Benign disease of vulva
พ.ญ.หทัยรัตน์ เรืองเดชณรงค์
อาจารย์ที่ปรึกษา ผ.ศ. น.พ.ชัยเลิศ พงษ์นริศร
Anatomy of vulva (3, 10)
Vulva หรือ ปากช่องคลอด คืออวัยวะสืบพันธุ์ภายนอกของสตรี ทางด้านหน้า( Anterior) เป็นส่วนของ mons pubis ด้านข้าง (Laterally) อยู่ระหว่างร่องพับขา (inguinogluteal folds) และทางด้านหลัง(Posterior) เป็นส่วนของทวารหนัก (Anus) โครงสร้างของ vulva ประกอบไปด้วย mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, hymen, clitoris, vestibular, urethra, Skene’s gland, Bartholin’s gland และ vestibular bulbs ผิวหนังบริเวณนี้จะมีด้วยกัน 2 ชนิดคือ keratinized squamous epithelial ซึ่งอยู่บริเวณ laterally ต่อ Hart line ซึ่งเป็นบริเวณที่เยื่อบุ 2 ชนิดมาบรรจบกัน และอีกชนิดคือ nonkeratinized squamous epithelial จะอยู่ภายใน Hart line ซึ่งใกล้กับส่วนของ vagina มากกว่า
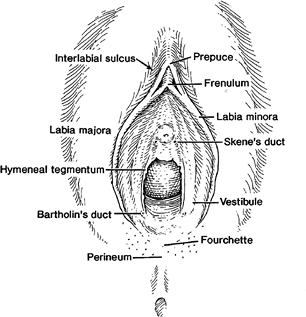
รูปที่ 1 vulva and perineum (7)
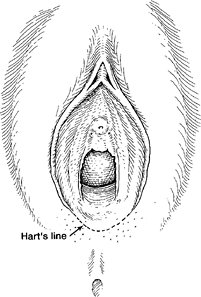
รูปที่ 2 The Hart line คือขอบนอกของ vulva vestibule (7)
เส้นประสาทของ vulva ได้แก่ ilioinguinal, genitofemeral, femoral cutaneous nerve และ perineal nerve (Branch of pudendal) ส่วนหน้าของ labia majora จะมี ilioinguinal และ pudendal nerveมาเลี้ยงด้านข้าง และด้านหลังจะมี posterior femoral cutaneous nerve เลี้ยง
ส่วนของ blood supply จะมี internal pudendal artery เป็นหลอดเลือดหลักบริเวณนี้และยังมี external pudendal artery ซึ่งเป็น สาขาของ femoral artery เลือดจะไหลกลับคืนผ่าน internal และ external pudendal vein
Terminology and Classification of vulvar disease
โรคของปากช่องคลอด เป็นโรคที่พบได้บ่อย และมักจะสร้างความรำคาญให้แก่คนไข้ แต่การเข้าใจโรค การวินิจฉัยรอยโรคของโรคทางปากช่องคลอดยังเป็นที่ไม่เข้าใจและลำบากในการวินิจฉัยสำหรับแพทย์ และเจ้าหน้าที่ที่ดูแลทางด้านนี้ โดยการวินิจฉัยจะอาศัยประวัติ การตรวจร่างกาย ดูลักษณะรอยโรคและการตรวจทางพยาธิวิทยา (pathology) เพื่อวินิจฉัย (15)
The International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease (ISSVD)(16) เป็นองค์กรที่ถูกจัดตั้งขึ้นเมื่อปี ค.ศ. 1970 เพื่อศึกษาเกี่ยวกับ vulvovaginal disease เกี่ยวกับตัวโรคและประชุมเพื่อออกแนวทางการรักษา หรือ guideline ต่างๆเพื่อเป็นแนวทางในการวินิจฉัยและการรักษาของ vulvovaginal disease ซึ่งสำหรับ vulvar disease นั้นได้มีการจะทำ ” 2011 ISSVD Terminology and Classification of Vulvar Dermatological Disorders: An Approach to Clinical Diagnosis” เพื่อเป็นแนวทางในการวินิจฉัย โดยอาศัยเพียงการซักประวัติ และตรวจร่างกายโดยดูจากรอยโรคทางผิวหนัง (dermatological disorder) เพื่อสะดวกและง่ายต่อการวินิจฉัยทางคลินิก โดย ISSVD ได้แนะนำการ classification และบรรยายรอยโรคโดยมีขั้นตอน 5 ขั้นตอนดังนี้(16)
Step 1 : บรรยายลักษณะรอยโรคหลัก (Define the lesion by choosing 1 or more of following nouns )
- Blister : ตุ่มน้ำที่ยกนูนจาก skin หรือ mucosa (fluid-filled)
- Bulla : ตุ่มน้ำที่มีขนาดใหญ่กว่า 0.5 cm
- Cyst : ถุงที่เป็นลักษณะปิดด้วยเยื่อบุ (Closed cavity lined by epithelium ) และภายในมี fluid หรือ seminal material
- Edema : ผิวที่ยกนูนขอบเขตไม่ชัดเจนจากการมีการสะสมของ fluid ในชั้น dermis และ/หรือ subcutaneous tissue ผิวหนังอาจจะมีสีชมพูหรือสีแดง
- Erosion : skin surface มีการหลุดลอกตื้นๆ มีการขาดหายไปของชั้น epidermis จนถึงชั้น basement membrane แต่ชั้น dermis ปกติดี (intact dermis)
- Excoriation : erosion /ulcer ที่เกิดจากการขีดข่วน
- Fissure : thin line erosion of skin surface
- Lesion : ผิวหนังที่มองเห็นหรือคลำได้ว่ามีความผิดปกติ
- Macule : ผิวหนังที่มีสีผิดปกติขนาด < 1.0 cm และไม่ยกนูน
- Papule : ตุ่มหรือผิวหนังที่ยกนูน ขนาดเล็ก < 1.0 cm
- Nodule : ตุ่มหรือผิวหนังที่ยกนูน ขนาดใหญ่ > 1.0 cm
- Patch : ผิวหนังที่มีสีผิดปกติขนาด > 1 cm และไม่ยกนูน
- Plaque : Large (>1 cm) elevated, palpable and flat topped lesion
- Pustule : ตุ่มหนอง (Pus-filled blister)
- Rash : Numerous or diffuse abnormalities
- Ulcer : แผลลึก(deep defect) ที่ไม่มี epidermis และบางส่วนของ dermis
- Vesicle : ตุ่มน้ำขนาดเล็ก < 0.5 cm
Step 2: เลือกลักษณะของรอยโรคเพิ่มเติมเพื่ออธิบายรอยโรคได้ชัดเจนขึ้น (Choose appropriated adjectives to modifly the noun(s) chosen previously
- Color: สีที่ใช่ส่วนใหญ่คือ Red, white, brown, blue, gray, black
- Surface: smooth, rough, palpation
- Margination: ขอบเขตชัด (well-circumscribed) หรือไม่ชัด (poorly marginated lesion)
Step 3: โรคที่อาจจะเป็นได้ (Formulate a list of differential diagnosis)
เรียงรายชื่อโรคที่อาจจะเป็นไปได้ตามรอยโรคที่ตรวจพบ(step1+stap 2) ตามการแยกโรค 8 ลักษณะตามตารางที่ 1 และใช้ข้อมูลความรู้อื่นที่ร่วมด้วย
Step 4: ลดจำนวนโรคที่อาจจะเป็นได้ (Reduce of the number of differential diagnosis)
อาศัยแหล่งข้อมูล Textbook เพื่อช่วยในการวินิจฉัยร่วมกับข้อมูลที่ได้จากประวัติและรอยโรคจากผู้ป่วย
Step 5: Confirm a clinical diagnosis : อาศัย laboratory testing เพื่อ confirm diagnosis
