{tab=Preface}
Why Ultrasound?
Appropriate use is helpful in obstetric practice, especially in gestational age estimation, fetal growth monitoring, obstetric hemorrhage, and anomaly screening
Indicated or Routine Ultrasound?
- Generally well accepted for examination with indication
- Routine screening at 18-20 weeks, recent more common practice, better or earlier diagnosis of GA, twins or anomaly but significant increase in cost and workload
- The policy must be considered for cost-effectiveness and cost-benefit
Common Indications
- Diagnosis: pregnancy, number of fetuses, fetal life
- Size inconsistent with date: multiple pregnancy, oligo-, polyhydramnios, hydrocephalus, fetal growth restriction
- Estimate gestational age
- Growth monitoring
- Bleeding: abortion, placenta previa, placental abrutpion
- Amniotic fluid evaluation
- Pathology in the pelvis
- Anomaly screening: Routine at 18-20 wk or pregnancy at risk (maternal DM, familial history,advanced maternal age)
- Guidance for invasive procedures, i.e. amniocentesis, cordocentesis
{tab=Sonoembryology}
Sonoembryology
Early Fetal Development
(Transvaginal Sonography; TVS)
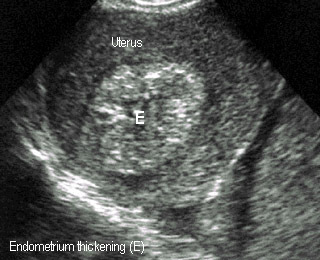
- 3-4 weeks (after LMP): Endometrial thickenings
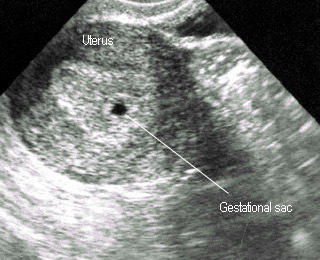
- 4-5 weeks: Gestational sac
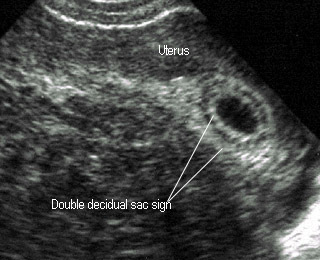
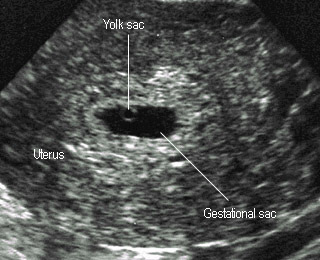
- 5-6 weeks: Yolk sac, double decidual sac sign (DDS)
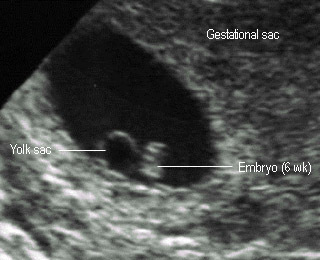
- 6-7 weeks: Embryo with heart beat
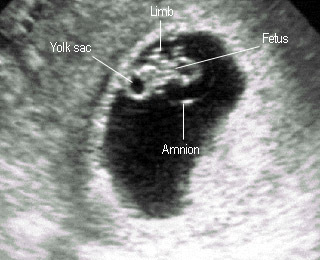
- 7-8 weeks: Embryo movement, Rhombencephalon, Amnion
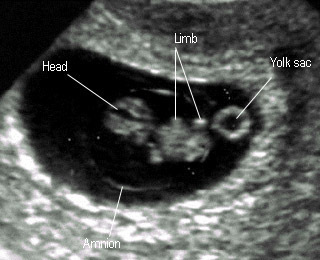
- 8-9 weeks: Physiologic omphalocele, limbs, choroid plexus, spinal line
- TVS demonstrates earlier than transabdomen (TAS) ~ 1-2 weeks
 |
 |
4-5 weeksEndometrial thickening, no obvious sac |
5 weeksGestational ring, white echogenic rim |
 |
 |
Double decidual sac signUsually seen at 5-6 weeks |
5 weeksNote yok sac |
 |
 |
6 weeksNote: yok sac and early embryo |
7-8 weeksRapid growth of embryo and amnion |
 |
 |
8 weeksFetal body compartments : head trunk limbs |
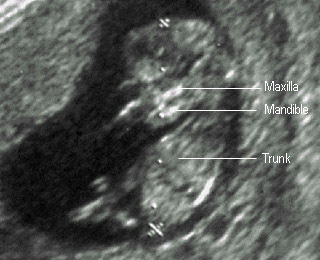
10 weeksFacial structures becoming seen |
Double Decidual Sac Sign (DDS)
- Strongly suggestive of intrauterine pregnancy
- Outer ring : Decidual vera
- Middle sonolucency : Endometrial cavity
- Inner ring : Decidual capsularis
- Typically seen : 5-8 weeks
 |
 |
Double decidual sac signUsually seen at 5-6 weeks |
5 weeksNote yok sac |
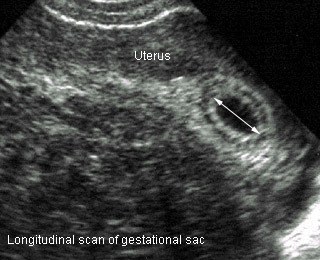
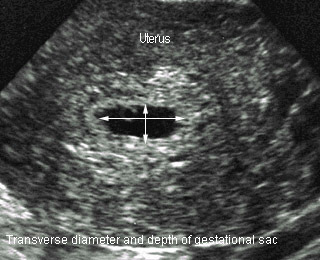
Mean Sac Diameter (MSD)
- MSD : Average gestational sac diameter = width + depth + length / 3
- MSD closely related to early GA
- When MSD > 25 mm. GA (days) = MSD + 30
 |
 |
Mean sac diameterLongitudinal diameter |
Mean sac diameterTransverse diameter and depth |
Yolk Sac
- Round, sonolucent with white border
- Average 5 mm (3-8 mm)
- Seen at 6-12 weeks peak 8-10 weeks
- Nearly all seen when MSD > 8 mm.
