Hypoplastic Thorax
The specific group of autosomal recessive disorders mainly involves ribs and thoracic hypoplasia including asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia, Ellis-van Creveld syndrome, and short-rib polydactyly syndrome. There is phenotypic overlap between these three entities. They may be a spectrum of the same entity.
Sonographic differential diagnoses of the hypoplastic thorax include:
- Asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia (Jeune syndrome)
- Ellis-van Creveld syndrome
- Short-rib polydactyly syndrome
- Other syndromes with a lesser degree of rib shortenings
- thanatophoric dysplasia
- atelosteogenesis
- fibrochondrogenesis
- achondrogenesis
- Jarcho-Levin syndrome.
Asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia (Jeune syndrome)
Asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia (Jeune syndrome) is an autosomal recessive skeletal dysplasia, an ATD gene located on chromosome 15q13, characterized by a small thorax, a varying degree of short limbs, renal anomaly, and polydactyly.
Incidence: Rare.
Sonographic findings:
Fig 1, Fig 2
- Narrow and bell-shaped thorax, with short, horizontal ribs.
- Normal or mildly shortened long bones, but not as short as those in short-rib polydactyly syndrome or thanatophoric dysplasia.
- Polydactyly and cleft lip/palate in many cases.
- Associated renal abnormalities.
- Normal bone echogenicity.
- Increased nuchal translucency at late first trimester.
- Associated anomalies: renal cystic dysplasia, pancreatic cyst.
- Usually diagnosed in the second or third trimester, but diagnosis in the first trimester has been reported.
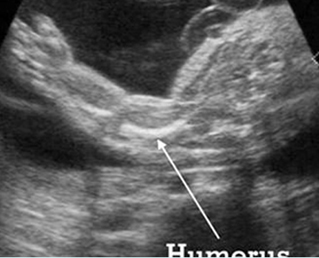
Fig 1: Short humerus Longitudinal scan of long bones: shortened but well ossified humerus of the fetus with Juene syndrome
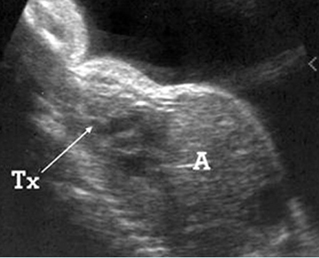
Fig 2: Small thorax Sagittal scan of the thorax and abdomen: disproportion in size of the thorax and abdomen of the fetus with Juene syndrome (Tx = chest, A = abdomen)
Management: Termination of pregnancy can be offered when diagnosed before viability.
Prognosis: Poor, but with a wide spectrum of severity from lethal to long-term survival.
Recurrence risk: Theoretically, the recurrent risk of these autosomal recessive disorders is 25%.
Short-rib polydactyly syndrome (SRP)
SRP is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by short ribs, micromelia and polydactyly. SRP may be associated with a gene defect involving 4q13 or 4p16.
Incidence: Rare.
Sonographic findings:
- Micromelia, usually severe.
- Constricted thorax with severe short ribs.
- Postaxial polydactyly.
- Normal bone echogenicity.
- Associated, genitourinary and gastrointestinal anomalies (Saldino-Noonan type).
- 3D ultrasound may provide additional details.
- SRP may be divided into three subtypes as follows (these subtypes are probably part of a continuous spectrum with variable expressivity):
- associated cleft lip and palate (Majewski type)
- associated renal abnormality (Naumoff type)
- associated cleft lip/palate, genitourinary, gastrointestinal anomalies (Beemer-Langer type).
- Usually diagnosed in the second half of pregnancy but possible as early as 13 weeks.
Management: Termination of pregnancy can be offered when diagnosed before viability.
Prognosis: Poor, but with a wide spectrum of severity from lethal to long-term survival.
Recurrence risk: Theoretically, the recurrent risk of these autosomal recessive disorders is 25%.
Chondroectodermal Dysplasia (Ellis-van Creveld syndrome; EVC)
EVC is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by short ribs, short limbs, polydactyly, dysplastic nails and teeth. EVC may be associated with a gene defect involving 4p16. DNA analysis for the first trimester diagnosis has been reported.
Incidence: Rare.
Sonographic findings:
Fig 3, Fig 4, Fig 5
- Acromesomelia with normal spine and skull.
- Long and narrow thorax with short ribs.
- Postaxial polydactyly.
- Congenital heart defects in 60% of cases.
- Normal bone echogenicity.
- Usually diagnosed in the second half of pregnancy but possible to diagnose as early as the late first trimester.
Management: Termination of pregnancy may be considered when diagnosed before viability. For the continuing pregnancy, ECV should not alter the standard obstetric management.
Prognosis: Depends on the severity, which varies from lethal to long-term survival. Overall the prognosis is rather good, but there is a significant mortality rate, due primarily to cardiorespiratory failure.
Recurrence risk: Theoretically, the recurrent risk of these autosomal recessive disorders is 25%.
Management: Termination of pregnancy can be offered when diagnosed before viability.