ตารางที่ 1 : 2011 ISSVD Clinical Classification of Vulvar Dermatological Disorders (16)
|
1) Skin-colored lesions
A. Skin-colored papules and nodules
1. Papillomatosis of the vestibule and medial labia minora
(a normal finding; not a disease)
2. Molluscum contagiosum
3. Warts (HPV infection)
4. Scar
5. Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia
6. Skin tag (acrochordon, fibroepithelial polyp)
7. Nevus (intradermal type)
8. Mucinous cysts of the vestibule and medial labia minora
(may have yellow hue)
9. Epidermal cyst (syn. epidermoid cyst; epithelial cyst)
10. Mammary-like gland tumor (hidradenoma papilliferum)
11. Bartholin gland cyst and tumor
12. Syringoma
13. Basal cell carcinoma
B. Skin-colored plaques
1. Lichen simplex chronicus and other lichenified disease
(see definitions in Discussion of Terms Related to Eczematous
and Lichenified Diseases)
2. Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia
|
2) Red lesions: patches and plaques
A. Eczematous and lichenified diseases (see definitions in Discussion of Terms Related to Eczematous and Lichenified Diseases)
1. Allergic contact dermatitis
2. Irritant contact dermatitis
3. Atopic dermatitis (rarely seen as a vulvar presentation)
4. Eczematous changes superimposed on other vulvar disorders
5. Diseases clinically mimicking eczematous disease (candidiasis,
Hailey-Hailey disease, and extramammary Paget disease)
6. Lichen simplex chronicus (lichenification with no preceding skin lesions)
7. Lichenification superimposed on an underlying preceding
pruritic disease
B. Red patches and plaques (no epithelial disruption)
1. Candidiasis
2. Psoriasis
3. Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia
4. Lichen planus
5. Plasma cell (Zoon) vulvitis
6. Bacterial soft-tissue infection (cellulitis and early necrotizing fasciitis)
7. Extramammary Paget disease
|
|
3) Red lesions: papules and nodules
A. Red papules
1. Folliculitis
2. Wart (HPV infection)
3. Angiokeratoma
4. M. contagiosum (inflamed)
5. Hidradenitis suppurativa (early lesions)
6. Hailey-Hailey disease
B. Red nodules
1. Furuncles (‘‘boils’’)
2. Wart (HPV infection)
3. Prurigo nodularis
4. Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia
5. M. contagiosum (inflamed)
6. Urethral caruncle and prolapse
7. Hidradenitis suppurativa
8. Mammary-like gland adenoma (hidradenoma papilliferum)
9. Inflamed epidermal cyst
10. Bartholin duct abscess
11. Squamous cell carcinoma
12. Melanoma (amelanotic type)
|
4) White lesions
A. White papules and nodules
1. Fordyce spots (a normal finding; may sometimes have a yellow hue)
2. M. contagiosum
3. Wart
4. Scar
5. Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia
6. Squamous cell carcinoma
7. Milium (pl. milia)
8. Epidermal cyst
9. Hailey-Hailey disease
B. White patches and plaques
1. Vitiligo
2. Lichen sclerosus
3. Postinflammatory hypopigmentation
4. Lichenified diseases (when the surface is moistVsee definitions in
Discussion of Terms Related to Eczematous and Lichenified Diseases)
5. Lichen planus
6. Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia
|
|
5) Dark-colored (brown, blue, gray, or black) lesions
A. Dark-colored patches
1. Melanocytic nevus
2. Vulvar melanosis (vulvar lentiginosis)
3. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation
4. Lichen planus
5. Acanthosiaas nigricans
6. Melanoma in situ
B. Dark-colored papules and nodules
1. Melanocytic nevus (includes those with clinical and/or
histological atypia)
2. Warts (HPV infection)
3. Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia
4. Seborrheic keratosis
5. Angiokeratoma (capillary angioma, cherry angioma)
6. Mammary-like gland adenoma (hidradenoma papilliferum)
7. Melanoma
|
6) Blisters
A. Vesicles and bullae
1. Herpesvirus infections (herpes simplex, herpes zoster)
2. Acute eczema (see definitions in Discussion of Terms Related
to Eczematous and Lichenified Diseases)
3. Bullous lichen sclerosus
4. Lymphangioma circumscriptum (lymphangiectasia)
5. Immune blistering disorders (cicatricial pemphigoid, fixed drug
eruption, Steven-Johnson syndrome, pemphigus)
B. Pustules
1. Candidiasis (candidosis)
2. Folliculitis
|
|
7) Erosions and ulcers
A. Erosions
1. Excoriations (see the disorders in group 2A)
2. Erosive lichen planus
3. Fissures arising on normal tissue (idiopathic, intercourse related)
4. Fissures arising on abnormal tissue (candidiasis, lichen simplex
chronicus, psoriasis, Crohn disease, etc.)
5. Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia, eroded variant
6. Ruptured vesicles, bullae and pustules (see all of
the disorders listed in group 6 ‘‘blisters’’)
7. Extramammary Paget disease
B. Ulcers
1. Excoriations (related to eczema, lichen simplex chronicus)
2. Aphthous ulcers (syn. aphthous minor), aphthous major,
Lipschu¨ tz ulcer (occurring either as an idiopathic process or secondary to other diseases such as Crohn, Behc¸ et, various viral infections)
3. Crohn disease
4. Herpes virus infection (particularly in patients who
are immunosuppressed)
5. Ulcerated squamous cell carcinoma
6. Primary syphilis (chancre)
|
8) Edema (diffuse genital swelling)
A. Skin-colored edema
1. Crohn disease
2. Idiopathic lymphatic abnormality (congenital Milroy disease)
3. Postradiation and postsurgical lymphatic obstruction
4. Postinfectious edema (especially staphylococcal and
streptococcal cellulitis)
5. Postinflammatory edema (especially hidradenitis suppurativa)
B. Pink or red edema
1. Venous obstruction (e.g., pregnancy and parturition)
2. Cellulitis (primary or superimposed on already existing edema)
3. Inflamed Bartholin duct cyst/abscess
4. Crohn disease
5. Mild vulvar edema may occur with any inflammatory
vulvar disease
|
Common benign vulvar disease
1. Skin – colored lesion
• Epidermal inclusion cyst / keratinous cyst (3)
เป็น cyst ที่คลุมด้วย stratified squamous epithelium มักพบที่ vulva และ perineal skin อาจจะเกิดตามหลังการบาดเจ็บเช่น female circumcision หรือเกิดจากการอุดตันของรูเปิดของต่อมไขมัน (pilosebaceous duct and gland) อาการและอาการแสดงมักจะมาด้วย คลำได้ก้อนที่ปากช่องคลอดและไม่มีอาการ บางส่วนอาจจะมาด้วยการติดเชื้อที่ก้อน (infected epidermal cyst) ด้วยอาการปวด บวมที่ก้อนและอาจจะมีน้ำที่มีกลิ่นเหม็นหรือ cheeselike drainage ออกจากก้อน ลักษณะของ epidermal cyst ที่ตรวจได้เป็นลักษณะ multiple nodules, mobile และ ไม่เจ็บหากไม่มีการติดเชื้อ และที่บริเวณก้อนจะมีรูเปิดจากก้อน (small opening)
รูปที่ 3(3): epidermal cyst บริเวณepisiotomy
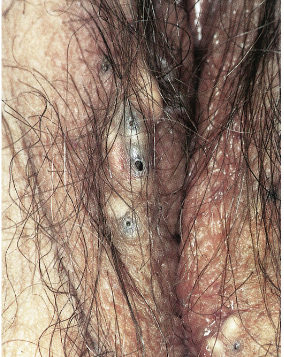
รูปที่ 4(3): multiple epidermal cyst with opening
การรักษา ส่วนใหญ่มักไม่ต้องการรักษา แต่ต้องให้คำแนะนำแก่ผู้ป่วยว่าเป็นแค่ benign โอกาสที่จะกลายเป็น malignancy น้อยมาก การผ่าตัดก้อนจะแนะนำทำในช่วงที่ไม่มีอาการหรือไม่มีการติดเชื้อ แต่หากมีการติดเชื้อควรได้รับยาปฏิชีวนะประมาณ 2 สัปดาห์ก่อนการผ่าตัด
• Skene duct cyst(3)
คือ cyst ของ Skene glands ซึ่งอยู่ใกล้กับ urethral meatus แต่อยู่ใน vulvar vestibule (Periurethral cyst) เกิดจาก congenitial หรือเป็นภายหลังจากการอุดตันของท่อเช่นการอักเสบ ลักษณะจะเป็น bilateral single มีรูปเปิดอยู่ข้าง urethral meatus อาจจะมาด้วยอาการปวดปัสสาวะ หรือลักษณะของลำปัสสาวะเปลี่ยนไป ส่วนมากไม่มีอาการ การรักษาสังเกตอาการของก้อนว่าโตขึ้นมากกทำให้มีอาการจึงพิจารณา Excision
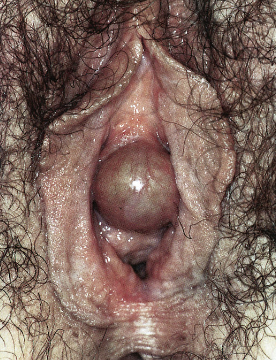
รูปที่ 5(3): skene duct cyst
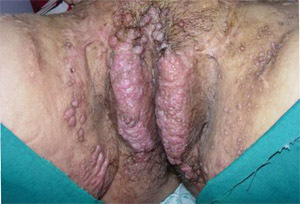
• Wart/ condyloma acuminatum หรือหูด(3, 15, 17)
