Other Abnormalities
Microcephaly
Microcephaly is a condition involving the reduction of brain mass and head size with an intact bony calvarium, usually defined as a fetal head circumference of 3 SD, though some used 2 SD, below the mean of each gestational week.
Sonographic findings:
- The head is small, with a fetal head circumference of 3 SD.
- The femur length/head circumference ratio is at 3 SD or higher.
- Doppler ultrasound may show reduced or absent flow in the intracranial arteries, suggestive of a vascular cause.
- Severe microcephaly may be difficult to differentiate from anencephaly.
- Microcephaly is diagnosed at a mean gestational age of 28 weeks, but may not be demonstrated until after 24 weeks, or even at late onset in the last trimester.
Causes of microcephaly:
- isolated microcephaly (16.7%)
- microcephaly due to holoprosencephaly (16.7%)
- microcephaly associated with chromosomal disorders (23.3%)
- microcephaly as part of a genetic syndrome (20.0%)
- microcephaly as part of multiple anomalies (23.3%)
- microcephaly as part of intrauterine infections (i.e.: Zika virus)
Intracranial Calcifications
Intracranial calcifications have been rarely demonstrated prenatally. They most commonly result from intrauterine infection but are sometimes associated with intracranial tumor. The differential diagnoses of intracranial calcifications include
- intrauterine infection (often also related to microcephaly, or ventriculomegaly, or growth restriction)
- cytomegalovirus (most common): usually subependymal calcification
- toxoplasmosis: usually scattered
- varicella-zoster syndrome
- rubella virus (very rare)
- intracranial tumor (usually localized to tumor mass)
- a normal second trimester ultrasound does not always exclude intracranial calcifications.
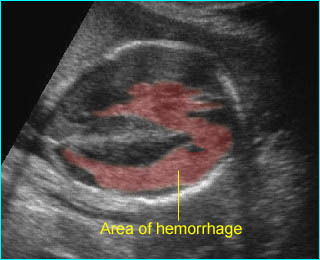
Intracerebral hemorrhage:
Irregular echogenic mass in the area of lateral ventricle and cerebral mantle
Specific abnormalities
Some specific anomalies have a characteristic shape of the head.
Lemon sign: a concave deformity of the frontal bones at the level of the coronal suture, which may be associated with
- normal fetus (1-2% of normal fetuses)
- spina bifida (common)
- occipital cephalocele (rare)
- thanatophoric dysplasia (rare)
- long-term oligohydramnios
Cloverleaf skull (found in 14% of cases of thanatophoric dysplasia)
- thanatophoric dysplasia (most common)
- homozygous achondroplasia
- Apert’s syndrome
- Pfeiffer’s syndrome
- Carpenter’s syndrome
Strawberry head shape (often associated with fetal trisomy 18).