- Yolk sac > 10 mm. related to poor prognosis
- Must be seen if MSD > 20 mm. by TAS or > 13 mm by TVS
Fetal Echo
- Crown-Rump Length (CRL): the most accurate parameter for GA estimation (+ 3-7 days)
- Useful only in the first trimester
- Short CRL related to high abortion rate and aneuploidy
- Head, trunk, limbs can be identified from 8 weeks
Amnion
- Seen from 7-8 weeks (TVS)
- Beginning with double bleb sign (yolk sac and amnionic sac)
- Fast growing, finally embryo is in the sac
-
Yolk sac is outside
 |
 |
Yolk sacYolk sac adjacent to fetal echo in early gestation |
Yolk sacNote: yolk sac separated from amnion |
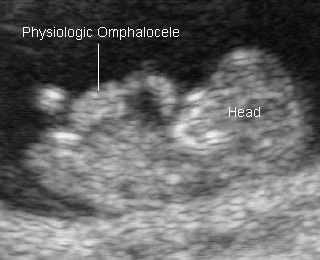
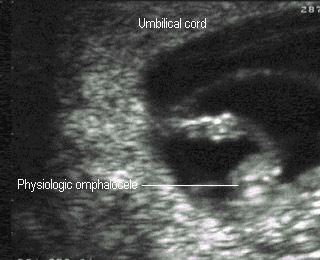
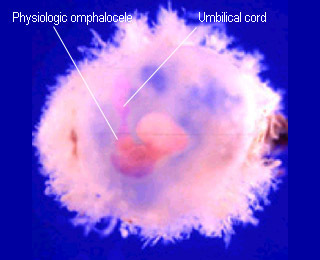
Physiologic Omphalocele
- Midgut herniation 8-12 weeks
- Only bowel (no liver) in the proximal umbilical cord
- Not seen if CRL > 44 mm
- Size 4-7 mm.
- Should be considered abnormal if > 7 mm, or seen after 12 weeks
 |
 |
Physiologic omphaloceleProminent at 8-9 weeks |
Physiologic omphaloceleAt 8 weeks |
 |
|
Physiologic omphalocelePhysiologic omphalocele in abortus |
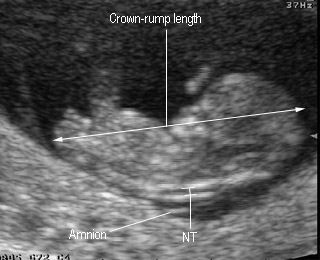
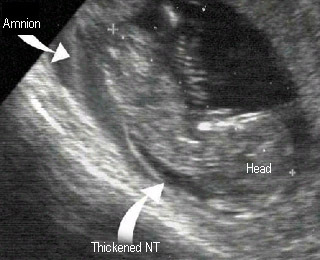
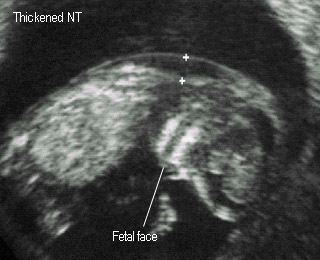
Nuchal Translucency (NT)
- NT : small fluid collection beneath skin at back of the fetal neck
- Measured at CRL 35-80 mm (10-14 week)
- Measured on midsagittal scan (plane for CRL)
- The best sonomarker for screening Down syndrome
- Abnormal if > 95th percentile (> 2.5-3.0 mm)
- Thickened NT increased of aneuploidy, anomaly especially cardiac defect
 |
 |
Nuchal translucencyNormal measured at 11 weeks |
Nuchal translucencyThickened nuchal translucency |
 |
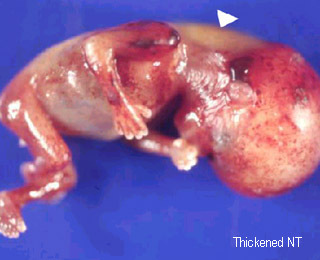 |
Nuchal translucencyThickened nuchal translucency at 14 weeks |
Nuchal translucencyThickened nuchal translucency after abortion |
{tab=Early Complications}
Early Pregnancy Complications
Threatened Abortion
- Ultrasound examinations see if viable or nonviable pregnancy
- Viable fetus with normal heart beat : very good prognosis
- Nonviable:
- blighted ovum
- missed / incomplete abortion
- fetal death
- ectopic pregnancy
- molar pregnancy
 |
 |
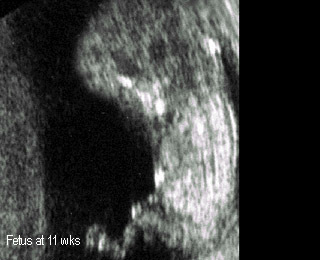
Threatened abortionNormal fetus at 11 weeks |
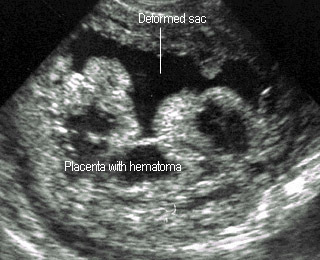