เป็น benign neoplasm ของผิวหนังชนิดหนึ่งที่เกิดจากเชื้อ HPV (Human papillomavirus) มักเกิดจากสายพันธุ์ 6 และ11 ซึ่งติดต่อผ่านทางเพศสัมพันธ์ อาจจะพบทั้งที่ vulvar, vagina และ cervix ได้ หูดสามารถวินิจฉัยจากอาการและอาการแสดงได้ไม่แนะนำให้ทำ HPV test หรือพิจารณา biopsyเมื่อสงสัยว่าเป็น invasive lesion เท่านั้น ซึ่งอาการและอาการแสดงมักจะไม่มีอาการมาก่อน อาจจะมาด้วยมีก้อนหรือผิวหนังโตผิดปกติที่บริเวณปากช่องคลอดหรือมาตรวจภายในแล้วแพทย์ตรวจพบ โดยที่ลักษณะเป็น white, exophytic, หรือ papillomatous growth (typical lesion) หรือลักษณะ skin color ,small, form like, cauliflower like mass อาจจะเป็น unifocal หรือ multiple lesion
การรักษา แนะนำให้รักษาโดย medication หากไม่ได้ผลพิจารณา surgical treatment ซึ่งยาที่แนะนำเป็น 1st line ได้แก่ imiquimod 3.75% cream โดยมี clearance rate 27-29% (17) แต่ไม่มีหลักฐานเรื่องความปลอดภัยในหญิงตั้งครรภ์ หญิงให้นมบุตรและผู้ป่วย immunosuppressed และการป้องกันการติดเชื้อ HPV โดยการให้ HPV vaccine
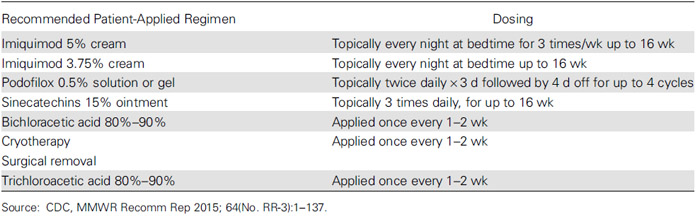
ตารางที่ 2 : Recommended and Alternative Regimens for Treatment of External Anogenital Warts(17)
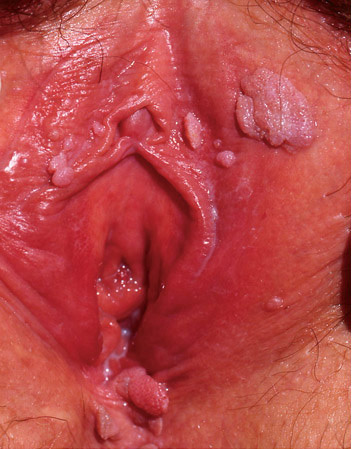
รูปที่ 6(1) condyloma acuminate of vulva
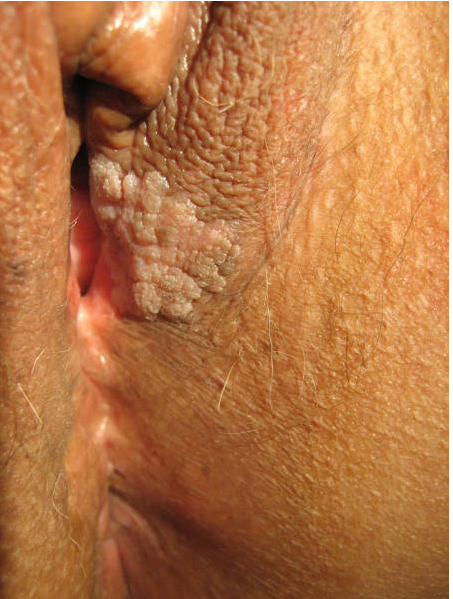
รูปที่ 7(8) : condyloma acuminate of vulva
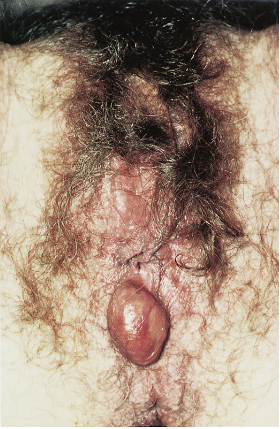
• Bartholin cyst/abscess(13)
เป็น most common disorder of Bartholin’s gland มักจะเกิดในวัยเจริญพันธ์ เกิดจากการอุดตันของท่อ โดยส่วนใหญ่มีขนาดเล็กประมาณ 1-3 cmและไม่มีอาการ แต่ถ้าขนาดใหญ่มากกว่า 5 cm อาจจะทำให้มีอาการปวดตึงจากก้อนได้ Bartholin abscess เกิดจากติดเชื้อของก้อนภายในจะเป็นหนองทำให้มีอาการปวด บวม แดงเชื้อที่ก่อโรคได้แก่ N. gonorrhoeae ,C. trachomatis และ E. coli
การรักษา Bartholin abscess รักษาโดยการ Marsupialization ซึ่งได้ประสิทธิภาพมาก ส่วน Bartholin cystsหากมีอาการพิจารณา Removal gland และในกลุ่ม postmenopausal พิจารณาส่ง biopsy สงสัย adenocarcinoma of Bartholin’s gland
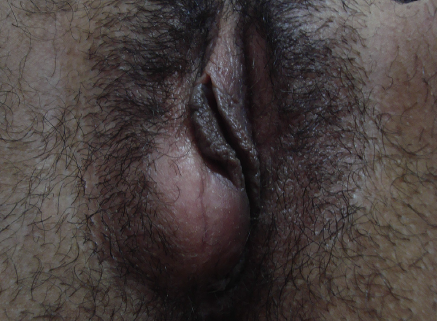
รูปที่ 8(13): Bartholin cyst (ซ้าย)
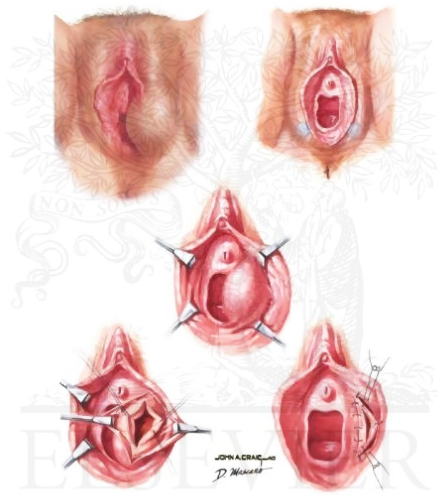
รูปที่ 9(14): Marsupilizarion (ขวา)
2. Red lesion: patch and plaque
• Psoriasis(15)
โรคสะเก็ดเงิน เป็นโรคผิวหนังเรื้องรัง พบร่วมกับผิวหนังบริเวณหนังศีรษะ บริเวณextensor surfaceของแขนและขา ลำตัวและที่vulva และอาจจะเป็นส่วนเดียวที่มีรอยโรค รอยโรคส่วนใหญ่มักจะเป็นปื้นหนาขอบเขตชัด แห้ง แดง และมีสะเก็ดสีเงินที่รอยโรค(silver scaly crusts) รักษาโดยการให้ Topical corticosteroid
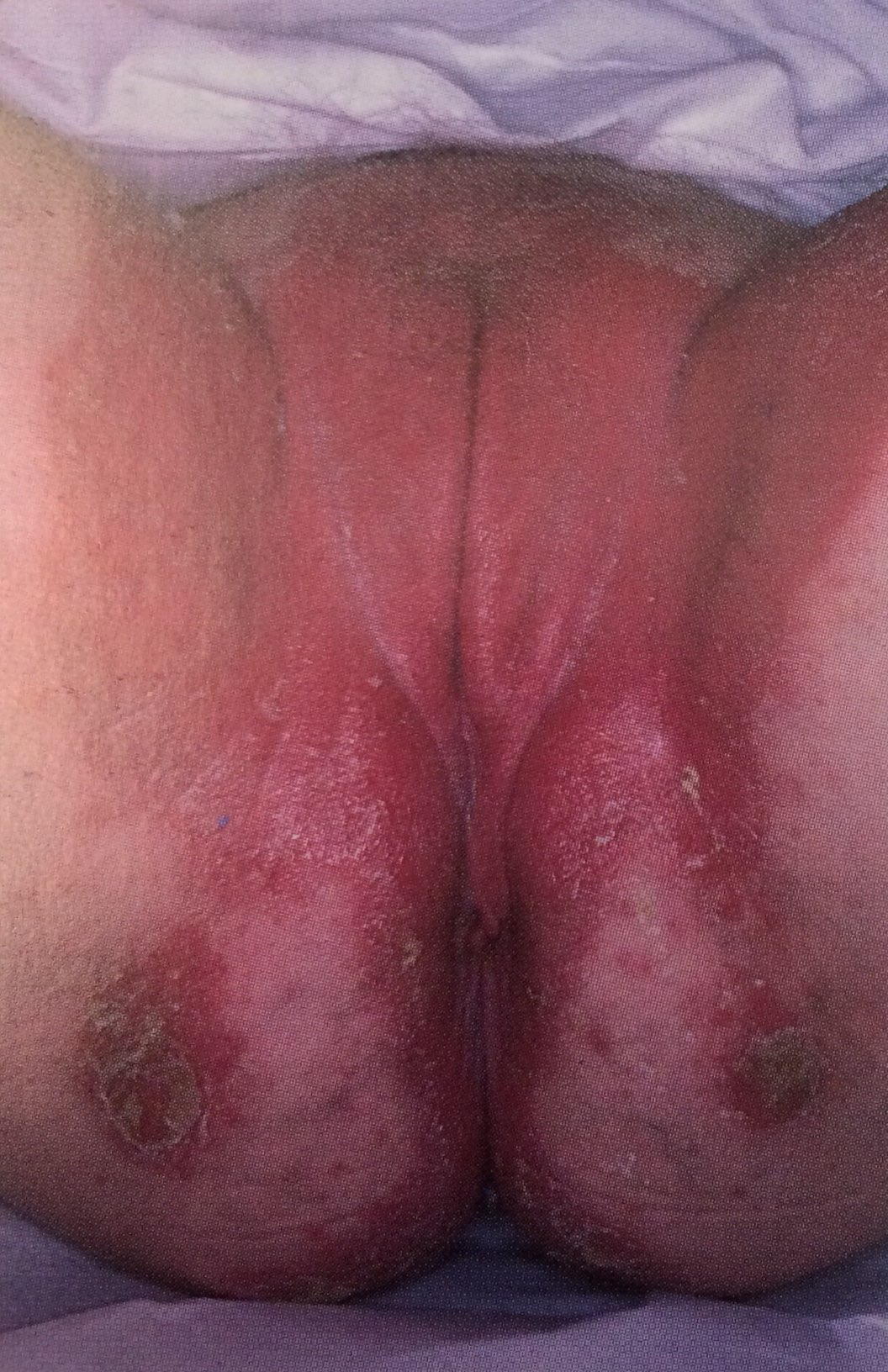
รูปที่ 10(5): Psoriasis : intense erythema and peripheral scale,shaply demarcated
• Eczema (Atopic dermatitis)(3)
เป็นการอักเสบของผิวหนัง ส่วนของ vulva อาจจะพบได้ไม่บ่อยแต่หากมาด้วยอาการมีผื่นคันที่ vulva จะต้องนึกถึงไว้เสมอ eczemaส่วนใหญ่มักเกิดจากการสัมผัส allergen พบได้ทั้ง acute, subacute และ chronic อาการจะมาด้วยผื่นคันที่ปากช่องคลอด ลักษณะผื่นมีได้หลายลักษณะได้แก่ ตุ่มน้ำเล็กๆ(vesicular eruption) ผื่นแดงขอบเขตไม่ชัดเจนและมีขุ่ย อาจจะมีลักษณะรอยการเกาเป็นแบบ thickened skin และ plaquelike

รูปที่11(3) : chronic eczema
การรักษา hydration and lubrication และใช้ Topical steroid ในกลุ่ม subacute และ chronic
• Lichen planus (3, 15)
