Exencephaly (Acrania)
Exencephaly is a developmental abnormality characterized by partial or complete absence of the cranial vault with relatively complete but heterogeneous and disorganized brain. It is an embryonic precursor of anencephaly. Some cases are an amniotic band sequence. The developing brain exposed to amniotic fluid is gradually destroyed and disappears or becomes residual tissue (angioma stroma).
Sonographic findings:
- Absence of the calvarial vault with brain tissue, relatively normal in amount, floating in amniotic fluid. Fig 1, Fig 2
- Frog-eye appearance face on the coronal view. Fig 3
- Abnormally-shaped brain with distorted specific structures such as the ventricles or choroid plexus and the visualization of surrounding membrane instead of skull.
- The first trimester exencephalic fetus may have a wide and bilobed head, a so-called Mickey Mouse head.
- Most diagnosed in the first trimester because of the rapid necrosis of brain tissue when exposed to amniotic fluid, subsequently leading to anencephaly.
- Echogenic amniotic fluid is found in nearly 90% of cases of acrania/anencephaly in the first trimester.
- The primary differential diagnosis includes sonolucent skulls such as osteogenesis imperfecta type II, hypophosphatasia.
- Pitfalls: An irregular fetal head outline in the first trimester can simply be overlooked.
- Diagnosable from 10 to 14 weeks of gestation, usually can be detected during NT scanning.
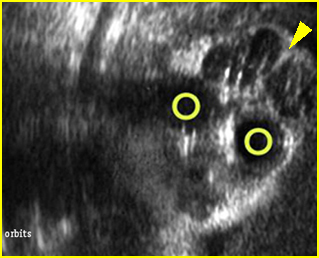
Fig 1: Exencephaly Coronal scan of the face: significant brain tissue (arrowhead) above the orbits (circle) without covering skull
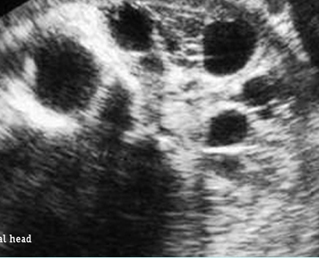
Fig 2: Exencephaly Free floating large brain mass without covering skull and skin
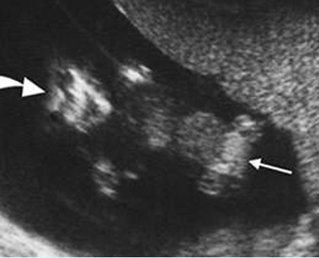
Fig 3: Exencephaly/anencepahly Coronal scan of the fetus at 11 weeks: no skull above the orbits (large arrow), omphalocele (small arrow)
Video clips of exencephaly
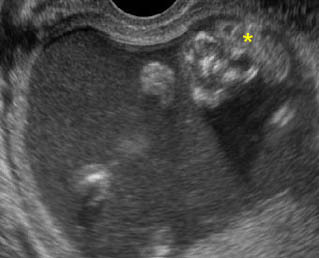
Exencephaly: Coronal scan of the fetal face at 12 weeks: frog-face appearance with free-floating brain (*) above the orbits
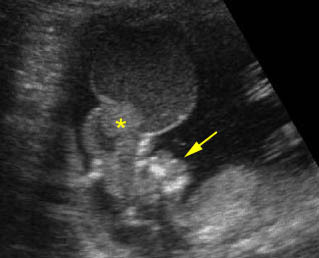
Exencephaly: Sagittal scan of the fetus at 12 weeks: free-floating brain with meningeal coverings (*) without skull (arrow = face)
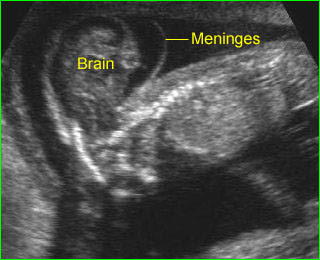
Exencephaly: Free-floating brain in the amniotic fluid without cranium
Associations: Spina bifida, non-specific anomalies, chromosome abnormality is found in about 2% of fetuses with acrania.
Management: Termination of pregnancy should always be offered.
Prognosis: Uniformly lethal.
Recurrence risk: About 2-4%. Periconceptional folic acid supplementation can significantly decrease the recurrent risk