Threatened abortionPlacental hematoma in case of blighted ovum |
 |
|
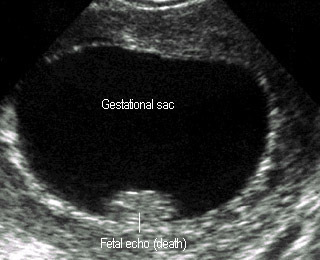
Early embryo deathEmbryo size and sac disproportion |
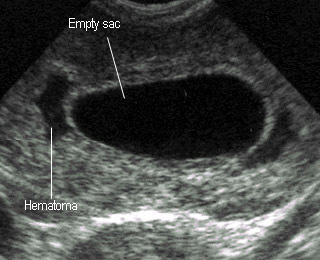
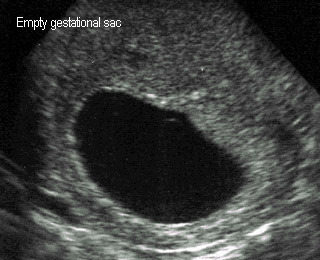
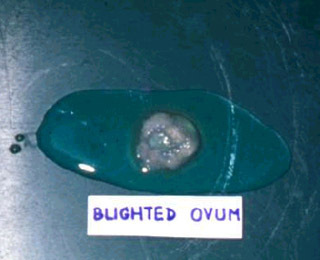
Blighted Ovum (Empty sac)
- Intrauterine pregnancy without embryo
- Diagnosed when
- MSD > 25 mm (TAS) or > 20 mm (TVS) with no embryo seen
- MSD > 20 mm (TAS) or >17 mm (TVS) with no yolk sac & embryo seen
- DDx :
- Early normal pregancy
- Pseudosac in ectopic pregnancy
- Blood or fluid collection
 |
 |
Blighted ovumGestational sac without embryo, subcorion hematoma |
Blighted ovumGestational sac without embryo, |
 |
|
Blighted ovumAborted sac: placenta and sac without embryo |
Ectopic Pregnancy
- Clinically suspected with stable vital sign : ultrasound
- Ultrasound results:
- Definite IUP : exclude ectopic pregnancy
- Definite EUP : extrauterine gestational sac
- Highly suggestive of EUP : empty uterus with complex mass (separate from ovaries), echogenic fluid, dilated tube (May treat EUP or laparoscopic diagnsois in some cases)
- Inconclusive : empty uterus without other abnormal finding (May need doubling time for beta-hCG)
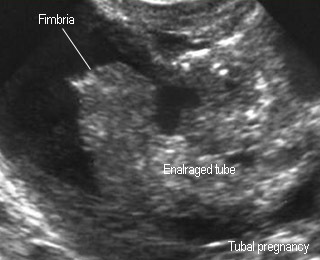
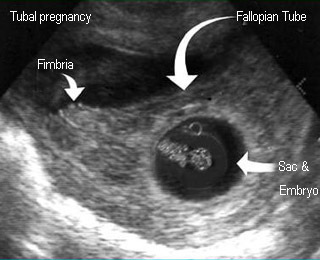
Ectopic pregnancy
Floating dilated fallopian tube in free fluid
Ectopic pregnancy
Gestational sac with embryo and yolk sac in the tube
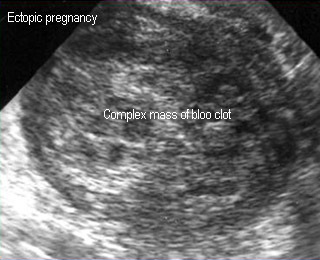
Ectopic pregnancy
Adnexal omplex mass of blood clot and concepitus
Molar Pregnancy
- Ultrasound findings:
- No fetus
- Snow storm pattern or
- Numerous small cystic echo or
- Placental-like echo
- May show complex area of blood clot
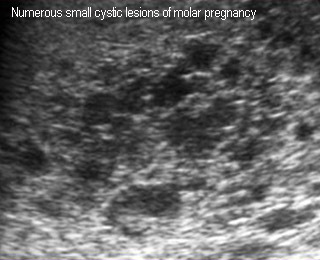
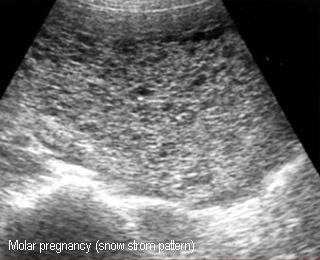
Molar pregnancy
Numerous small cystic space in uterine cavity mass
Molar pregnancy
Snow storm appearance
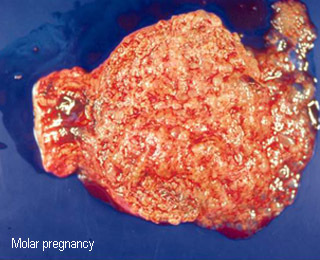
Molar pregnancy
The opened uterine specimen after hysterectomy
{tab=Biometry}
Fetal Biometry
Mean Sac Diameter (MSD)
- MSD : Average gestational sac diameter = width + depth + length / 3
- MSD closely related to early GA
- When MSD > 25 mm. GA (days) = MSD + 30
 |
 |
Mean sac diameterLongitudinal diameter |
Mean sac diameterTransverse diameter and depth |
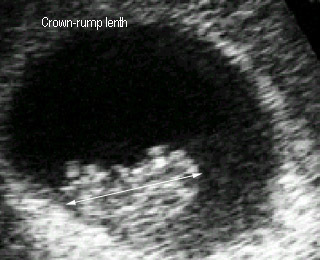