Lichen planus เป็นโรคทางผิวหนัง (mucocutaneous) พบที่ vulva น้อย เป็น inflammatory disease ที่ไม่ทราบสาเหตุพบที่ ผิวหนังและmucosal surface มักไม่มีอาการอาจจะมาด้วย dyspareunia ลักษณะรอยโรคเป็น shaply marginated flat-topped papaule,velvety plaquelike และ erosive lesion ตรวจพบ oral lesion และผมร่วงได้ การรักษาเป็น Topical steroid ได้แก่ betamethasone,clobetasol หรือ hydrocortisone 25 mg vagina suppository ทุกวัน และTopical 0.1% tacrolimus ointment
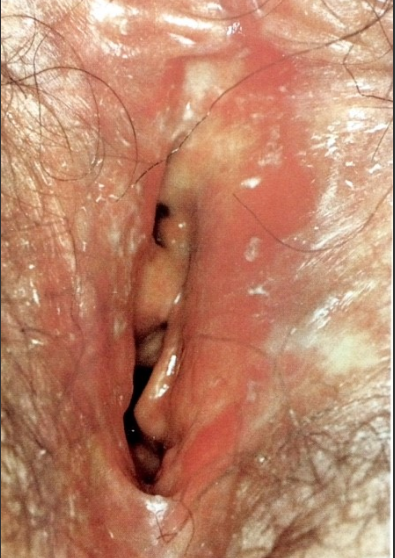
รูปที่ 13(3): Lichen planus
• Candidiasis(3, 4, 18)
เป็น fungal infection เกิดจากเชื้อ Candida albicans อาการของโรค external dysuria, vulvar pruritus, pain, swelling และ redness อาการแสดงได้แก่ vulvar edema, fissures, excoriations และ thick curdy vaginal discharge ในบางกรณี candidiasis อาจเป็นอาการแสดงของเบาหวาน
การรักษา(4) ให้ short-course topical antifugal drug กลุ่ม azole drugเป็นยาที่ใช้รักษาได้ประสิทธิภาพกว่า nystatin ซึ่งทำให้บรรเทาอาการและ negative cuture ได้ถึง 80-90%
ตารางที่ 3: Recommended regimen for Treatment(4)

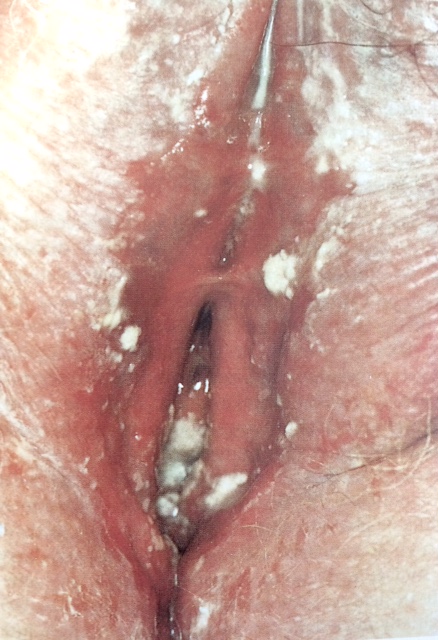
3. Red lesion : papules and nodules
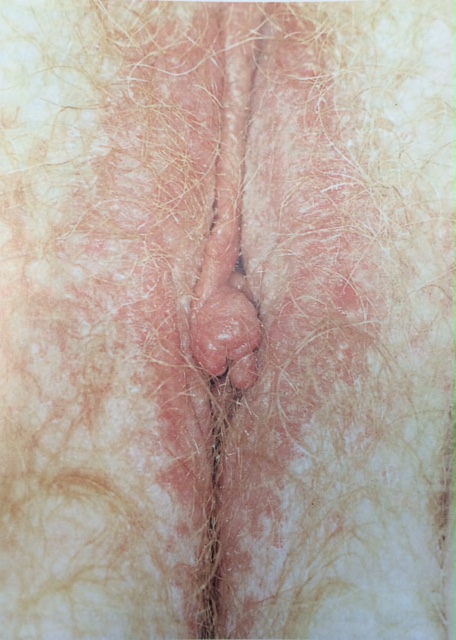
• Urethral caruncle (3, 19)
เกิดจากภาวะ hypoestrogenemic มีการปลิ้นออก(everted)ของ distal urethral mucosa ส่วนใหญ่ไม่มีอาการมักจะตรวจเจอพร้อมกับตรวจภายใน บางรายอาจจะมีอาการ dysuria ลักษณะจะเป็น pink or reddish exophytic lesion ที่ urethral meatus บางรายอาจจะเป็นสีม่วงเกิดจาก thrombosis การรักษา conservative therapy ได้แก่ warm sitz baths, topical estrogen creams และtopical anti-inflammatory drugs จะพิจารณาผ่าตัดในรายที่ก้อนมีขนาดใหญ่
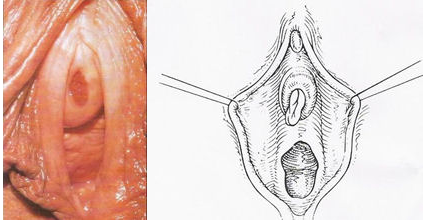
รูปที่ 15(2) : Urethral caruncle
4. White lesion
• Lichen sclerosus(9, 15)
เป็น chronic inflammatory skin disease พบได้ทั้งสองเพศแต่พบในผู้หญิงมากกว่า และพบมากในกลุ่มอายุมากกว่า 60ปี หรือ postmenopausal สาเหตุไม่ทราบชัดเจนแต่พบว่ามี 10% ของผู้ป่วยจะมีญาติที่เป็น lichen sclerosus อาจะเกิดจาก local trauma และ estrogen deficit อาการมาด้วย คันบริเวณปากช่องคลอด(Pruitus) หรือ dyspareunia ลักษณะของผื่นจะเป็น whitish patch and nodules (hyperkeratpsos and sclerosis), atrophic skin,wrinkled,subepithelial hemorrhage จากการเกา อาจจะพบเป็นสีแดง(slight redness)ในช่วงแรก อาจจะพบ narrow vaginal introtus ทำให้มี dyspareunia นอกจากนั้นยังพบ perineal stenosis และถ่ายลำบาก ร่วมด้วย หากรอยโรคอยู่ใกล้กับ urethra meatus จะทำให้เกิด urethral stenosis หากรักษาแล้วอาการไม่ดีขึ้นยังมีรอยโรคอยู่ให้พิจารณา biopsy เพราะอาจจะเกิด malignant tranformation ได้
การรักษา
- Potent topical steroid ได้แก่ clobetasole dipropionate 0.05% (Dermovate) เป็นเวลา 3เดือน จะช่วยลดภาวะแทรกซ้อน และลดโอกาสเกิด malignant tranformation
- ห้ามเกา ใส่เสื้อผ้าหลวมๆ และใช้ skin care product เป็น long term therapy
- การผ่าตัดพิจารณาทำเพื่อรักษา introital narrowing
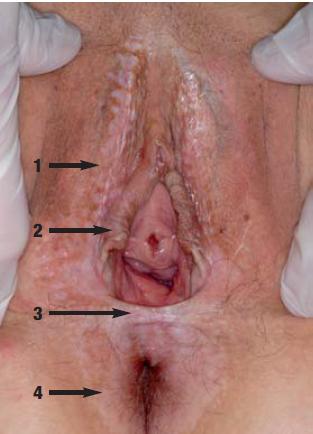
รูปที่ 16(9): White nodules and plaques in the interlabial sulcus (1), adhesion of the labia minora (2), perineal (3) and perianal (4)
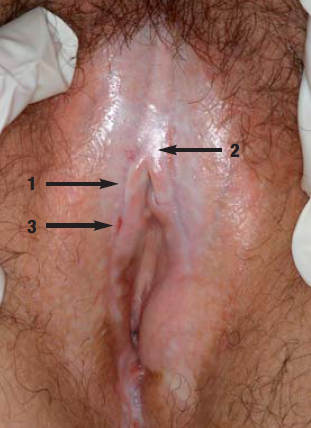
