Noninvasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
Noninvasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
พญ.ลินลดา วิจักขณ์อุรุโรจน์
รศ.นพ.ชเนนทร์ วนาภิรักษ์
เซลล์ลูกในเลือดแม่ มี 2 ชนิดคือ Intact fetal cell และ cell- free fetal DNA(1)
- Intact fetal cell คือเซลล์ลูกที่พบในเลือดแม่และคงอยู่ในกระแสเลือดแม่ได้ถึง 10ปี หลังคลอด เป็นเซลล์ที่พบได้ในปริมาณน้อย และเป็นส่วนหนึ่งในการก่อให้เกิดโรค autoimmune diseaseในแม่ เช่น SLE ,scleroderma, Hashimoto Thyroiditis เป็นต้นในทางปฏิบัติไม่สามารถนำมาใช้ในการ prenatal diagnosis ได้เนื่องจากเป็นเซลล์ที่มีปริมาณน้อย คงอยู่นานหลังคลอด และแยกจากเลือดแม่ได้ยาก
- Cell-free fetal DNA คือ สิ่งที่ปล่อยจาก apoptotic placental trophoblast เข้าสู่เลือดแม่ สามารถตรวจพบได้ตั้งแต่ อายุครรภ์ 7 สัปดาห์ และพบในกระแสเลือดแม่ถึง 3-6% และปริมาณจะเพิ่มขึ้นตามอายุครรภ์ และขับออกจากกระแสเลือดแม่ภายใน1-2 ชั่วโมงหลังคลอด โดยเซลล์ชนิดนี้เป็นสิ่งที่สามารถนำมาใช้ตรวจหา โรคทางพันธุกรรม( single gene disorder), หมู่เลือดในลูก( fetal Rh D genotype evaluation), เพศลูก(Fetal Sex determination) และ การตรวจคัดกรอง aneuploidy(NIPT)
NIPT ( Noninvasive prenatal testing )
เป็นวิธีหนึ่งในการตรวจคัดกรองเพื่อหาfetal aneuploidy โดยใช้ cell- free fetal DNA มา sequence DNA fragment เพื่อดูอัตราส่วนของ โครโมโซมที่สงสัยว่ามีปริมาณมากเกินปกติหรือไม่ เช่น หากทารกมีภาวะเป็น Trisomy 21 จะตรวจพบDNA sequence ของ โครโมโซมคู่ที่ 21 มากกว่าปกติ
วิธีนี้มี ความไวในการตรวจคัดกรอง(sensitivity) 98% และอัตราการเกิดผลบวกลวง(false positive rate)<0.5% ในการตรวจคัดกรองโรคกลุ่มดาวน์(Down’s syndrome)ซึ่งจัดว่าเป็นวิธีที่มีdetection rate ที่สูงกว่าวิธีตรวจคัดกรองอื่นๆตามตารางที่1(1)
{tabulizer:style[gr.alterora.elemental_1_green.css]}