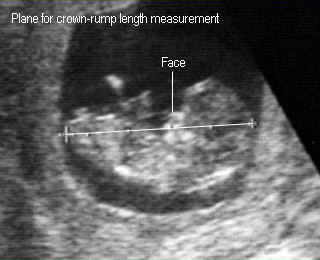
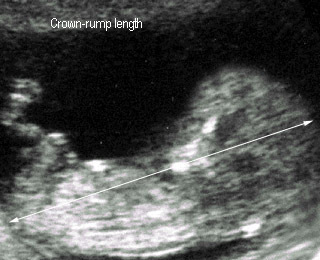
Crown-Rump Length (CRL)
- The most accurate parameter for GA (+ 3-7 days)
- Most accurate during 6.5-10 weeks
- Limitation: Appropriate only in first trimester
- Technique:
- Mid-sagittal scan (note fetal nose, spine, crown and rump)
- Measurement from the topmost of head to rump end
- Precaution: best done in neutral position, not include yolk sac or limbs
 |
 |
Crown-rump length8 weeks |
Crown-rump length9 weeks |
 |
|
Crown-rump length12 weeks |
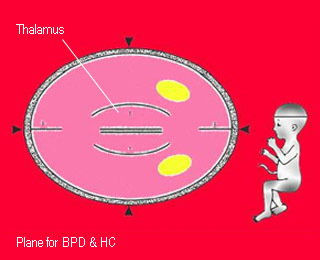
Biparietal Diameter (BPD)
- The best parameter during 2nd trimester (+ 7-11 days during 14-26 weeks)
- Technique: the distance from outer-to-inner skull table in the plane visualized of
- Ovoid and symmetry
- Thalamus
- Midline echo / third ventricle
- Cavum septum pellucidum
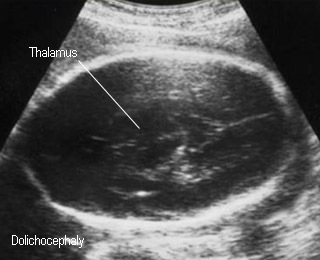
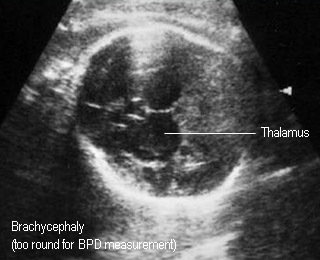
- Limitation: less reliable in case of
- Cephalic index (CI: BPD/OFD x 100) < 75% (dolichocephaly) or > 85% (brachycephaly) (normal CI 85%; 75-85%)
- Irregular skull shape or hydrocephalus
- Varied in 3rd trimester (+ 2-3 wks)
Head Circumference (HC)
- Measurement on the same plane as BPD
- The accuracy similar to BPD (+ 1 wk before 20 wk and + 2-3 wk in the 3rd trimester)
- Theoretically better than BPD, but practically less accurate due to poor imaging of anterior and posterior of the skull secondary to acoustic shadow
 |
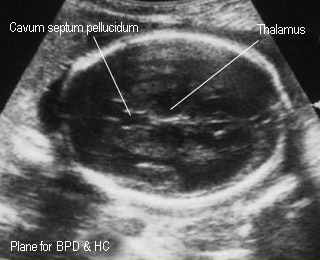 |
Biparietal diameterStandard plane for BPD measurement |
Biparietal diameterStandard plane for BPD measurement |
 |
 |
DolichocephalyBPD not proper for gestatational age calculation |
BrachycephalyBPD not proper for gestatational age calculation |
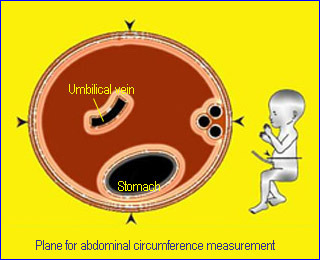
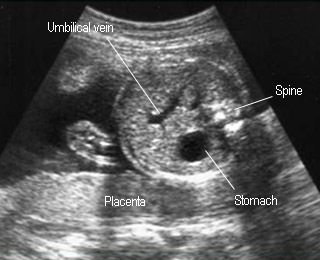
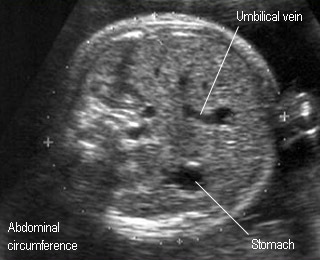
Abdominal Circumferece (AC)
- Most varied among the standard parameter
- Less accurate for GA estimation
- Best parameter for fetal growth evaluation or estimate fetal weight
- Plane for AC:
- as round as possible
- umbilical vein (middle-third) running to portal sinus in the liver (Note: if umbilical vein seen closely to anterior wall the plane is too low or oblique)
- stomach
- Measurement: perimeter around fetal skin
- Limitation: not accurate for GA, not round due to pressure effect
