By Assoc. Prof. Dr. Direk Phatikulsila
Diabetes (diabetes mellitus) is a disease characterized by high blood sugar levels. It causes complications of the body in many systems, such as coronary artery disease, kidney failure, diabetic retinopathy, foot ulcers, etc. Nowadays, diabetes is increasingly found. and is a major problem worldwide.
Diabetes can cause many eye complications such as corneal peeling, glaucoma, cataracts, peripheral nerve degeneration, etc. However, the main complication that causes blindness is Diabetic retinopathy
Diabetes mellitus upward to Retina
Prolonged high blood sugar levels can cause retinal vascular disorders, including:
1. There is a weakening of the vascular walls of the retina. Causing the capillary to swell, known as microanurism. Microaneurysms are the first detection in early-onset diabetic retinopathy. Microanurism often ruptures causing scattered dot and blot hemorrhages. Often there is a leak causing water and grease to leak out. Causes retinal edema and yellow fat spots (lipid exudates).
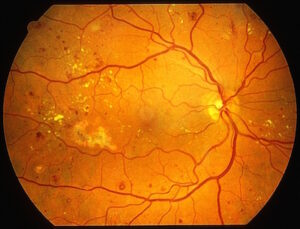
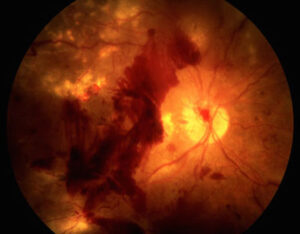
2. In patients with long-term and severe diabetes will cause small capillaries to be clogged causing the retina to lack blood If there is a lack of blood in the clear vision area, it will make the eyes very blurry. In cases with severe retinal ischemia, new capillaries will grow to form a fan-like network. During neovascularization, these abnormal capillaries may rupture. causing severe vitreous hemorrhage followed Or these abnormal blood vessels may have a membrane covering and pulling the retina to severely detachment.
Diabetic retinopathy is divided into 2 stages:
1. Early diabetic retinopathy or the stage where no new capillaries have grown (non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy or NPDR)
2. Severe diabetic retinopathy or the stage where new capillaries grow (proliferative diabetic retinopathy or PDR)
The presence of macular edema is a common cause of amblyopia in patients with diabetic retinopathy. It can be found in both early and severe diabetic retinopathy. Therefore, although overall diabetic retinopathy is not severe, But if there is retinal edema in the area of clear image It can make your eyes very blurry. which needs treatment
Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy
Factors that affect having more or less diabetic retinopathy are as follows:
1. Length of time with diabetes The longer you have diabetes The more likely to be found to have diabetic retinopathy more often and more severely.
2. Controlling blood sugar levels, the better it can be controlled, the more likely it is to reduce and reduce the severity of diabetic retinopathy.
3. Having kidney failure from diabetes It is an indicator that there is likely to be diabetic retinopathy as well. Treatment of kidney disease contributes to improving diabetic retinopathy.
4. High blood pressure can cause abnormalities of the blood vessels of the retina. aggravate diabetic retinopathy even more
5. High blood lipids Treatment of hyperlipidemia may reduce the leakage of fatty deposits in the retina.
6. Women with diabetes and pregnancy Can cause diabetes in the retina or can make diabetic retinopathy already more severe
Symptom
In the early stages of diabetic retinopathy, there will be no symptoms, but as it progresses, it often causes blurred vision. Seeing a cobweb-like shadow floating around Some people see distorted images. or have a curtain to cover But some people may have no symptoms at all, even with severe diabetic retinopathy. Only an eye examination by an ophthalmologist will know if you have diabetic retinopathy.
Eye examination by an ophthalmologist
Eye examination by an ophthalmologist It will start from taking history. duration of diabetes history of diabetes control Other congenital diseases found together with Family history of diabetes Symptoms brought to the doctor After that, vision is checked. Examine the front of the eye. and intraocular pressure was measured The iris will need to be dilated to examine the retina thoroughly. to check if there is diabetic retinopathy or not
Dilated pupils usually cause blurred vision for about 4-6 hours, so driving during this time is not recommended. and should accompany relatives
When should people with diabetes get their eyes checked?
Diabetic patients who do not rely on insulin injections You should get your eyes checked as soon as you know you have diabetes. As for diabetics who depend on insulin, in the first 5 years may not need an eye exam. (But you can check) if the results of the first examination show that diabetes has not yet appeared. Should be rechecked at least once a year, but if found to have diabetic retinopathy It may be necessary to check more often, such as every 3-6 months, depending on the severity.
Treatment
How to treat diabetic retinopathy depending on the stage of diabetic retinopathy
1. Early diabetic retinopathy (NPDR)
If there is only microanurism and a small amount of hemorrhage visibility is still good There is no need for eye treatment. Just to control diabetes well.
but if more until there is a clear image edema It is necessary to start with laser light therapy.
2. Severe diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
This group of patients is at risk of developing Bleeding from capillary rupture causing severe vitreous hemorrhage followed Or in some cases, the membrane pulls back to cause the retina to peel off.
At the stage, only capillaries were found. But there is still no bleeding in the vitreous or the retina is detached from the fascia. The doctor will provide treatment with laser irradiation. which will cause the capillaries to atrophy
But in the case of vitreous bleeding or retinal detachment from the fascia pulling back, the eye is very blurry, the doctor will recommend vitreous surgery. Some patients may need to apply gas or silicone oil to press down on the detached retina to reattach.
Treatment Effect
The retina is a very delicate and sensitive organ. Retinal swelling or lack of blood supply usually partially deteriorates depending on the severity of the disease. even after receiving full treatment Vision may not return to normal. Generally after laser treatment Vision is almost the same as before, compared to before the laser.
Vitreous surgery In cases where there is only vitreous hemorrhage but the retinal degeneration is not much Vision could be greatly improved. but the retina detachment from the fascia pulls back There is often a poor prognosis. (some may be better But many cases are not getting better. or a minority may be completely blind)
Nowadays, injections are used that block capillary leakage. (anti-vascular endothelial growth factor) is used in the treatment by injecting into the vitreous. But there are also limited uses. and is only an option
Protection
Diabetic retinopathy is common nowadays. and more and more It is a serious disease that can lead to blindness. It is essential that there is team coordination in treatment. among diabetic patients, physicians and ophthalmologists as well as relevant physicians such as cardiologists, nephrologists and surgeons (if there is a foot ulcer).
Patients with diabetes need periodic eye exams. At least once a year or more often depending on the severity of diabetic retinopathy Immediately see an ophthalmologist if you notice any visual disturbances.
Patients must control their sugar levels, blood pressure and lipids to the appropriate level. should exercise regularly and absolutely avoid smoking
This is because blood sugar control is very important for the long-term progression of the disease. The blood sugar test detects the sugar at that time and can fluctuate a lot. Currently, there is a test for Hemoglobin A1c, which is the average of sugar in the past 2-3 months. The normal value for people without diabetes is 5 milligrams percent. Patients with well-controlled diabetes should be below 7 mg% if the Hemoglobin A1c is greater than 8 mg%. Will have to change the treatment, such as medication, diet control exercise, stress
