Abnormal Spinal Curvature
These abnormalities include kyphoscoliosis, hemivertebrae, angulations or disorganized vertebral structures. Scoliosis, an abnormal lateral deflection of the spinal column, is the most common in this category.
Fig 1, Fig 2, Fig 3, Fig 4
Sonographic differential diagnosis:
- Normal
- Meningomyelocele (common)
- LBWC (uncommon)
- Amniotic band syndrome (uncommon)
- Skeletal dysplasia
- VATER or VACTERL associations (rare)
- Isolated hemivertebrae
- Iniencephaly (very rare)
- Caudal regression syndrome
Note:
- Hemivertebrae are an example of congenital scoliosis resulting from failure of segmentation, which is mostly associated with other anomalies.
- The normal flexible skeleton can be subject to strong deformation forces in utero resulting in transient scoliosis.
- Gross skeletal defects, including absent ribs or hemivertebrae, associated with lateral spinal deflection probably represent truly pathologic scoliosis.
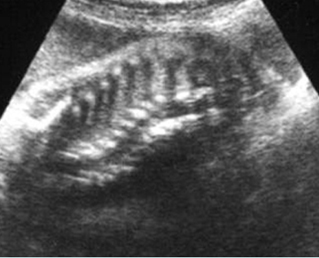
Fig 1: Scoliosis Coronal scan of the spine: scoliosis of spine at the thoracic region (arrow)
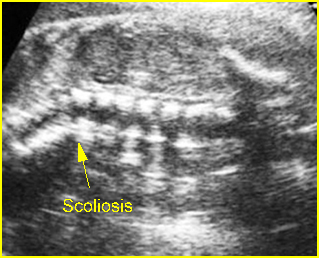
Fig 2: Angulation of spine Coronal scan of the spine: angulation of spine at the thoraco-lumbar region (arrow)
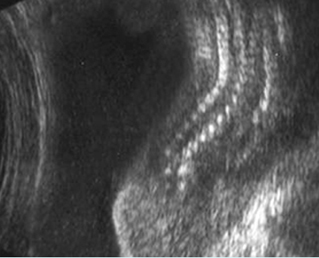
Fig 3: VATER associations Coronal scan of the spine: scoliosis
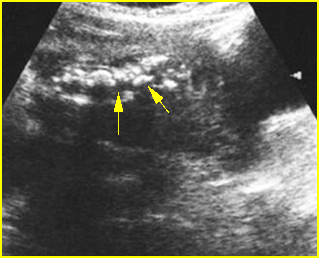
Fig 4: Disorganized spine : Coronal scan of the spine: scoliosis and disorganized
Video clips of abnormal spinal curvature
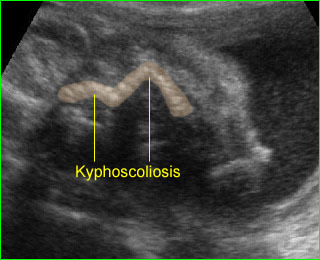
Limb-body wall complex: Coronal scan of the fetal spine: scoliosis associated with limb body wall complex
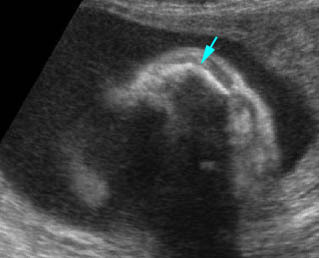
Severe kyphoscoliosis : Severe kyphoscoliosis in case of iniencephaly

