Hypotelorism
Hypotelorism, abnormally close spacing of the orbits, is an uncommon disorder, which is usually associated with many other conditions including chromosome defects. Holoprosencephaly is the most common associated malformation. It should be diagnosed when both the interocular and outer or binocular distances are below the 5th percentile, usually first diagnosable in the second trimester, but possibly in the first trimester. The extreme case, median ocular fusion or cyclopia, is almost always related to holoprosencephaly. Binocular biometric parameters may be useful sonographic markers for trisomy 13 or holoprosencephaly.
Fig 1
The differential diagnoses of hypotelorism include:
- Holoprosencephaly (most common)
- Median facial clefts
- Chromosome abnormalities, especially trisomy 13
- Meckel syndrome
- Microcephaly.
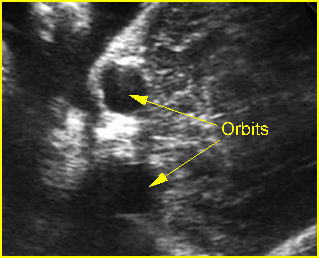
Fig 1: Hypotelorism Coronal view of the face: hypoteloism associated with trisomy 13
Video clips of neck masses
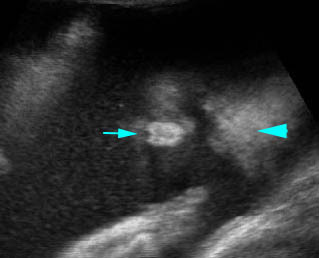
Hypotelorism & Proboscis: Coronal scan of the face: arrowhead = forehead, arrow = proboscis)
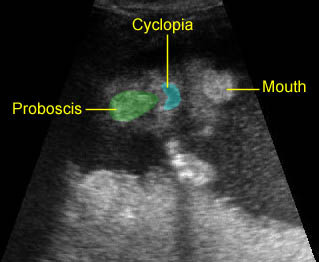
Hypotelorism & Proboscis: Coronal scan of the face showing a proboscis above the cyclopia
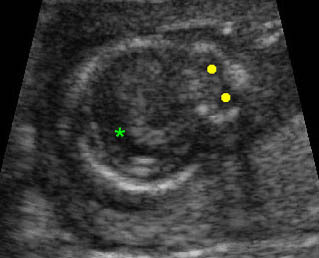
Holoprosencephaly: Transverse scan of the head: fusion of the lateral ventricle (*), no falx cerebri, marked hypotelorism (solid circle)

