Abnormal Great Artery View
Example: Fig 1, Fig 2, Fig 3, Fig 4
Enlarged aortic root
- Tetralogy of Fallot (most common)
- Truncus arteriosus
- Pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect
Small aortic root
- Hypoplastic left ventricle (most common)
- Coarctation or interruption of aorta
Small pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary stenosis or atresia
- Tetralogy of Fallot
Overiding aorta
- Tetralogy of Fallot (most common)
- Pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect
- Truncus arteriosus
- Double-outlet right ventricle
Parallel of the great arteries
- Transposition of great arteries
- Double-outlet right ventricle
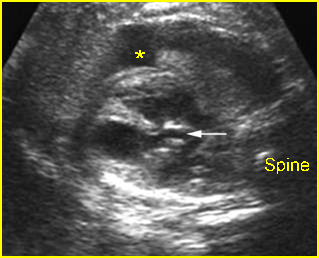
Fig 1: Aortic stenosis Long axis view: small aorta (arrow) (* = pleural effusion)
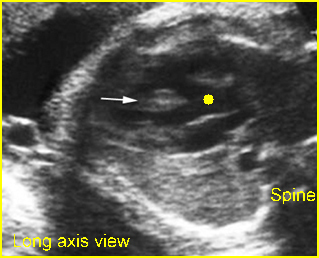
Fig 2: Overriding aorta Long axis view: aortic root (solid circle) running from both ventricles (arrow = interventricular septum)
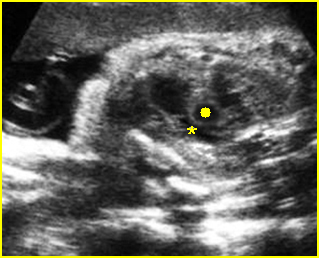
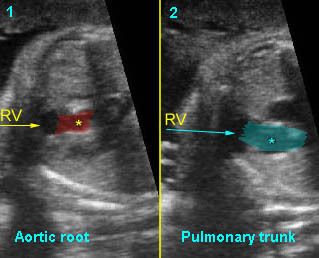
Fig 3: Pulmonary stenosis (in case of TOF) Long axis view of the heart: small pulmonary trunk (*) compared to aortic root (solid circle)
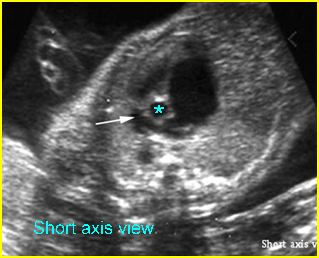
Fig 4: Hypoplastic right heart syndrome Short-axis view: small pulmonary trunk (arrow) compared to aorta (*) with large atrium
Video clips of abnormal great artery view
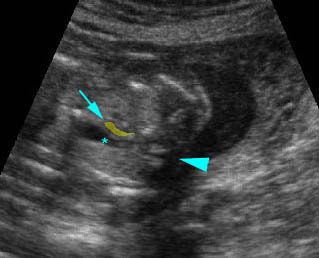
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome:
– Long-axis view: small aortic root (*) arising from small left ventricle (arrowhead = spine)
– Arch view: small aortic arch (*), compared to large ductal arch (arrowhead = spine)
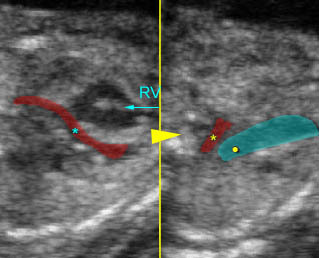
Double outlet of right ventricle :
Long-axis view
1) Aortic root arising from right ventricle
2) Pulmonary trunk arising from right ventricle
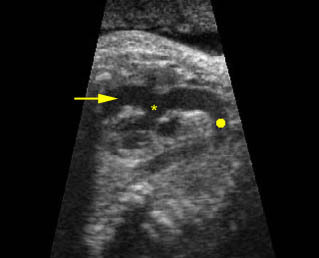
Coarctation of aorta: Arch view at the upper thorax, extremely small aortic arch (arrow) compared to ductal arch (*) (arrowhead = spine)
Overding aorta: Longitudinal scan of the aoratic arch; * overiding aorta, solid circle = aortic arch, arrow = right ventricle
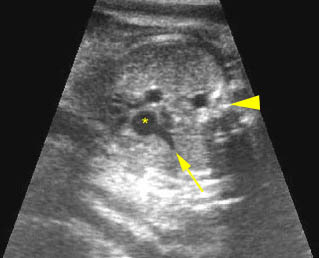
Truncus arteriosus: Common trunk (aortic root) overiding both ventricles; small pulmonary artery (arrow) originating from the common trunk (*), (arrowhead =spine)

