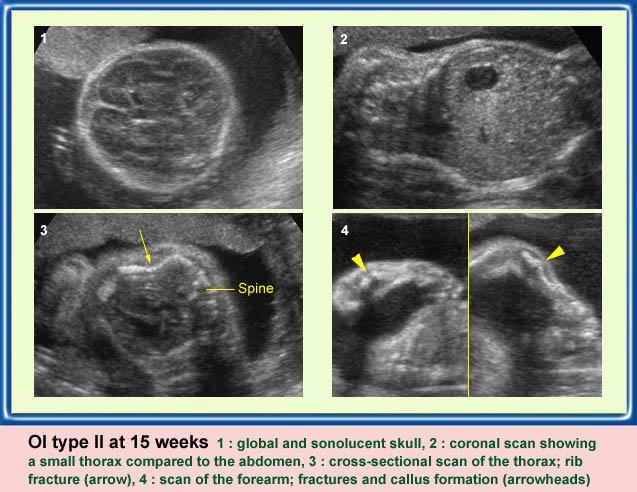
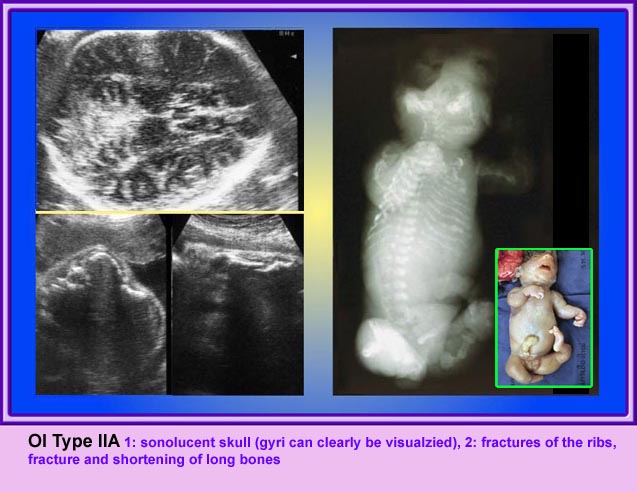
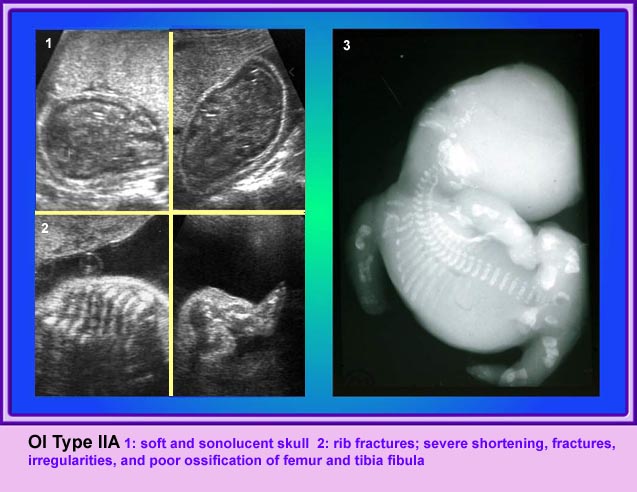
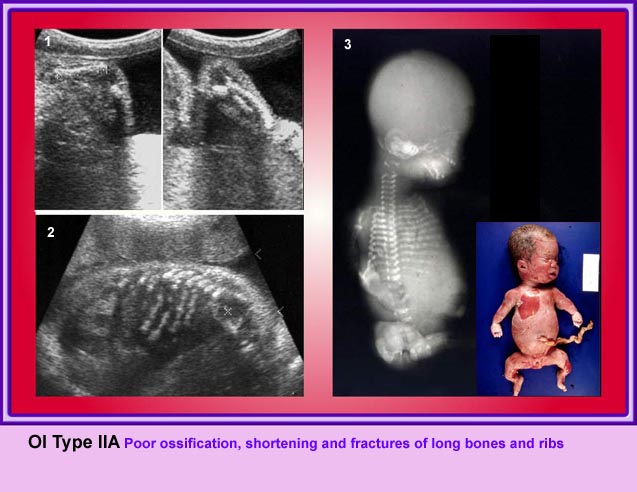
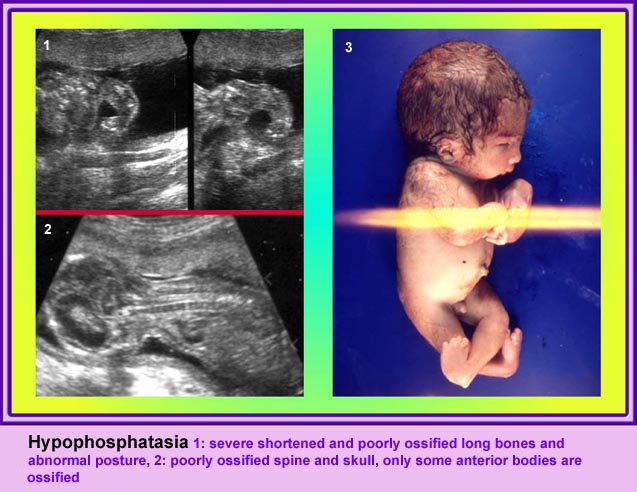
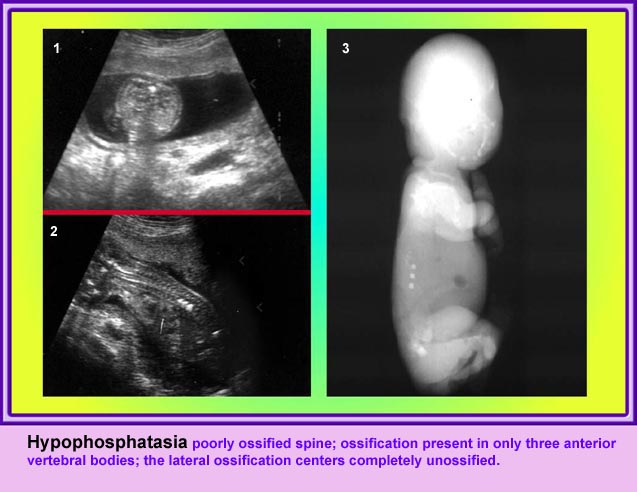
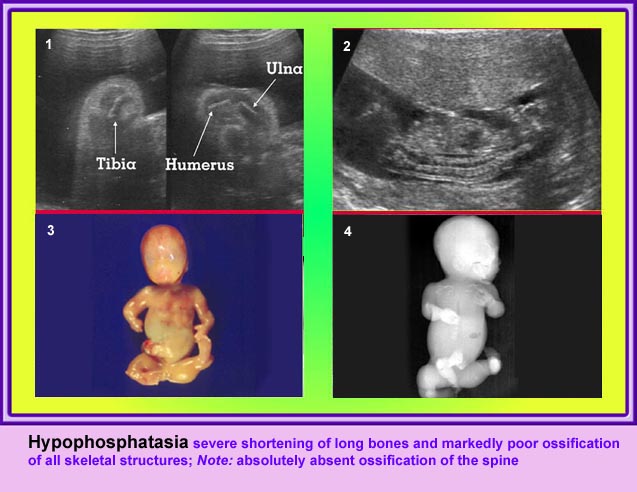
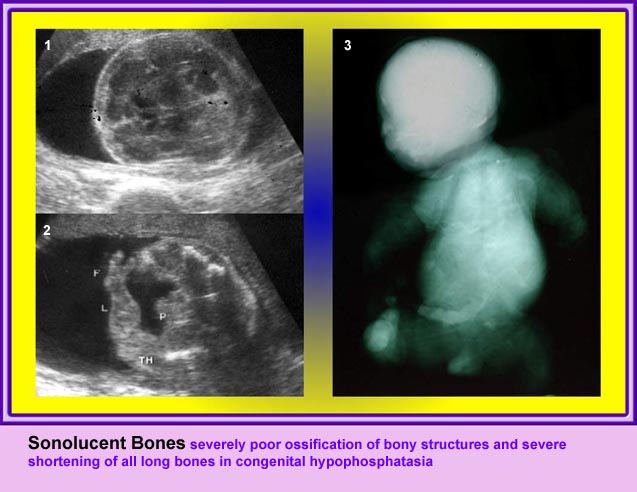
Thanatophoric Dysplasia
Thanatophoric Dysplasia
บทนำ
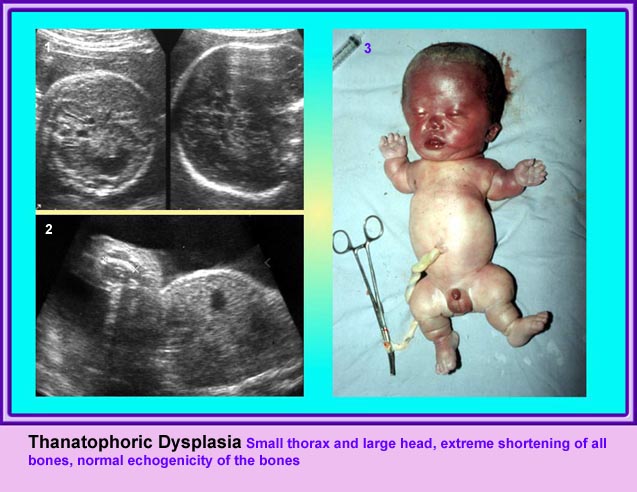
Thanatophoric Dysplasia เป็น lethal dysplasia ที่พบได้บ่อยที่สุด เกิดจากความผิดปกติของ endochondral ossification เซลล์ chondrocyte ลดลง และกระจัดกระจายไม่เป็นระบบ ทำให้กระดูกไม่เจริญ มีลักษณะจำเพาะคือ rhizomelia กระดูกแขนขาโก่ง สั้น แต่ความยาวของลำตัวปกติ ทรวงอกแคบ ไม่สามารถมีชีวิตรอดได้