| Screening Strategy | Detection Rate(%) |
| First trimester screening (NT+PAPP-A+hCG) | 79-87 |
| NT alone | 64-70 |
| Triple test | 61-70 |
| Quadruple Test | 74-81 |
| Integrated screening | 94-96 |
| Stepwise sequential screen | 90-95 |
| Contingent sequential screen | 88-94 |
| Cell-free fetal DNA | 98 |
ตามความเห็นจาก ACOG (American College of Obstetrician and Gynecologists) และ sMFM opinion ปี 2012 แนะนำว่าNIPT เป็นวิธีการตรวจคัดกรองที่มีประสิทธิภาพที่สุดในกลุ่ม high risk pregnancy ซึ่งข้อบ่งชี้ที่สามารถแนะนำให้ตรวจคัดกรองได้แก่(2)
- สตรีตั้งครรภ์ที่มีอายุ ≥ 35 ปี
- มีหลักฐานจาก ultrasound ตรวจพบว่าทารกมีความเสี่ยงสูงต่อการเกิด aneuploidy
- มีประวัติบุตรคนก่อนเป็น fetal aneuploidy
- เคยตรวจคัดกรองด้วยวิธีอื่น เช่น serum marker แล้วพบว่าทารกมีความเสี่ยงสูงต่อการเกิด fetal aneuploidy
- สตรีตั้งครรภ์หรือสามีตรวจพบเป็น balanced Robertsonian translocation ของโครโมโซมคู่ที่21หรือ13
Consensus statement จาก ISUOG (International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology) ได้กล่าวถึงประเด็นเพิ่มเติมดังนี้(3)
- หาก ทำ ultrasound anomaly screening แล้วพบว่ามี structural anomaly แนะนำให้ทำ fetal karyotyping แม้ว่าจะตรวจพบว่า ผล NIPT ปกติก็ตาม
- สตรีตั้งครรภ์ทุกรายควรได้รับการทำ first-trimester ultrasound แม้ว่าจะทำ NIPT หรือไม่ก็ตาม
- เสนอ 3 ทางเลือกเพื่อการประเมิน fetal trisomy 13,18,21 ได้แก่
- Maternal age + NT+/-serum marker
- PND in high risk group
- NIPT เป็น primary screening แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม การใช้NIPT ใน low risk group ยังไม่มีข้อมูลการศึกษาที่เพียงพอ อีกทั้งประชากรกลุ่มนี้เป็นกลุ่มที่มี PPV ต่ำอยู่แล้ว ปัจจุบันจึงแนะนำให้ใช้เฉพาะในกลุ่ม intermediate group