รูปที่ 17(9): Atrophy and sclerosis of the skin in the interlabial sulcus (1), adhesion of the labia minora above the clitoris (2), ecchymosis of the right labium minus(3)
• Lichen Simplex Chronicus(3, 15)
เกิดจาก chronic irritation เช่น การใช้น้ำหอมของผ้าอนามัย หรือ infectionme ทำให้เกิด epithelial thickening และ hyperkeratosis หรือ chronic eczema อาการมาด้วยคันที่ปากช่องคลอดทำให้เกิดการเกาหรือถู ลักษณะรอยโรคเป็น irregular, plaquelike, white epithelium และ unilateral การBiopsy มีความจำเป็นเพื่อแยก intraepithelial neoplasia และ invasive tumor ให้ได้
การรักษา
- ดูแลสุขภาพความสะอาดของบริเวณปากช่องคลอด
- การใช้ lubricant ช่วยให้มีความชุ่มชื้น
- Tropical medium potency steroid
- oral antihistamine เพื่อช่วยลดอาการคัน
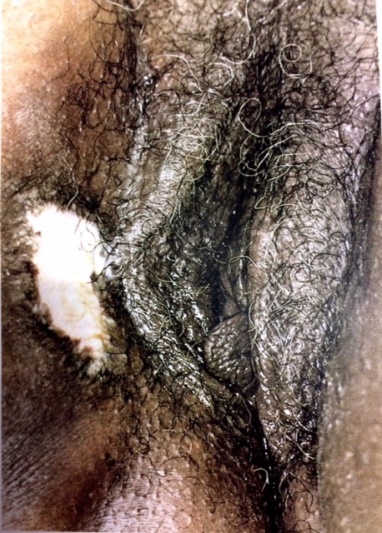
รูปที่ 18(3) : Lichen Simplex Chronicus
5. Dark-colored (Brown,blue,gray,or black)
• Vulva melanosis (Vulva lentiginosis)(3)
เป็น benign hyperpigmented macular lesion เกิดบริเวณ non-sun exposed skin และเป็น most common hyperpigmented lesion ที่เกิดที่ vulva เกิดจากการผลิต melaninมากเกิน ส่วนใหญ่พบในผู้สูงอายุ อาการมาด้วย hyperpigmented lesion ที่ vulva มักตรวจพบพร้อมกับตรวจภายใน ลักษณะรอยโรคเป็น multiple,brown flat,irregular border,uniformed pigmented ส่วนใหญ่มีขนาดเล็กกว่า 4 mm ในรอย หากมีขนาดใหญ่มากกว่า 10mm และเกิดที่ mucous membraneให้สงสัย melanoma การวินิจฉัยใช้อาการและอาการแสดงเป็นหลักหากสงสัย melanoma พิจารณา biopsy
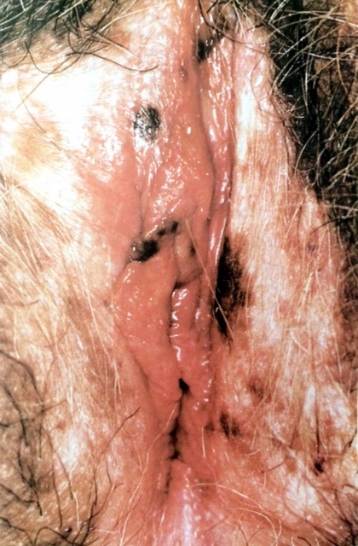
รูปที่ 19(3) : multiple hyperpigmented lesion typical of melanosis
• Seborrheic keratosis(3)
เป็น benign papular intraepithelial lesion มักเกิดในผู้สูงอายุ โดยส่วนใหญ่จะพบที่บริเวณลำตัวและใบหน้า อาจจะพบที่ปากช่องคลอดได้แต่พบได้น้อย มักจะไม่มีอาการ แต่หากโตเร็วและเพิ่มจำนวนอย่างรวดเร็วอาจจะสัมพันธ์กับ Internal malignancy โดยเฉพาะ GI tract โดยลัษณะรอยโรคจะยกนูกจากผิวหนังเล็กน้อย well demarcated ,pigmented ,waxy surface การรักษาโดยการ Excision biopsy
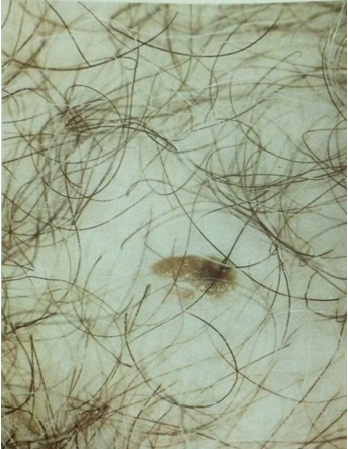
รูปที่ 20(3): Seborrheic keratosis
6. Blisters
• Lymphangioma (12)
เป็นโรคที่เกิดจากการ dilatation of lymph vessles ที่บริเวณผิวหนังและ subcutaneous tissue สามารถพบได้ทุกอายุ พบที่บริเวณ vulva ได้น้อย ลักษณะเป็น papule,nodule,vesicle และมี clear/milky fluidออกจากรอยโรค การวินิจฉัยโดยการ biopsy การรักษา ปัจจุบันแนะนำการทำ vaporization ด้วย CO2 laser การผ่าตัดมักจะไม่ค่อยประสบความสำเร็จและเกิด rapid relapse ได้หลังการผ่าตัด
รูปที่ 21(12): Lymphangioma
7. Erosion and ulcer(11)
โรคในกลุ่มนี้มีทั้ง infectious และ non infectious ในกลุ่ม infectious ส่วนใหญ่เป็น Sexually transmitted infection (STIs) โดยที่ Herpes simplex virus infection และ Syphilis พบได้บ่อยที่สุด
ตารางที่ 4 : Diagnosis and Treatment of Genital/vulvar ulcer(4, 11)
|
Disease/Etiology
|
Clinical presentation
|
Diagnosis
|
Treatment
|
|
Infectious
|
|||
|
Herpes simplex virus infection (HSV1,HSV2)
|
– Multiple vesicular lesion, painful,shallow ulcer
-Systemic symptom; fever, headache,malaise, lymphadenopathy in 1st time infections
|
– HSV culture/PCR of ulcer scraping or vesicle fluid aspirate