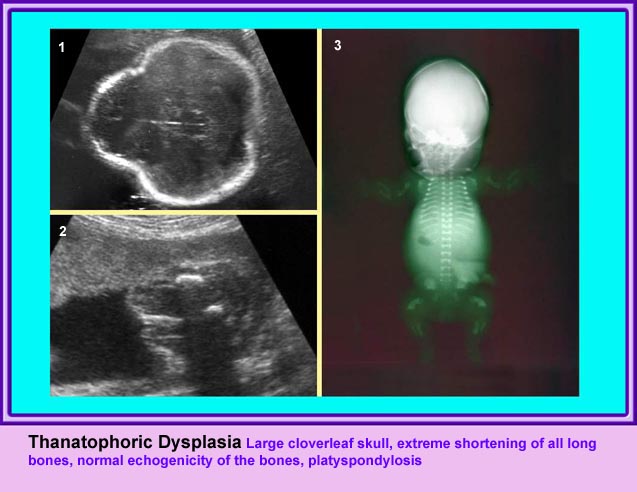
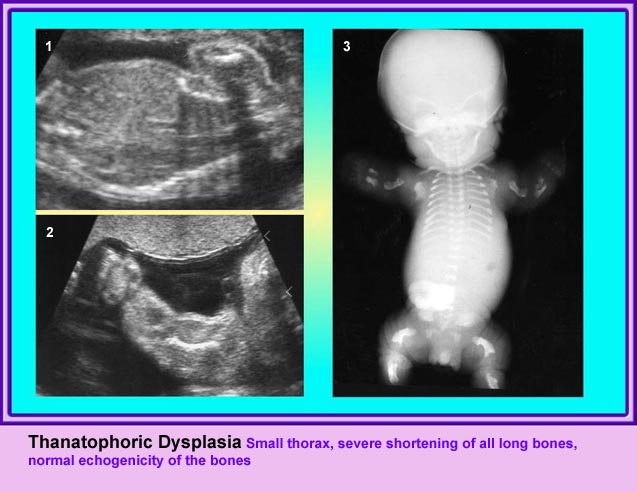
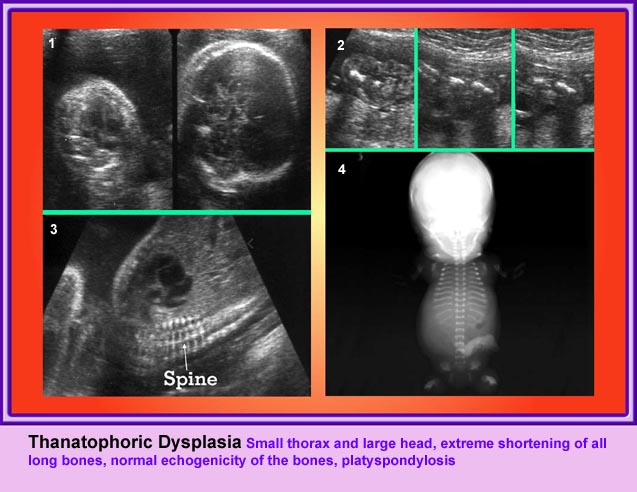
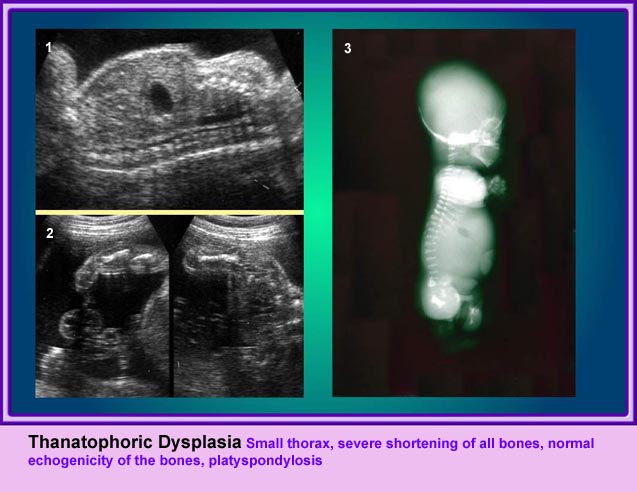
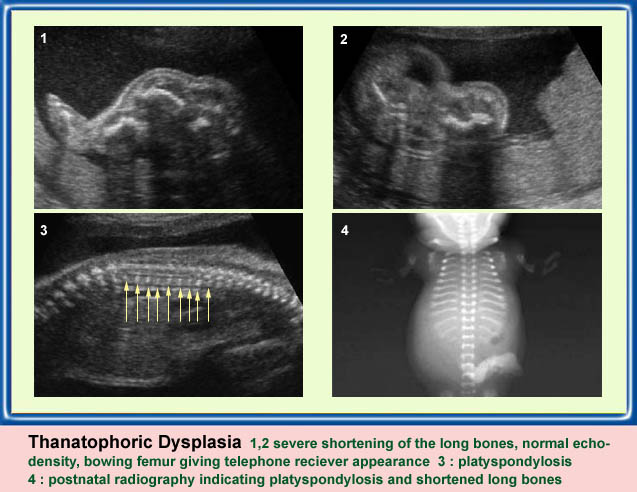
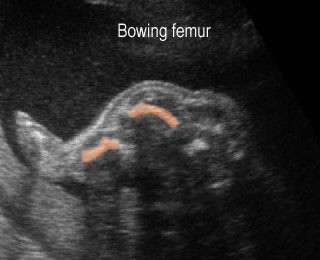
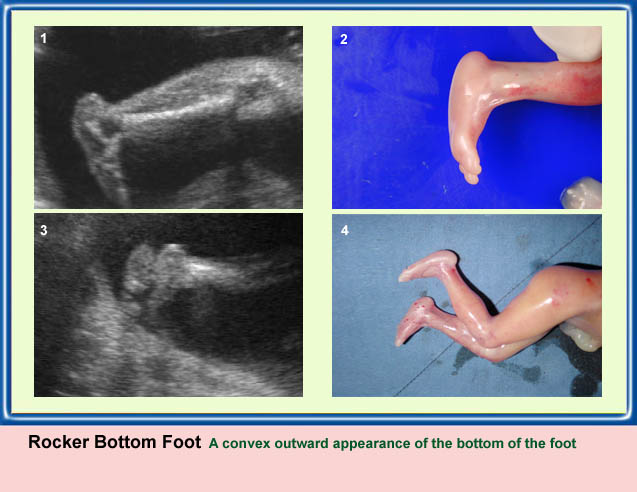
แขนขาสั้นมาก โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่ง femur จะสั้นมาก และโก่งคล้ายหูรับโทรศัพท์ กระดูกซี่โครงสั้น ทรวงอกแคบในแนวหน้าหลัง แต่ความยาวลำตัวปกติ ตัวกระดูกไขสันหลังแบน มีรูปร่างคลายตัว H (platyspondylosis) ฐานกระโหลกสั้น หน้าผากยื่นเด่น ตาห่าง สันจมูกแบน ประมาณร้อยละ 14 ของภาวะนี้มีกระโหลกเป็นรูปดอกจิก (cloverleaf)
ลักษณะทางคลื่นเสียงความถี่สูง