Prognosis: Poor, but with a wide spectrum of severity from lethal to long-term survival.
Recurrence risk: Theoretically, the recurrent risk of these autosomal recessive disorders is 25%.
Short-rib polydactyly syndrome (SRP)
SRP is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by short ribs, micromelia and polydactyly. SRP may be associated with a gene defect involving 4q13 or 4p16.
Incidence: Rare.
Sonographic findings:
- Micromelia, usually severe.
- Constricted thorax with severe short ribs.
- Postaxial polydactyly.
- Normal bone echogenicity.
- Associated, genitourinary and gastrointestinal anomalies (Saldino-Noonan type).
- 3D ultrasound may provide additional details.
- SRP may be divided into three subtypes as follows (these subtypes are probably part of a continuous spectrum with variable expressivity):
- associated cleft lip and palate (Majewski type)
- associated renal abnormality (Naumoff type)
- associated cleft lip/palate, genitourinary, gastrointestinal anomalies (Beemer-Langer type).
- Usually diagnosed in the second half of pregnancy but possible as early as 13 weeks.
Management: Termination of pregnancy can be offered when diagnosed before viability.
Prognosis: Poor, but with a wide spectrum of severity from lethal to long-term survival.
Recurrence risk: Theoretically, the recurrent risk of these autosomal recessive disorders is 25%.
Chondroectodermal Dysplasia (Ellis-van Creveld syndrome; EVC)
EVC is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by short ribs, short limbs, polydactyly, dysplastic nails and teeth. EVC may be associated with a gene defect involving 4p16. DNA analysis for the first trimester diagnosis has been reported.
Incidence: Rare.
Sonographic findings:
Fig 3, Fig 4, Fig 5
- Acromesomelia with normal spine and skull.
- Long and narrow thorax with short ribs.
- Postaxial polydactyly.
- Congenital heart defects in 60% of cases.
- Normal bone echogenicity.
- Usually diagnosed in the second half of pregnancy but possible to diagnose as early as the late first trimester.
Management: Termination of pregnancy may be considered when diagnosed before viability. For the continuing pregnancy, ECV should not alter the standard obstetric management.
Prognosis: Depends on the severity, which varies from lethal to long-term survival. Overall the prognosis is rather good, but there is a significant mortality rate, due primarily to cardiorespiratory failure.
Recurrence risk: Theoretically, the recurrent risk of these autosomal recessive disorders is 25%.
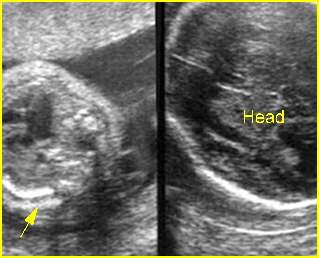
Fig 3: Small thorax Cross-sectional scan of the thorax and skull: disproportion in size of the thorax and head of the fetus with Ellis-van Creveld syndrome (arrow = short rib)
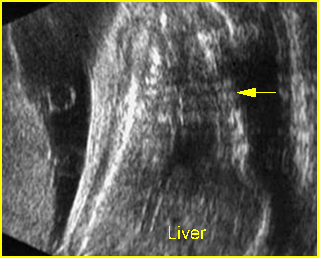
Fig 4: Small thorax Coronal scan: showing disproportion in size between thorax and abdomen of the fetus with Ellis-van Creveld syndrome
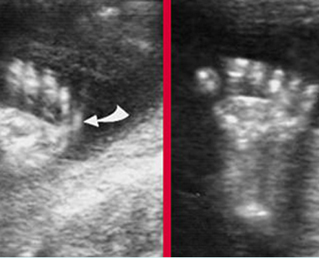
Fig 3: Polydactyly
Video clips of hypoplastic thorax
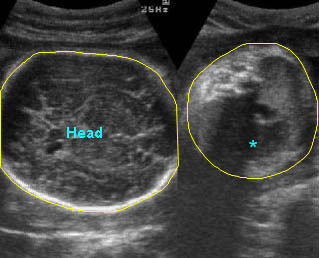
Lung hypoplasia / SRP Syndrome : Small thorax (*) with short ribs compared to the head size in case of fetal short-rib polydactyly syndrome
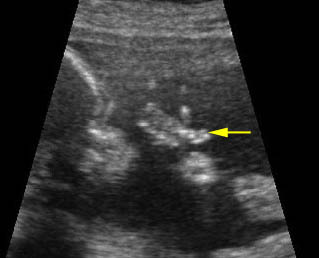
Post-axial polydactyly
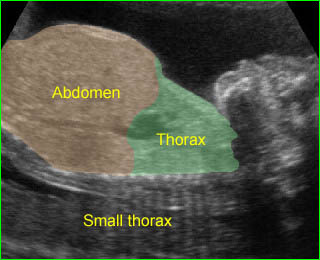
Short-rib polydactyly syndrome : Markedly small thorax compared to the abdomen in case of short-rib polydactyly syndrome