– Tzanck smear of ulcer scraping
– antiody titer
|
1st episode:
-acyclovir 400 mg orally tid
Or 200 mg orally 5 times/day
-valacyclovir 1 g orally bid
-Famciclovir 250 mg orally tid
(for 7-10days)
Recurrent episode
-acyclovir 400 mg orally tid or 800 mg orally bid for 5 days or 800 mg orally tid for 2 days
-valacyclovir 500 mg orally bid for 3 days or 1 g orally OD for 5 days
-Famciclovir 125 mg oral bid for 5 days or 1 g orally bid for 1 day or 5oo mg once then 250 mg orally bid for 2 days
Suppressive therapy
-acyclovir 400 gm orally bid
-Valacyclovir 500 mg orally OD or 1 g orally OD
– Famiciclovir 250 mg bid
|
|
Syphillis(primary): systemic diseas cause by Treponema pallidum
|
-Single,painless,well demarcated ulcer (Chancre) with clean base,indurated border
-Mild tender inguinal lymphadenopathy
|
–T. pallidum identified on darkfield microscopy/direct fluorescent antibody
-serologic nontreponemal test(VDRL/TPHA)
|
Benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units IM in a single dose
|
|
Chancroid
Haemophilus
Ducreyi
|
-nonindurated,painful with seriginous border and friable base;covered with necrotic often purulent exudate
-tender,suppurative unilateral inguinal lymphadenopathy
|
-Gram stain: gram negative,rod/coccobacillus in a school of fish pattern)
-H. ducreyi culture
|
-Azithromycin 1 g orally in a single dose
-Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM in a single dose
-Ciprofloxacin 500 mg orally twice a day for 3 days
–Erythromycin base 500 mg orally three times a day for 7 days
|
|
Noninfectious
|
|||
|
Behçet syndrome
-rare inflammatory disorder
|
Classic symptom triad 1.Recurrent oral apthae/ulcers
2.Recurrent genital apthae/ulceration
3.uveitis
|
-Consider Rheumatoid factor,ANA testing
-Biopsy:diffuse arteritis with venulitis
-clinical diagnosis (Triad)
|
-Spontaneous regression
-Pegylated interferon alfa-2a(pegasys),6 million unit sc 3 times weekly for 3 months for mucocutaneous involvement
|
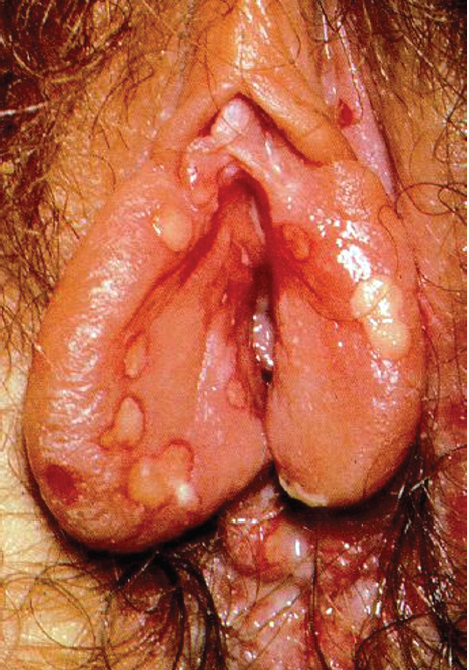
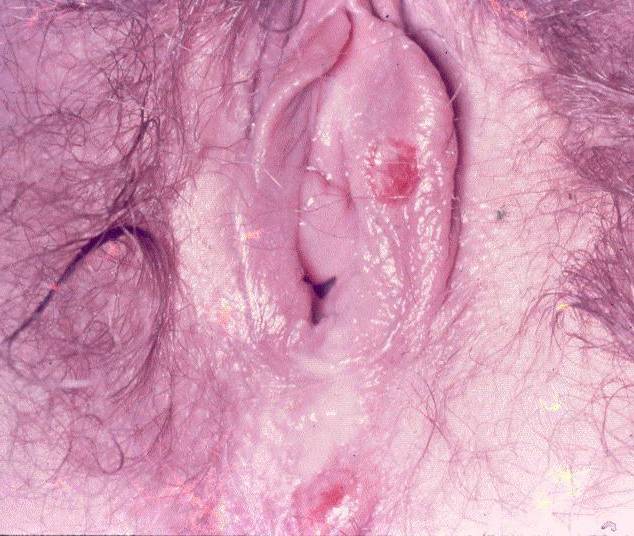
รูปที่ 22(11): Genital HSV; Painful, shallow ulcer
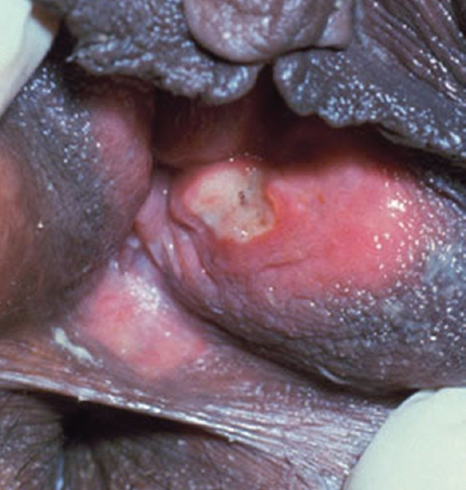
รูปที่ 24(11): Chancroid ulcer; painful, nonindurated with serpiginous border and friable base, covered with purulent exudate
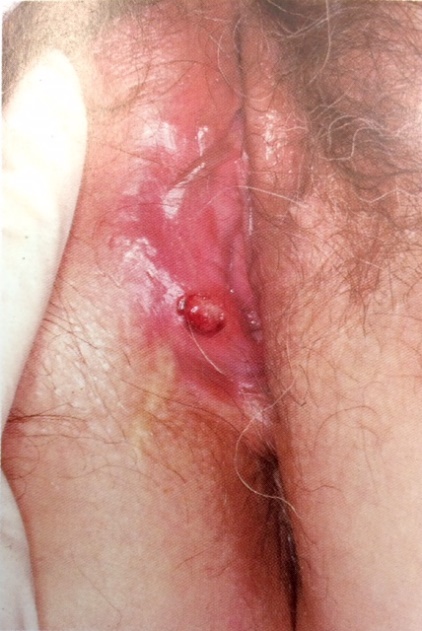
รูปที่ 25(5): Behçet syndrome; genital apthae, oral apthae must be present
8. Edema (diffuse genital swelling)
• Cellulitis /abscess(20)
ผิวหนังอักเสบหรือ abscess เกิดจากเชื้อ Staphylococcus aureus(64%) และเชื้ออื่นได้แก่ E. coli, Proteus, GBS (36%) ลักษณะผื่นจะบวม แดง ปวด อาจจะมีลักษณะ fluctuant mass การรักษาโดย antibiotic กลุ่ม penicillin(ceftriaxone) หรือ clindamycin ในกลุ่มที่รุนแรงพิจารณาให้ Vancomycin+piperacillin/tazobactam หรือ Penicillin+clindamycin
เอกสารอ้างอิง
- Human Papillomavirus. Available from: http://mizzouderm.weebly.com/virus.html.
- Saporta L. URETRAL CARUNCLE 2015. Available from: http://www.leonsaporta.com/en/conditions/female-urology/uretral-caruncle/.