- แขนขาสั้นมาก แขนขาที่สั้นจะเด่นแบบ rhizomelia แต่โดยรวมแล้วจะสั้นทุกส่วน และไม่มีกระดูกหัก สำหรับกระโหลกรูปดอกจิก แม้จะเป็นลักษณะจำเพาะแต่ก็พบได้เพียงร้อยละ 14 เท่านั้น แต่ส่วนใหญ่แล้วขนาดของศีรษะโตกว่าที่ควรจะเป็น
- ความเข้มเสียงสูงของกระดูก (ossification) ปกติ ซึ่งต่างจากกลุ่ม hypophosphatasia และ osteogenesis imperfecta
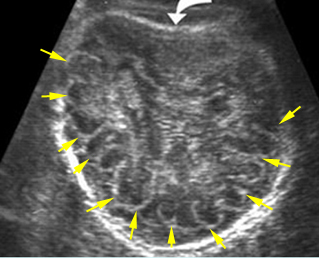
- กระโหลกศีรษะรูปดอกจิก (ร้อยละ 14)
- ตัวกระดูกไขสันหลังแบน (platyspondylisis) และรอยต่อแคบ
- ภาวะครรภ์แฝดน้ำ (ราวร้อยละ 50)
- กระดูกแขนขาโก่ง เนื้อเยื่อเด่นดูจ้ำม่ำ ทรวงอกแคบ
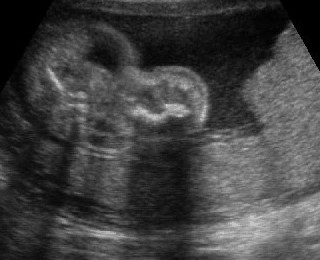
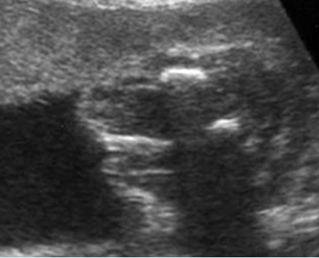
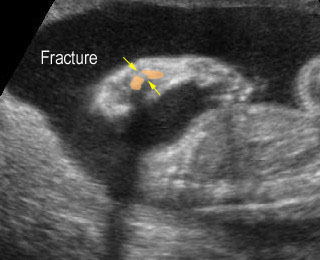
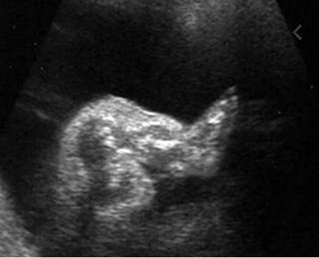
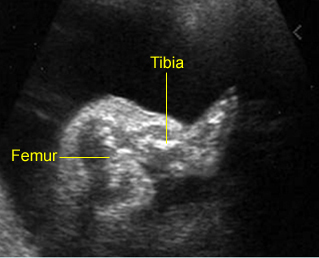