 |
 |
Abdominal circumferenceStandard plane for abdominal circumference measurement |
Abdominal circumferenceStandard plane for abdominal circumference measurement |
 |
|
Abdominal circumferenceStandard plane for abdominal circumference measurement |
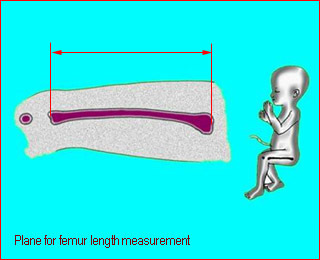
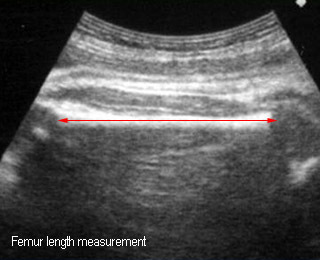
Femur Length (FL)
- The accuracy for GA similar to BPD, may be slightly less accurate and more accurate than BPD in 2nd and 3rd trimester respectively
- Plane: the longest plane and straight with least curve as possible
- Measurement between the both end, not include epiphysis
- Precaution: FL among Thai is shorter than that of western pregnanc
 |
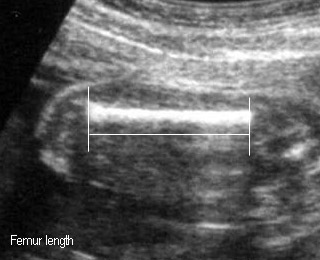 |
Femur lenghtStandard plane for femur length measurement |
Femur lenghtStandard plane for femur length measurement |
 |
|
Femur lenghtStandard plane for femur length measurement |
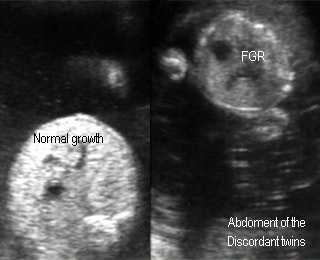
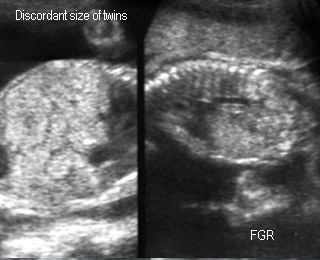
Fetal Growth Restriction (FGR)
- AC : most commonly used for diagnosis
- HC/AC ratio : increased in FGR ( the ratio is date dependent ; decreasing with GA, > 1 before 32 week, ~ 1 during 32-36 wk, > 1 after 36 wk) unreliable for symmetrical FGR
- FL/AC ratio : (date-independent) constant after 20 wk (normal ratio ~22+2 abnormal if > 24), unreliable for symmetrical FGR
- Umbilical artery Doppler waveforms: high resistance or absent end-diastole for true FGR but normal for constitutional small fetus
- Oligohydramnios is common among FGR
- Estimate fetal weight (< 10th percentile)
- Grade 3 placenta before 36 week
 |
 |
Fetal Growth Restriction (FGR)FGR due to twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome |
Fetal Growth Restriction (FGR)FGR due to twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome |
{tab=Placenta}
Placenta & Amniotic Fluid
Amniotic Fluid
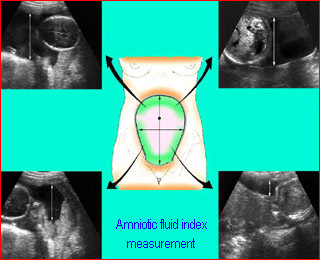
- Amniotic fluid index (AFI): Sum of the four deepest depth of AF four quadrant
- Oligohydramnios (AFI < 5) : commonly associated with FGR, rupture of membranes, and anomaly i.e. renal agenesis, polycystic kidney
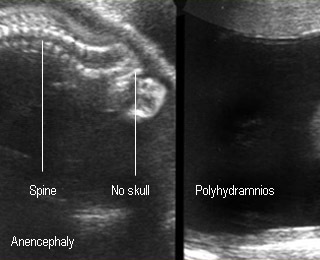
- Polyhydramnios (AFI > 95th centile or > 20-25) : commonly related to maternal DM, anomaly i.e.
- esophageal atresia
- neural tube defects
- aneuploidy etc.
