Ebstein’s Anomaly
Ebstein’s anomaly is characterized by the congenital downward displacement of the tricuspid valve on the interventricular septum and posterior displacement of the valve with severe dysplasia of the right ventricle. As a result, the right atrium is typically massively enlarged. The valvular orifice is formed within the ventricular cavity at the junction of the atrialized inlet and functional ventricular components.
Fig 1
Incidence: Rare, accounting for only 1% of cardiac anomalies.
Sonographic findings:
Fig2
- Low insertion of the tricuspid valve, demonstrated in FCV.
- The right atrium is unusually enlarged.
- Small right ventricle or dysfunction.
- Doppler study may often show some degree of tricuspid regurgitation, possibly leading to hydrops fetalis.
- Normal FCV excluding the possibility of Ebstein’s anomaly.
- The normal reference range of the mitral valve-tricuspid valve distance has been described for each gestational week, allowing identification of abnormal downward displacement of the medial tricuspid cusp in the case of Ebstein’s anomaly.
- Differential diagnosis:
- Pulmonary atresia with infarct ventricular septum.
- Tricuspid valve regurgitation can occur in 6-7% of normally grown fetuses, but the valve morphology and size are normal.
- Uhl’s anomaly (right anterior ventricular wall dilated due to the defect of cardiac muscle) of the heart mimicking Ebstein’s anomaly.
- Usually diagnosed after 16-18 weeks
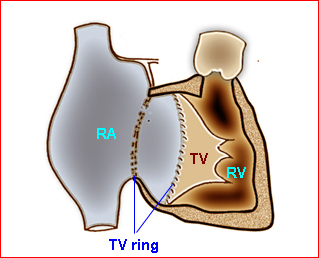
Fig 1: Schematic drawing of Ebstein anomaly showing downward displacement of the tricuspid valves (RA = right atrium, RV = right ventricle, TV = tricuspid valves)
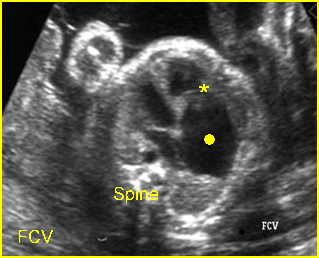
Fig 2: Ebstein anomaly Four-chamber view: enlarged atrium (solid circle) with low attachment of tricuspid valve (*)
Video clips of Ebstein’s anomaly
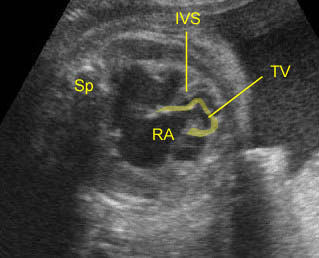
Ebstein’s anomaly: Extremely low insertion of the tricuspid valve (TV) with marked cardiomegaly (IVS = interventricular septum, RA = right atrium, Sp = spine)
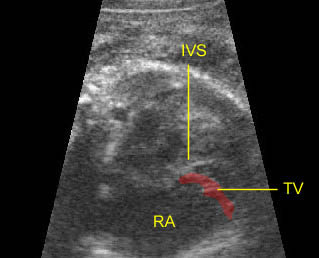
Ebstein’s anomaly: Low insertion of the tricuspid valve (TV) with marked cardiomegaly (IVS = interventricular septum)
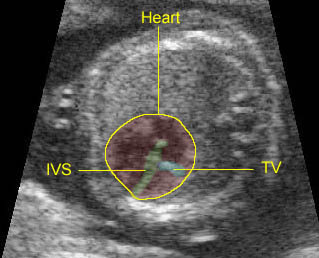
Ebstein’s anomaly: Ebstein’s anomaly in case of corrected transposition of great arteries: Low insertion of the tricuspid valve (TV) of the left-sided right ventricle (IVS = interventricular septum)
Associations: Other cardiac defects; e.g. pulmonary stenosis, ASD, TOF, TGA.
Management: Termination may be offered in the case of fetuses with associated anomalies or pulmonary atresia or severe tricuspid regurgitation with enlarged right ventricle. In continuing pregnancies, serial ultrasound examinations should be performed and delivery should be performed where immediate pediatric cardiac consultation is available.
Prognosis: Poor in most cases but better in mild cases with appropriate surgical correction.