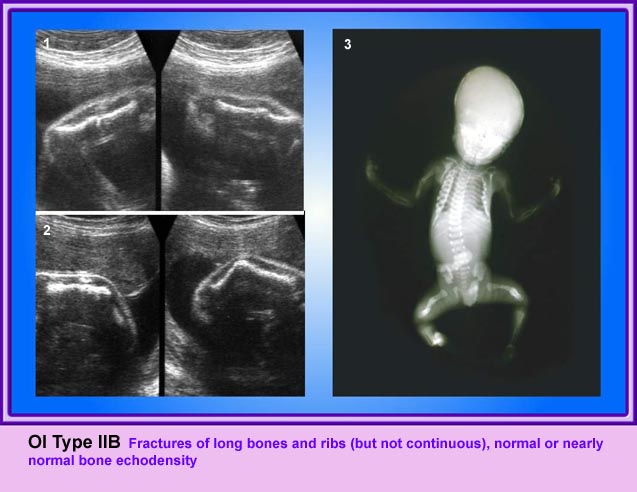
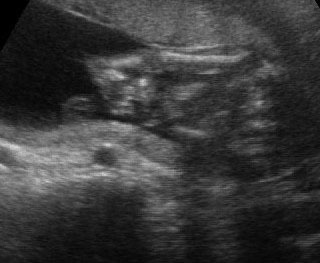
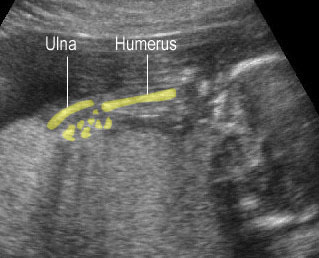
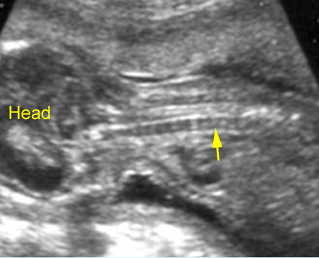
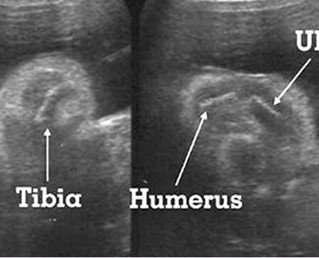
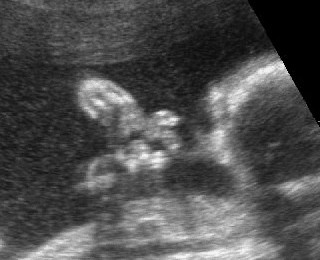
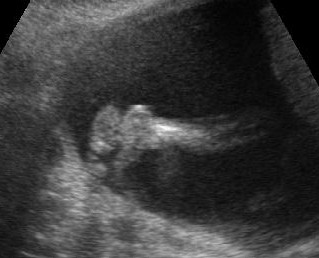
Micromelia in Thanatophoric dysplasia
Severe shortenings of femur and tibia with bowing femur
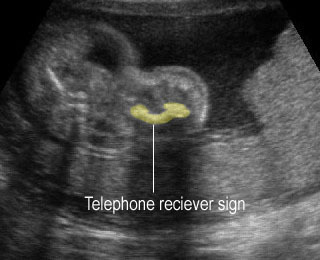
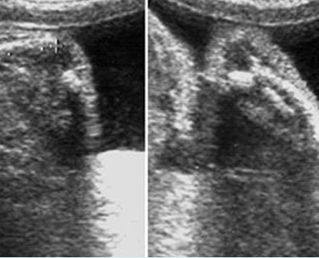
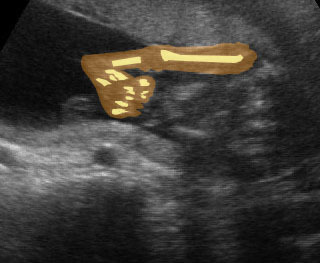
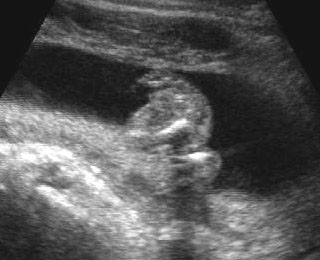
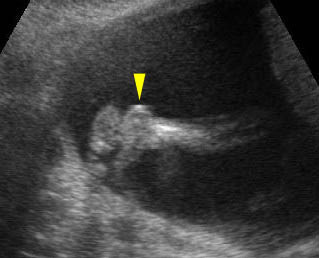
Micromelia in Thanatophoric dysplasia
Severe shortenings and bowing of long bone: telephone reciever appearance