- หากทำ NIPT แล้วพบว่าผลปกติ จะไม่มีความจำเป็นที่จะต้องทำ genetic sonogram (soft marker ของ Down’s syndrome ) เนื่องจาก มี false positive rate ที่สูงกว่าและมี PPV ที่น้อยกว่าเมื่อเทียบกับ NIPT
- ไม่แนะนำให้ใช้ NIPT แทนการทำ PND ในกลุ่ม high risk group จากการทำ serum marker screening
- หากผลตรวจ NIPT ปกติ ไม่มีความจำเป็นต้องตรวจ NTและ serum marker ซ้ำอีก
- ความแม่นยำในการใช้ NIPT ในกรณีที่เป็นครรภ์แฝด ยังไม่เป็นที่สรุปแน่ชัด
Bioinformatics techniques in NIPT(4-9)
ตั้งแต่ ค.ศ.1999 มีการศึกษาพบว่าสามารถสตรีตั้งครรภ์ที่ทารกในครรภ์เป็น Down’s syndrome จะมีปริมาณ fetal DNA ในเลือดแม่ในระดับที่สูงกว่าครรภ์ปกติ จึงมีการใช้เทคนิคต่างๆในการตรวจหาปริมาณ DNA ดังกล่าวได้แก่ DNA Methylation, circulating fetal RNA analysis ,allelic ratio measurement อย่างไรก็ตามวิธีดังกล่าวต้องใช้ markerที่หลากหลายในการตรวจเนื่องจากไม่สามารถหา markerที่เป็นตัวแทนของทุกtest ได้ จึงทำให้การตรวจมีข้อจำกัดมาก(4)
ในปี ค.ศ.2007 ได้มีการศึกษาวิธีการตรวจโดยใช้ digital PCR techniqueซึ่งเป็นการนับปริมาณ DNA moleculeและหากยิ่งมีปริมาณมาก ประสิทธิภาพในการแยก DNA ก็จะสูงขึ้นตามลำดับดังนั้นการใช้วิธีนี้จะมีข้อจำกัดในรายที่มีปริมาณของ cffDNAน้อย(4, 8, 9)
ในปี ค.ศ.2008 มีการศึกษาเกี่ยวกับการนำ MPS(Massively parallel sequencing)มาใช้ในการหาปริมาณDNA ซึ่งพบว่ามีข้อดีกว่าการใช้ digital PCRเนื่องจาก digital PCR จะตรวจพบเฉพาะ DNA ที่จำเพาะต่อ RNA primer เท่านั้น ในปัจจุบัน MPSที่ใช้อย่างแพร่หลายมี 2 วิธีคือ 1.Shotgun sequencing 2.Targeted sequencing(4)
1. Shotgun sequencing(5)
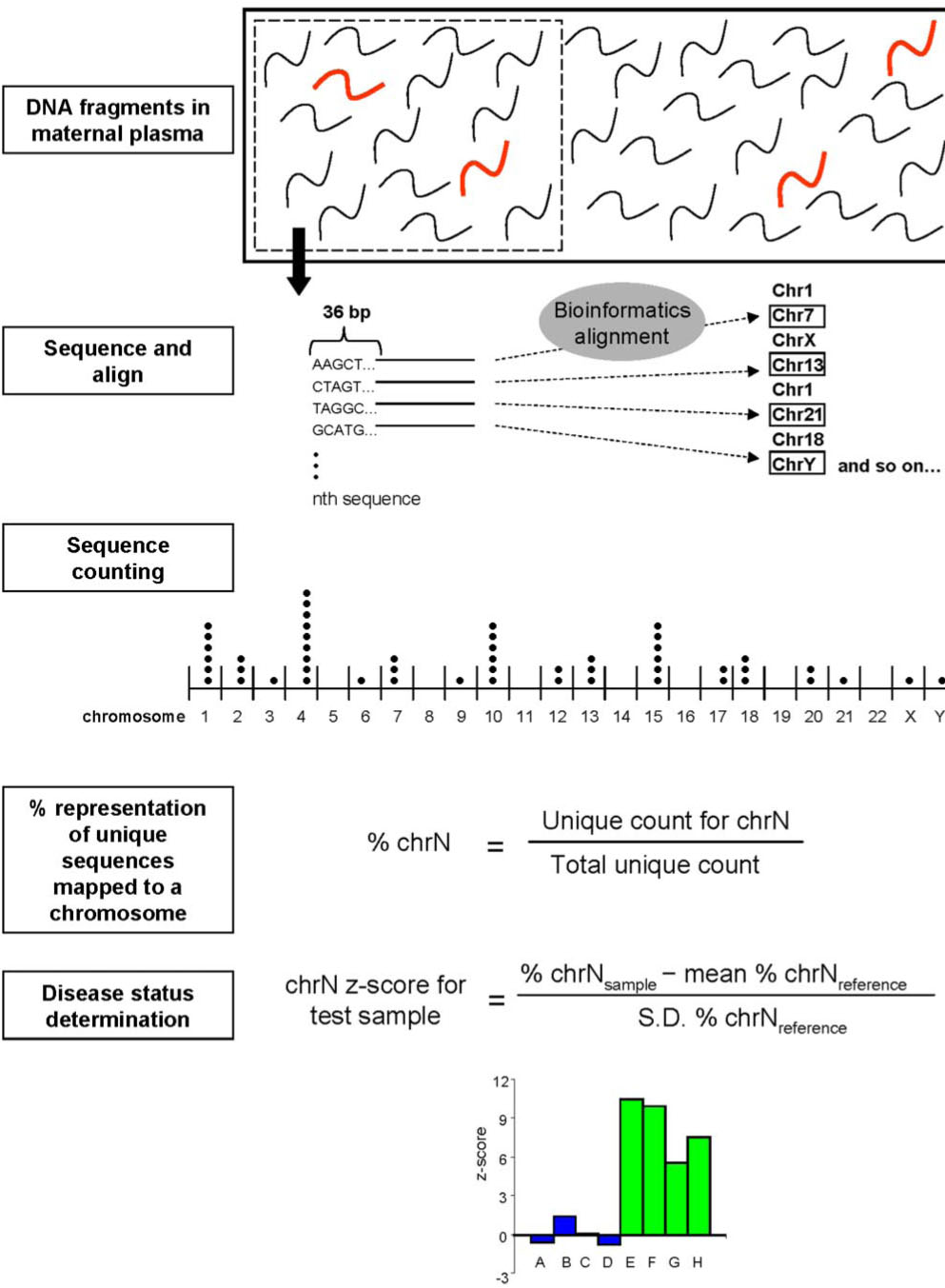
หลักการ : DNA ใน maternal serum จะถูกนำมาsequence แบบสุ่มในรูปแบบอัตราส่วนของ DNA ของโครโมโซมที่เราสนใจกับ DNAของโครโมโซมอื่นใน genomeดังแสดงตามรูปที่1
