosomal recessive polycystic kidneys
- bilateral enlarged echogenic kidneys with reniform shape
- oligohydramnios
Multicystic kidney disease
- multiple round non-communicating cysts of variable size
- multiple cysts with grape-like appearance in many cases
- unilateral (77%)
- abnormalities in the contralateral kidney (39%)
Renal cystic dysplasia
- echogenic parenchyma and subcapsular or cortical cyst
- evidence of hydronephrosis in some cases
- evidence of an underlying cause such as bladder outlet obstruction in some cases