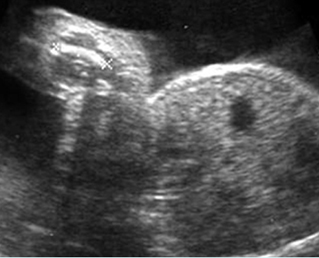
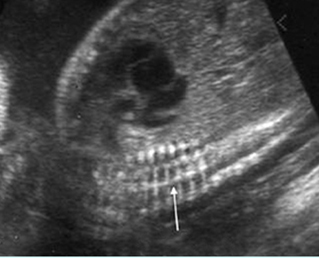
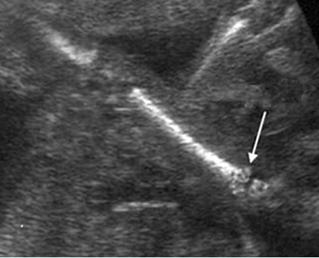
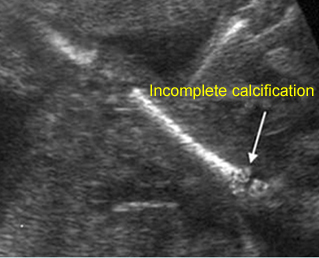
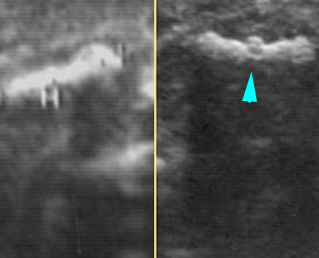
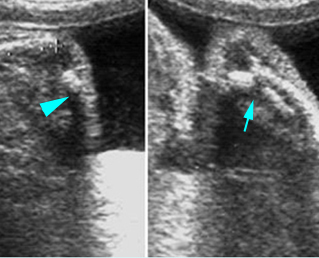
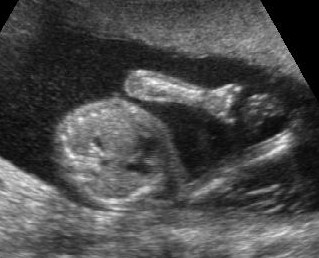
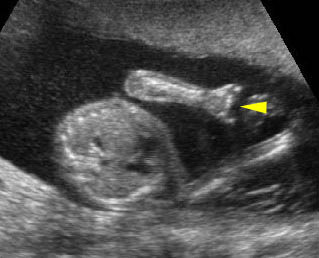
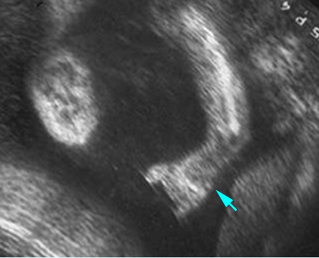
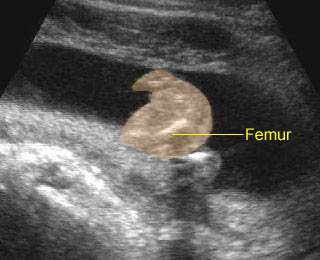
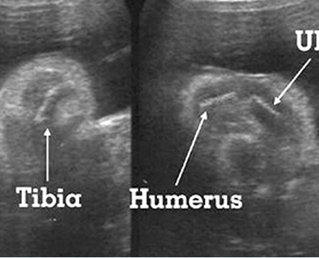
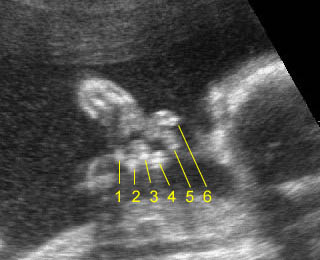
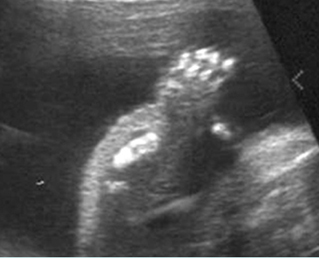
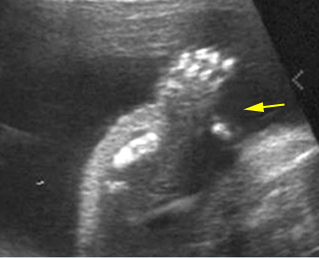
Micromelia in Thanatophoric dysplasia
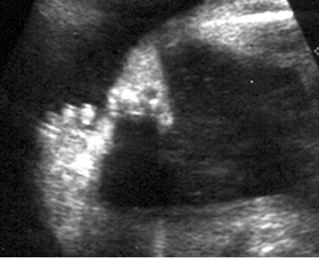
Severe shortenings of humerus (arrow) but normal ossification