ข้อดีคือ ขั้นตอนในการ DNA sequencingของโครโมโซมที่เราสนใจจะไม่ขึ้นกับ genomic location ทำให้สามารถตรวจพบ genomic aberration ทุกที่ใน genomeและสามารถหา fetal whole genome sequencing จาก maternal serum ได้
2. Targeted sequencing(6, 7, 10)
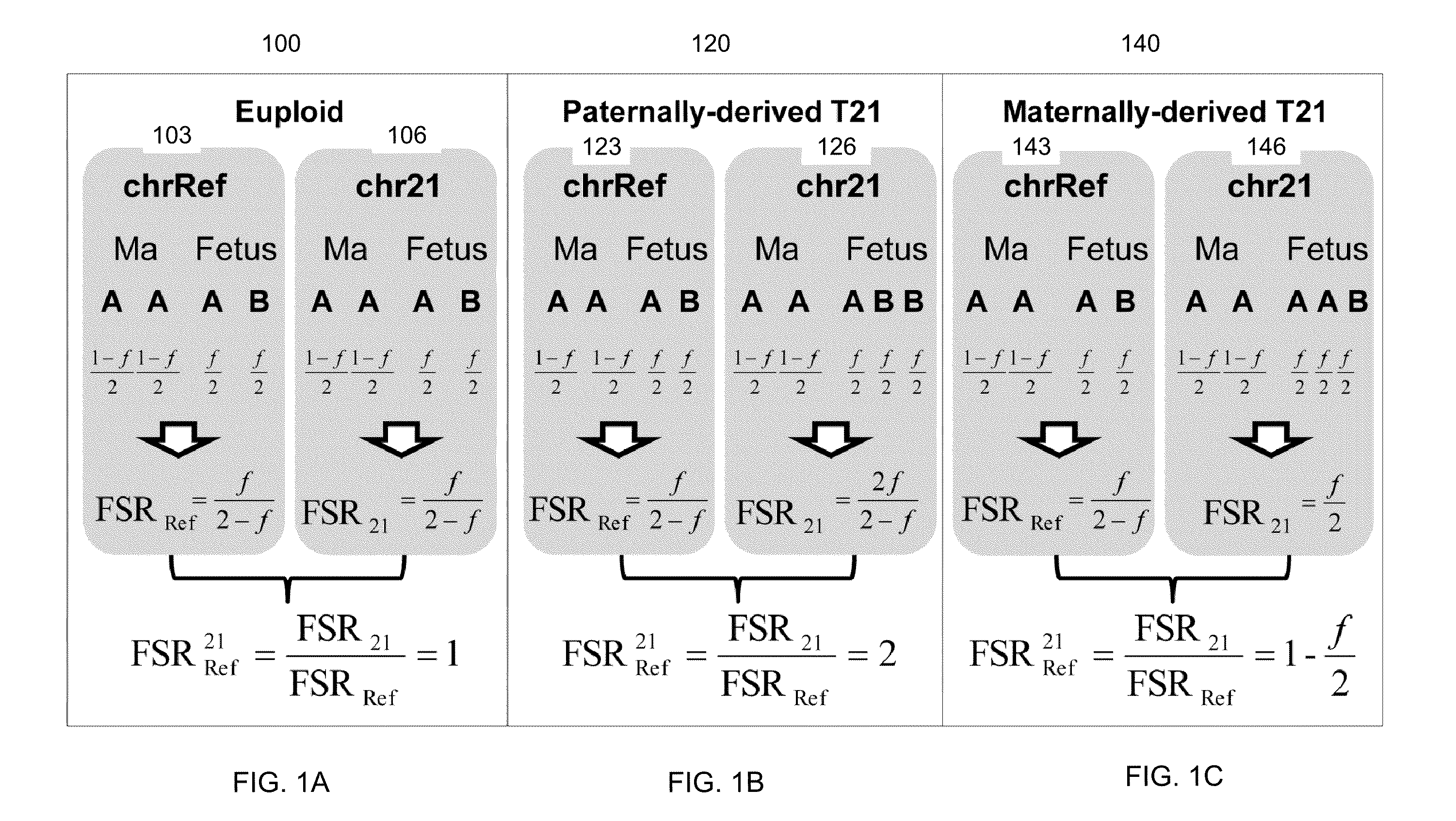
หลักการ:เป็นการเลือกsequenceเฉพาะ regionของgenomeที่มีโครโมโซมที่เราสนใจ(targeted region) เทียบกับ regionอ้างอิง ในปัจจุบัน มี 2วิธีที่ใช้คือ 1.ใช้ Digital Analysis of Selected Region essay (DANSR)(10)กับ targeted genome ที่ไม่มีความแตกต่างระหว่างบุคคล 2.ใช้วิธี allelic ratio analysis หากtargeted genome มี polymorphic ในกลุ่มประชากร ตามแสดงในรูปที่ 2
ข้อดี คือ sequencing power สูงและสามารถเลือก region ที่ต้องการให้ sequence ได้ แต่ข้อเสียคือ ต้องมี panel ที่จำเพาะต่อการทำ DNA hybridization probe, PCR primer
Possible causes of errors
RCOG( Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists )ได้กล่าวถึงข้อควรระวังในการใช้ NIPT ในกรณีต่างๆต่อไปนี้(4)
1. Early Gestational age
ปริมาณของ cffDNAเพิ่มขึ้นตามอายุครรภ์ ดังนั้นหากตรวจในช่วง early gestation อาจพบปัญหา false negative ของ Y chromosome และ RhDในขณะที่ aneuploidy screening จะสามารถตรวจพบความผิดปกติได้เมื่อมีปริมาณ fetal cell อย่างน้อย 4-5% หรือตั้งแต่หลัง GA 10 wkเป็นต้นไป ดังนั้นหากคนไข้ต้องการตรวจ NIPT ควรทำ ultrasound เพื่อยืนยันอายุครรภ์ก่อนทุกครั้ง
2. Maternal Obesity
จากการศึกษาพบว่าในมารดาที่น้ำหนักมากจะพบปริมาณของ cffDNAได้น้อยกว่าคนที่น้ำหนักปกติ โดยกลไกยังไม่เป็นที่ทราบแน่ชัดแต่เชื่อว่าเกิดจากการที่มีปริมาณของ maternal plasma DNA ที่เพิ่มขึ้น หรืออาจเกิดจาก blood volume ที่มากขึ้นและเกิด hemodilutionจึงทำให้ปริมาณ cff DNA ลดลงอย่างมีนัยสำคัญ จึงเป็นข้อที่ควรพิจารณาและแจ้งให้คนไข้ทราบก่อนทุกครั้ง
3. Multiple pregnancies