- Wilkinson EJ. Atlas of vulvar disease. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer / Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2008.
- Prevention CfDCa. Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines, 2015. 2015.
- Black MM, ed. Obstetric and gynecologic dermatology. 2nd ed. London: Mosby International; 2002.
- C. D. Female GU Lecture 1 Vulva vagina 2013. Available from: https://www.studyblue.com/notes/note/n/female-gu-lecture-1-vulva-vagina/deck/5382102.
- Mills SE, ed. Histology for pathologists 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007.
- Vaginal condylomata acuminata (genital warts) 2008. Available from: http://pictures.doccheck.com/com/photo/1270-vaginal-condylomata-acuminata-genital-warts.
- Kirtschig G. Lichen Sclerosus-Presentation, Diagnosis and Management. Deutsches Arzteblatt international. 2016;113(19):337-43.
- ทองสง ธ. นรีเวชวิทยา : ฉบับสอบบอร์ด. 4th ed. กรุงเทพฯ: พี.บี. ฟอเรน บุ๊คส์ เซนเตอร์; 2559.
- Roett MA, Mayor MT, Uduhiri KA. Diagnosis and management of genital ulcers. American family physician. 2012;85(3):254-62.
- Ucmak D, Aytekin S, Sula B, Akkurt ZM, Turkcu G, Agacayak E. Acquired vulvar lymphangioma circumscriptum. Case reports in dermatological medicine. 2013;2013:967890.
- Maldonado VA. Benign vulvar tumors. Best practice & research Clinical obstetrics & gynaecology. 2014;28(7):1088-97.
- Bartholin Cyst 2005-2016. Available from: https://www.netterimages.com/bartholin-cyst-unlabeled-gynecology-craig-mascaro-4349.html.
- Bornstein J. Benign Disorders of the Vulva & Vagina. In: Alan H. DeCherney ea, editor. Current diagnosis & treatment : obstetrics & gynecology 11th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2013.
- Lynch PJ, Moyal-Barracco M, Scurry J, Stockdale C. 2011 ISSVD Terminology and classification of vulvar dermatological disorders: an approach to clinical diagnosis. Journal of lower genital tract disease. 2012;16(4):339-44.
- Park IU, Introcaso C, Dunne EF. Human Papillomavirus and Genital Warts: A Review of the Evidence for the 2015 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines. Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2015;61 Suppl 8:S849-55.
- Prevention CfDCa. Genital / vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) 2014. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/fungal/diseases/candidiasis/genital/index.html.
- Sajadi KP. Urethral Caruncle 2015. Available from: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/443099-overview?pa=QOV8aNkOJ0HTLFXyxLDtBgw8XK9Ns%2FwmxV7K3jsQG1ycLrz96HeTaJhJraH5o0aN2aUKwFpH47ZoQEabxxABLMxINcH%2BsxRbWLj4dpGggpU%3D#a10.
- Wood SC. Clinical Manifestations and Therapeutic Management of Vulvar Cellulitis and Abscess: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Necrotizing Fasciitis, Bartholin Abscess, Crohn Disease of the Vulva, Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Clinical obstetrics and gynecology. 2015;58(3):503-11.