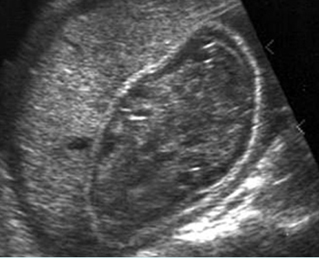
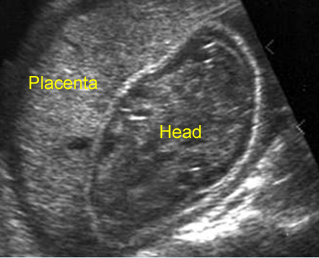
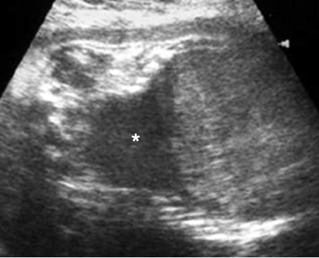
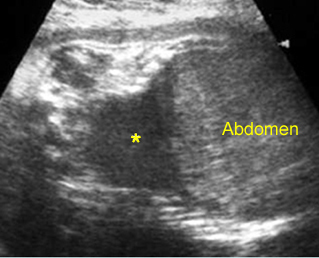
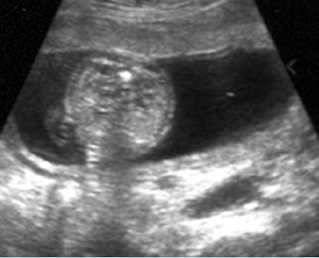
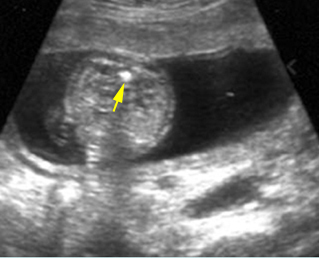
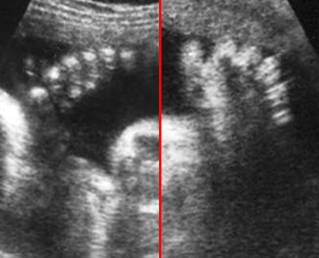
Large head
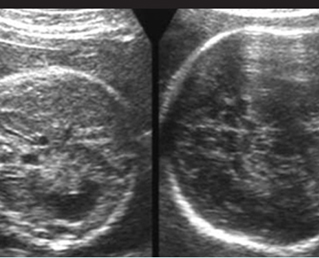
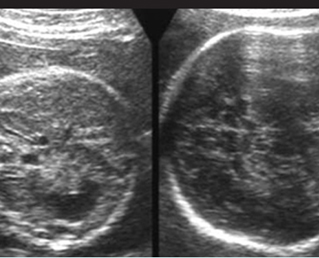
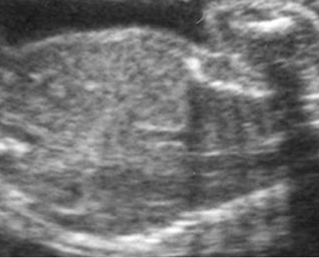
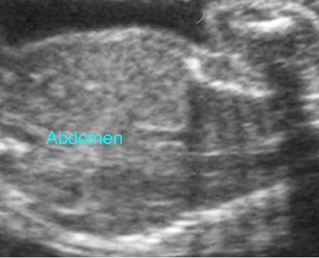
Cross-sectional scan of the abdomen and skull: disproportion in size of the trunk and head of the fetus with Thanatophoric dysplasia
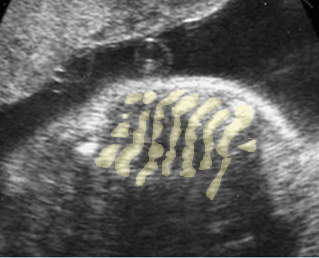
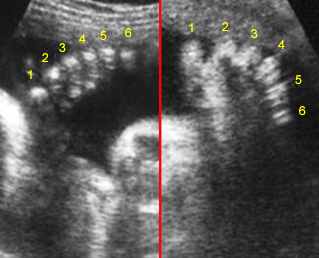