ในการตั้งครรภ์แฝดชนิด Monochorionการตรวจจะให้ผลที่มีประสิทธิภาพมากกว่า Singleton pregnancy เนื่องจากหากจะพบปริมาณ cff DNA ได้เป็น 2 เท่าของครรภ์ปกติ แต่ในรายที่เป็นครรภ์แฝดชนิด Dichorionการแปลผลจะทำได้ยากกว่าเนื่องจากอาจมีแฝดปกติและผิดปกติในครรภ์เดียวกันเช่นเดียวกับtwin pregnancy with one vanishing twin อย่างไรก็ตามมี 2การศึกษาที่รายงานว่าการใช้วิธี shotgun-MPS สามารถแปลผลในรายที่เป็น twin pregnancy ได้และยังสามารถบอก zygosityของ twinได้อีกด้วย
4. Placental mosaicism
เนื่องจาก cffDNAมาจาก apoptotic trophoblast ดังนั้นหากมีภาวะ CPM (Confined Placental Mosaicism )ซึ่งพบได้1% แต่หากมีภาวะนี้ จะส่งผลให้เกิดการแปลผลโครโมโซมผิดพลาดเกิดเป็น false positiveได้ทั้งที่ทารกปกติ ดังนั้นจึงต้องมีการทำ confirmatory test ด้วย PNDทุกครั้งหากผล NIPT ผิดปกติ
5. Maternal condition
หากมารดามีภาวะ mosaicism หรือมีmalignancy condition อยู่ จะทำให้เกิดfalse- positive ได้
Comparison between commercial NIPT
ในปัจจุบันได้มีการใช้ NIPT ในการ screening โดย commercial kit จากบริษัทที่มีในปัจจุบันได้แก่ NIFTY, NIPS, Harmony และ Panorama โดยมีคุณสมบัติแตกต่างกันเล็กน้อยดังตาราง
{tabulizer:style[gr.alterora.elemental_1_blue_green.css]}
| NIFTY | NIPS | Harmony | Panorama | |
| Chromosome coverage | All | All | 13,18,21,X,Y | 13,18,21,X,Y |
| Timing to Test | GA10 wk (singleton) / GA12wk (Twin) | GA10wk (both) | GA10wk (both) | GA9 wk |
| Available for twin | Yes | Yes(Monozygote) | Yes | No |
| Available for triplet | Yes | No | No | No |
| Surrogate mother | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Insurance for false positive rate | 1,000,000 baht | 2,000,000baht | No | No |
| Resample | 1-3% | 1-3% | 1-3% | 5-12% |
| Time to report | 10 days | 8-12days | 8-12days | 10-14days |
บทสรุป
