Amniotic Band Syndrome (ABS)
ABS is a destructive fetal complex caused by disruption of the amnion. It may be a sequela of intrauterine rupture of the amnion, resulting in oligohydramnios and passage of the fetus into the chorionic cavity, causing fetal compression and localized fetal ischemia, possibly resulting in a pathogenic mechanism of extremely variable malformations. A focal development error of connective tissue may be involved. The malformations range from minor constriction rings and lymphedema of the digits to complex, bizarre multiple anomalies that are attributed to amniotic bands that stick, entangle and disrupt fetal parts, particularly the cranium base, spine, or extremities.
Incidence: 1 in 1200 to 1 in 15,000 live births.
Sonographic findings:
- A wide variety of anomalies, including neural tube defect, unusual asymmetric or bizarre clefts of the lip/palate, abdominal wall defects, and amputation-type defects.
- Constriction rings of the limbs, typically edema distal to the constriction ring.
- Amputation defect of the extremity.
- Craniofacial defects such as acrania, craniosynostosis.
- Unusual pattern of facial clefting.
- Occasionally, amniotic bands themselves are visualized.
- The differential diagnosis depends on the body part involved. For example, cranial defects caused by ABS must be differentiated from acrania or cephaloceles. Abdominal wall defects secondary to ABS should be differentiated from limb-body wall complex (LBWC). Focal musculoskeletal anomalies should be differentiated from other causes such as mesomelic dysplasia, radial ray defects, etc.. Multisystem abnormalities favor the diagnosis of ABS.
- Usually first diagnosable in the second trimester.
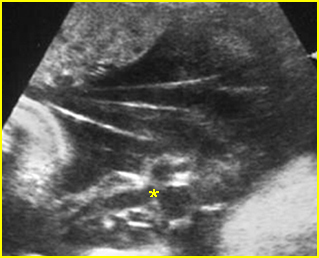
Fig 1: Amniotic bands Several amniotic bands (arrows) in amniotic cavity (* = umbilical cord)
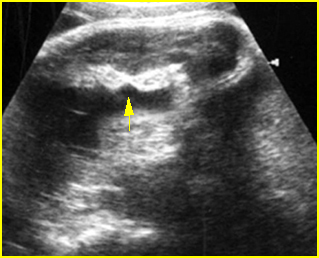
Fig 2: Amniotic band syndrome Constricted ring on the forearm of the fetus with amniotic band syndrome (arrow)
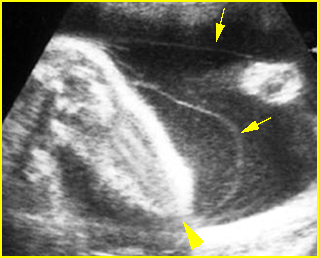
Fig 3: Amniotic band syndrome The lower leg abruptly ends (arrowhead) and surrounded by thin amniotic bands (arrows)
Video clips of amniotic band syndrome (ABS)
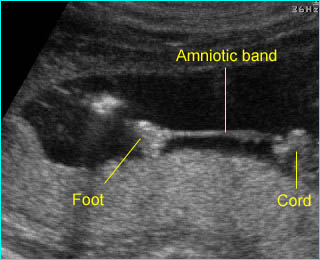
Amniotic band syndrome : The fetal foot with restricted movement secondary to amniotic band
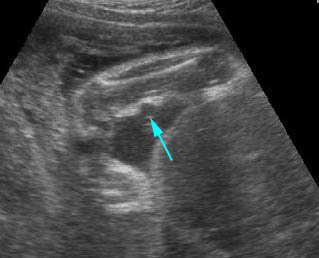
Amniotic band syndrome : Constriction ring on the forearm (arrow) secondary to amniotic band
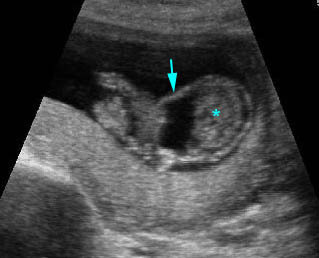
Amniotic band syndrome : Abnormal band (arrow) surrounding visceral organs (*) outside the body
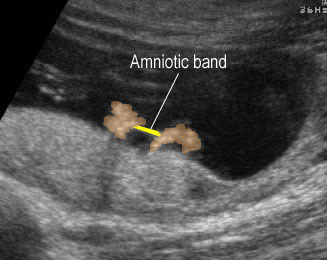
Amniotic band syndrome : Amniotic band adhered between the both hands
Associations: Non-specific multiple defects.
Management: Depends on the extent of the anomalies. Termination of pregnancy can be offered for severe forms. Expectant management is preferred in most cases of mild forms. Endoscopic release when a limb is at risk of amputation.
Prognosis: Depends on the severity and distribution of anomalies; usually a fatal prognosis for severe craniofacial deformities but a good prognosis for mildly affected infants with isolated limb defects.
Recurrence: Not known to be increased