 |
 |
Amniotic fluid indexFour quadrant deepest verical pocket measurement |
PolyhydramniosPolyhydramnios due to fetal anencephaly |
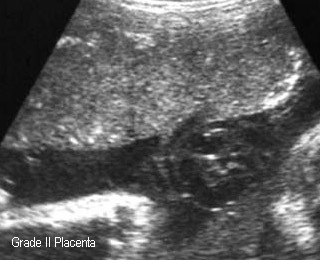
Placental grading
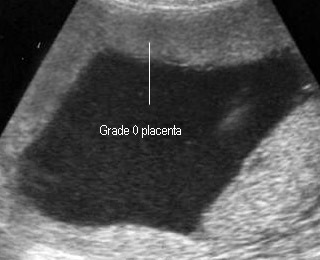
- 0 : no calcifications
- 1 : scattered calcifications
- 2 : basal calcifications
- 3 : basal and septal calcification; outline the cotyledons; commonly seen in postterm, FGR, PIH
- Extensive calcification < 36 wk related to FGR
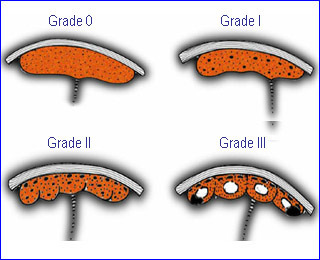
Placental Grading
Placental Grade 0
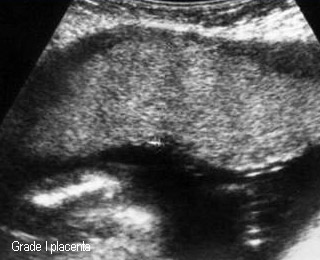
Placental Grade 1
Placental Grade2
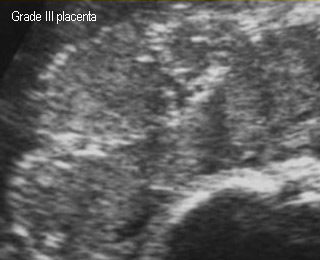
Placental Grade 3
Placenta Previa
- Marginal previa : adjacent to the internal os
- Partial previa: placenta covers a portion of internal os (indistinguishable from marginal previa in prenatal practice)
- Total previa: placenta covers the os
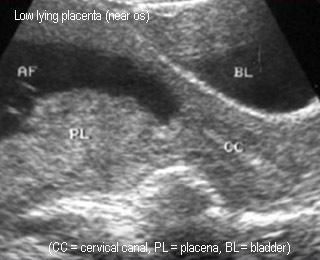
- Low-lying placenta: nearly the os, not true previa and vaginal deliver is possible
- Ultrasound: should be done with an empty bladder because the cervix is spuriously long by full bladder leading to false previa
- Most placenta previa diagnosed in the 2nd trimester is away from the os at term
- The cervix could be visualized using TAS, TVS or transperineal approach
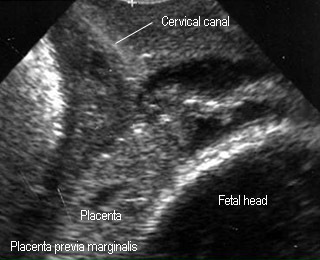
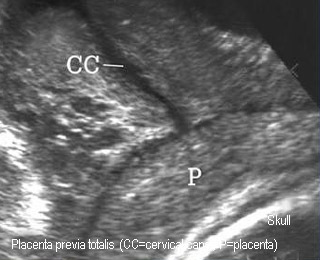
Placenta previa totalis
Standard plane for BPD measurement
Placenta previa totalis
Standard plane for BPD measurement
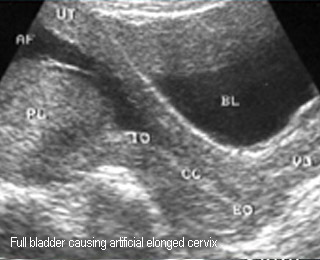
False placenta previa totalis
Full bladder compress lower segment, simulating placenta previa totalis
False placenta previa totalis
The same case (after voiding)
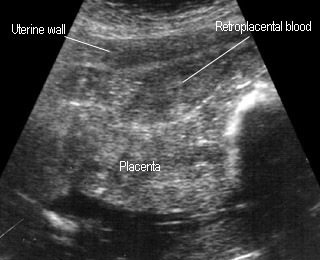
Placental Abruption
- cystic, complex, or hypoechoic areas may be seen between placenta and uterine wall
-
Placental thickening
-
reveal type may be not diagnosed
- retro placental hematoma may be isoechoic like placenta
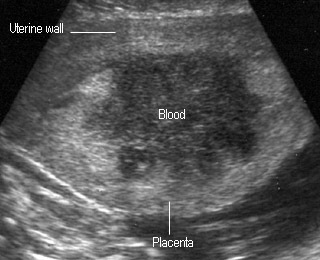
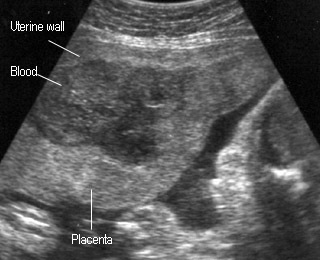
Placental abruption
Placental abruption
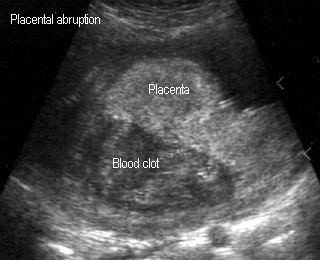
Placental abruption
Placental abruption
{tab=Fetal Anomaly}
Fetal anomaly
Fetal Hydrops
- Fluid accumulation : subcutaneous edema, ascites, pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, placentomegaly
- Most due to Hb Bart’s disease (1 : 1000 birth in northern Thailand), usually not related to other anomaly
- Other causes
- Rh isoimmunization
- Fetal anomaly: cystic hygroma, cardiac anomaly, supraventricular tachycardia
- Aneuploidy: 45XO, Down syndrome
- Infections: parvovirus B 19, syphilis
- Miscellaneous: chorioangioma, twin-twin transfusion syndrome etc.