Small thorax in Thanatophoric dysplasia
Coronal scan of fetal trunk: disproportionately small thorax, compared to the abdomen
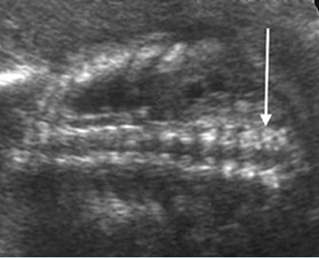
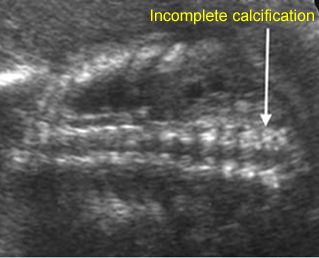
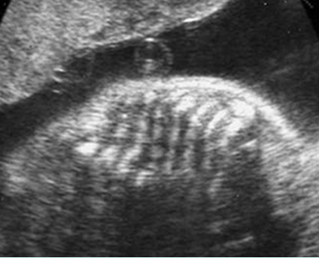
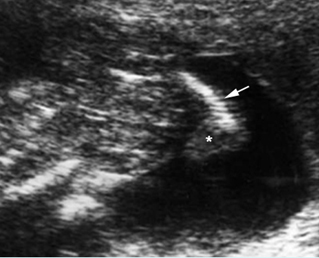
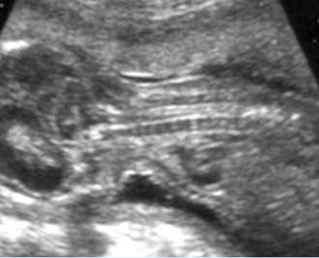
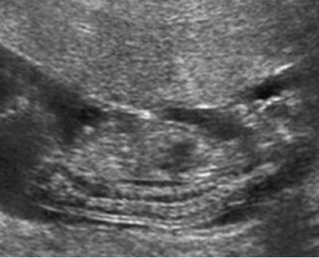
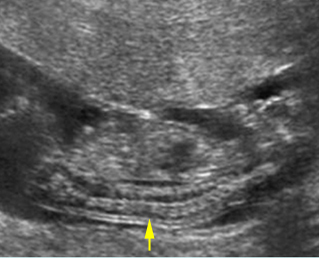
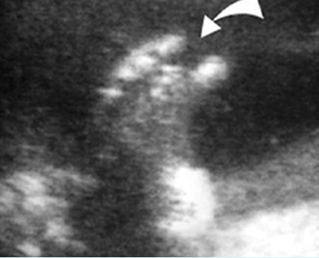
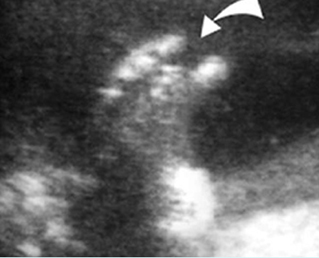
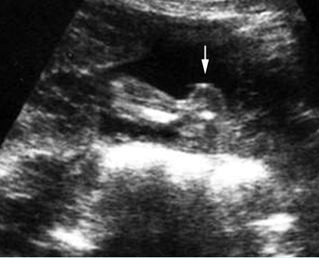
Platyspondylosis
Oblique sagittal scan of the spine: relatively flattened vertebra (arrow) in case of Thanatophoric dysplasia
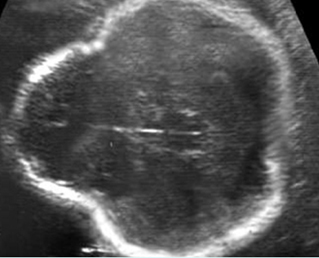
