Facial Masses
Most abnormal masses of the face are located in the periorbital areas.
Fig 1, Fig 2
The major differential diagnoses for periorbital masses are as follows:
- Proboscis: solid mass of abnormal nose formation, almost always associated with hypotelorism and holoprosencephaly.
- Daccryocystoceles: lacrimal duct cyst, hypoechoic mass inferomedial to the fetal orbit without displacement of the globe but with synchronous eye movements.
- Hemangioma: cystic or solid, placenta-like echogenicity, well-defined vascular space with characteristic Doppler signal.
- Anterior cephalocele: usually midline mass, displacing orbit inferiorly and laterally, anterior cranial defect.
- Teratoma or dermoid cyst: solid or cystic or complex, occasional calcifications.
- Anterior cystic hygroma: (rare) cystic or multicystic with loculations and septations varying in size.
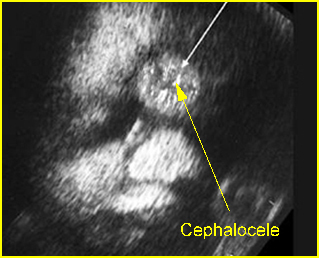
Fig 1: Anterior cephalocele Coronal scan of the face: round solid mass above the nose (arrow)
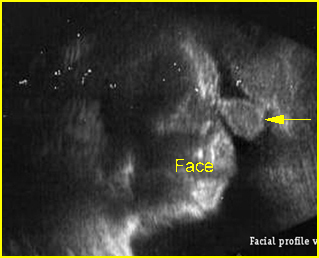
Fig 2: Proboscis Facial profile view: proboscis (arrow), absent nose
Video clips of facial masses
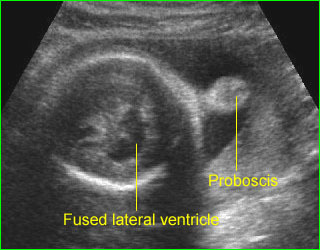
Proboscis (holoprosencephaly) : Midline solid mass at the forehead (proboscis) and fused ventricle
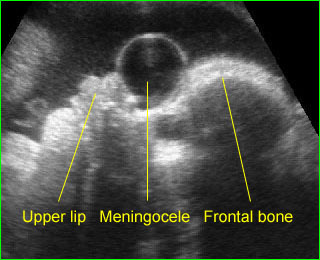
Anterior meningocele: Sagittal scan of the fetal face: frontal bone defect with midline cystic mass (meningocele)