Sonographic Findings of Hb Bart’s disease
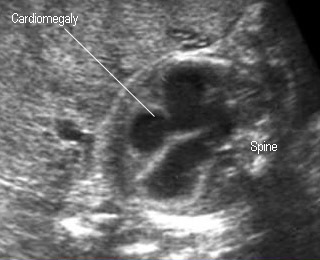
- cardiomegaly (increased cardio-thoracic ratio from midpregnancy) (The earliest sign)
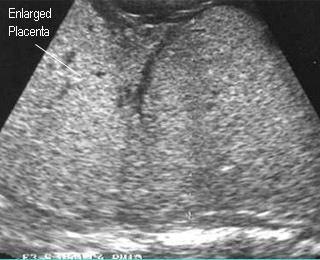
- Placentomegaly
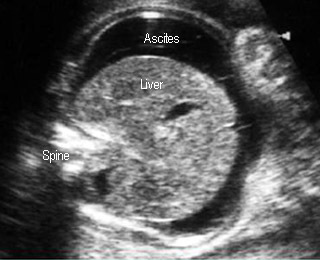
- Ascites
- Pleural or pericardial effusion
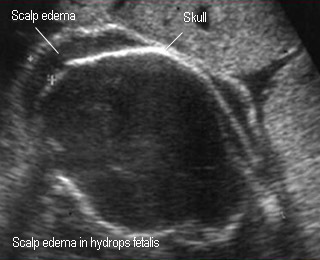
- Subcutaneous edema (late sign)
- Oligohydramnios (in late pregnancy) (unlike other causes which commonly related to polyhydramnios)
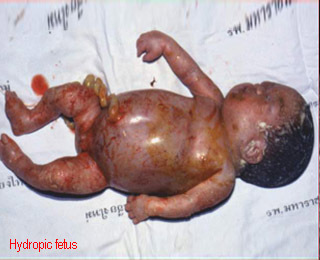 |
 |
Hydrops fetalisHydropic fetalis due to Hb Bart’s diisease |
Hydropic placentaHydropic fetalis due to Hb Bart’s diisease |
 |
 |
CardiomegalyMarkedly enlarged heart in fetal Hb Bart’s diisease |
AscitesAscites in fetal Hb Bart’s diisease |
 |
|
Subcutaneous edemaScalp edema in fetal Hb Bart’s diisease |
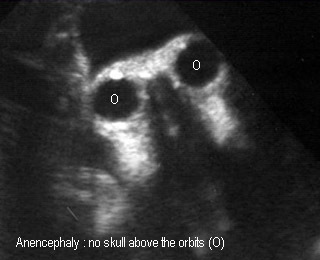
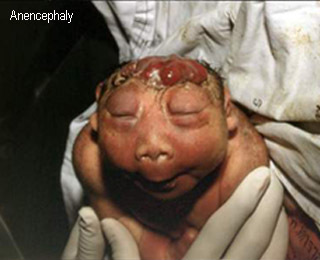
Anencephaly
- The most common NTDs (1: 1000 births)
- Ultrasound findings
- Absent skull
- Prominent orbit
- Often related to polyhydramnios
 |
 |
AnencephalyBase of skull contact with uterine wall / polyhydramnios |
AnencephalyNo skull above the orbits : Spectacle sign |
 |
|
AnencephalyPostnatal appearance of a term anencephalic fetus |
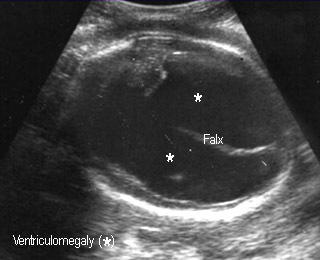
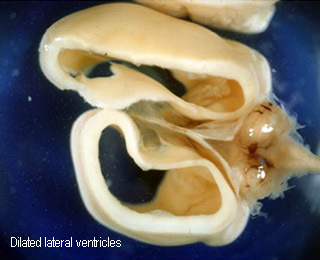
Ventriculomegaly
- Enlargement of cerebral ventricles or with increased pressure (hydrocephalus)
- Most cases of marked ventriculomegaly caused by obstruction of aqueduct of Sylvious
- Ventriculomegaly (> 10 mm)
- Dilated 3rd ventricle (> 3 mm)
- Dangling choroid plexus sign
- Thin cerebral mantle
 |
 |
HydrocephalusMarkedly enalarged lateral ventricles |
HydrocephalusAutopsy : markedly enalarged lateral ventricles |
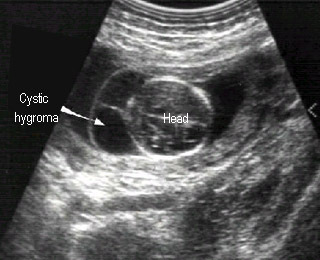
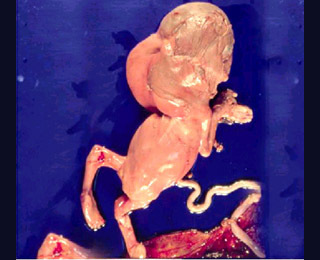
Cystic Hygroma
- Lymph collections due to obstruction, especially jugular lymph sac