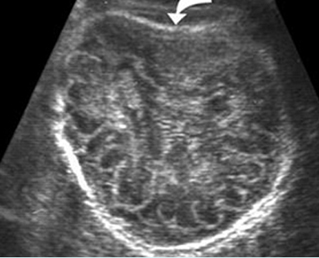
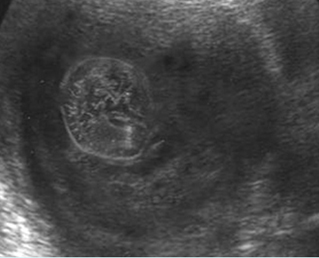
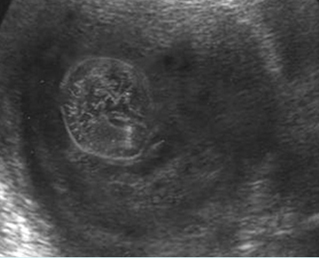
Thanatophoric dysplasia
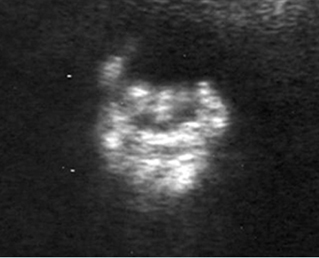
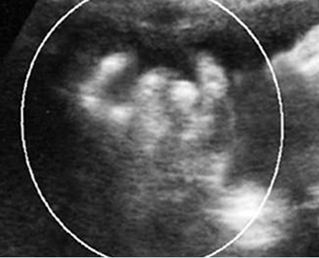
Cross-sectional scan of the skull: Cloverleaf skull; prominent parietal bone
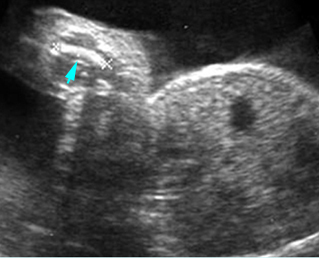
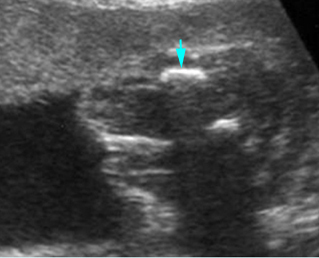
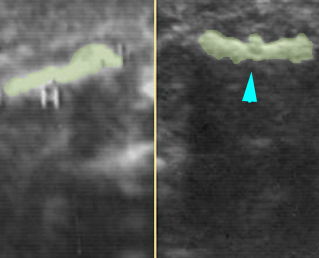
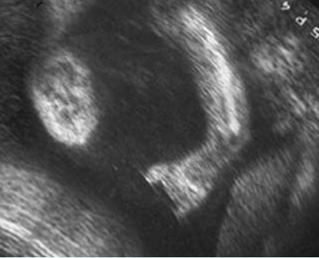
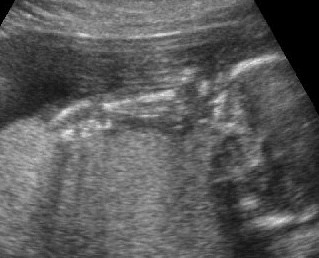
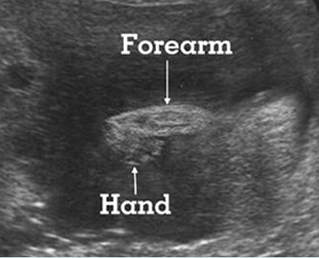
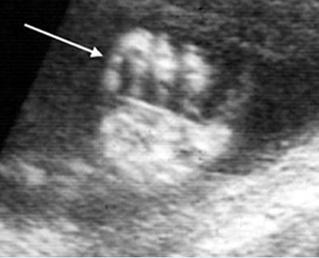
Micromelia in Thanatophoric dysplasia
Severe shortenings of long bones (arrow) but normal ossification
Classic Images