- Commonly associated with 45XO (70%), and trisomy 21, 18
- Cyst at the posterolateral neck, septate or nonseptate
- Lethal if hydrops occurs, but simple cyst may regress and disappear
 |
 |
Cystic hygromaSeptate cyst at the back of fetal neck |
Cystic hygromaPostnatal finding |
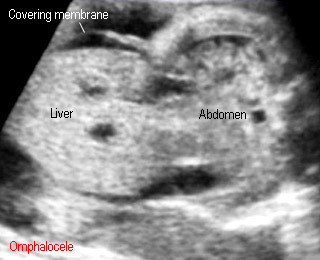
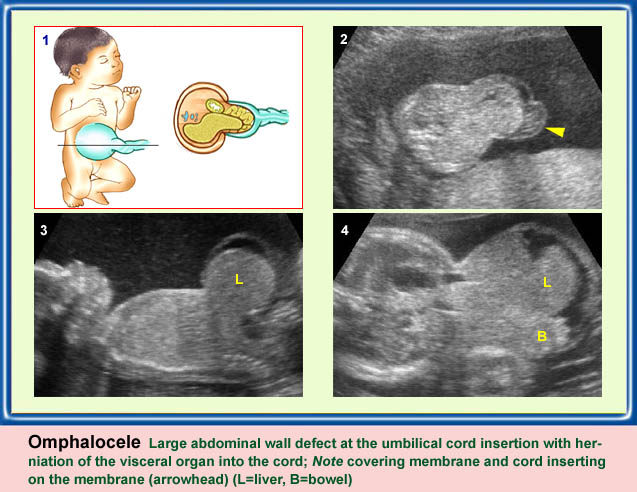
Omphalocele
- A protrusion of bowel / liver through abdominal wall at the umbilicus
- The protrusion covered by a membrane
- 50% associated with other anomalies, especially cardiac defects
- If containing bowel, 80% associated with abnormal chromosomes
- Liver-containing omphalocele: 20% associated with abnormal chromosomes
 |
 |
OmphaloceleProtruding mass containg liver with membrane covering |
OmphaloceleNote: extra-abdominal mass with covering membrane |
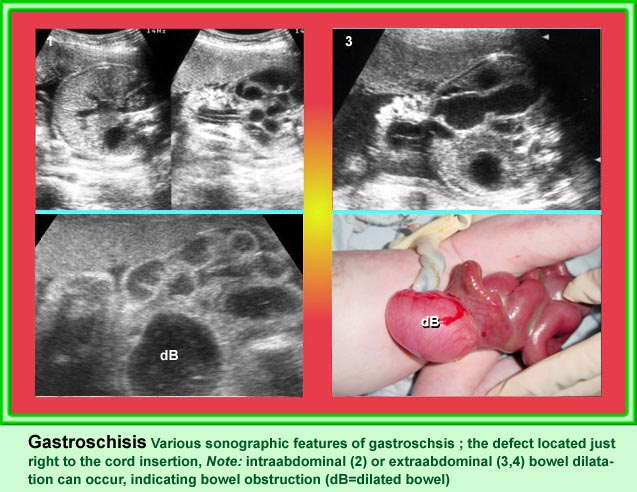
Gastroschisis
- A protrusion of bowel (rarely other visceral organ) through a defect of the abdominal wall, typically to the right of the cord insertion
- No membrane covers the mass
- Not related to chromosome abnormalities or other anomalies other than GI
 |
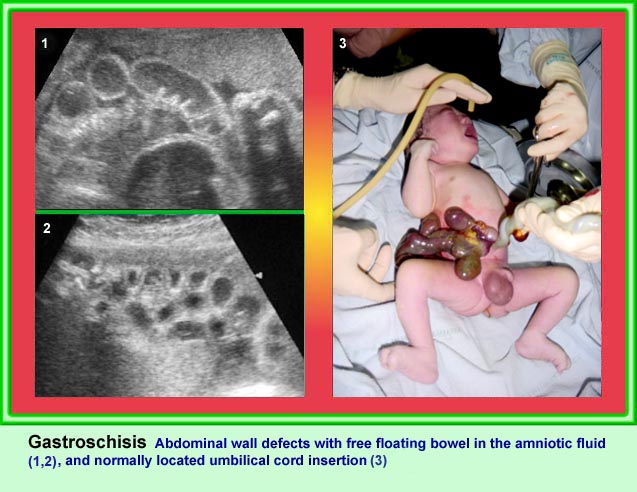 |
GastrochisisFree floating bowels in amniotic fluid |
GastrochisisPostnatal appearance: no covering membrane |
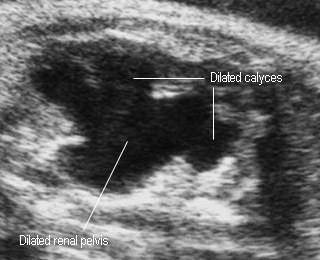
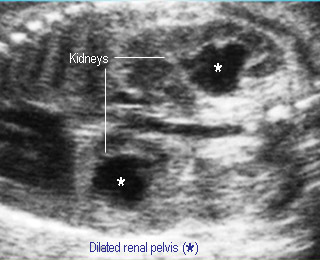
Hydronephrosis
- > 75% related to renal abnormalities
- Ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) obstruction is the most common cause: dilated renal pelvis (> 10 mm) and calyces, often bilateral
- Thin renal parenchyma suggestive of poor renal function
- Renal pelvic dilation < 10 mm is often a normal variant but needs follow up and slightly increased risk of Down syndrome
 |
 |
HydronephrosisDilated renal pelvis and calyces |
HydronephrosisDilated renal pelvis and calyces |
{/tabs}