- สตรีตั้งครรภ์ทุกรายควรได้รับคำแนะนำในการตรวจคัดกรองต่อความเสี่ยงในการมีลูกเป็นtrisomy
- มีการคัดกรองมีหลายรูปแบบ ควรเลือกตามความพร้อมของทรัพยากรและบุคคล
- NIPT เป็นวิธีการตรวจคัดกรองที่ได้รับการยอมรับว่ามี ความไวสูงสุดและผลบวกลวงน้อยที่สุด
- แม้ว่า NIPT จะเป็นวิธีการคัดกรองที่ได้ผลดีแต่ก็ไม่สามารถนำมาใช้แทนการตรวจวินิจฉัยได้
- เนื่องจาก NIPT คือการตรวจหาปริมาณ cell free fetal DNA(cffDNA) ดังนั้นยิ่งอายุครรภ์มากก็จะตรวจพบได้ในปริมาณที่มากขึ้น ปกติแล้วจะแนะนำให้ตรวจได้ตั้งแต่อายุครรภ์ 10 สัปดาห์เป็นต้นไป
- นอกจากประโยชน์ในการตรวจคัดกรองเรื่อง fetal aneuploidy แล้ว NIPT ยังสามารถใช้ในการตรวจหา RhD blood group,Single gene disorder, fetal sex determination ได้อีกด้วย
เอกสารอ้างอิง
- F.Gary Cunningham KJL, Steven L.Bloom,Catherine Y.Spong,Jodi S.Dashe,Barbara L. Hoffman,Brian M.Casey,Jeanne S. Sheffield. Williams obstetrics. 2014 ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2014.
- Committee Opinion No. 545: Noninvasive Prenatal Testing for Fetal Aneuploidy. Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2012;120(6):1532-4 10.097/01.AOG.0000423819.85283.f4.
- Salomon LJ, Alfirevic Z, Audibert F, Kagan KO, Paladini D, Yeo G, et al. ISUOG consensus statement on the impact of non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) on prenatal ultrasound practice. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2014;44(1):122-3.
- Scientific Impact Paper No. 15: Non-invasive Prenatal Testing for Chromosomal Abnormality using Maternal Plasma DNA. The Obstetrician & Gynaecologist. 2014;16(2):148-.
- Chiu RWK, Chan KCA, Gao Y, Lau VYM, Zheng W, Leung TY, et al. Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal chromosomal aneuploidy by massively parallel genomic sequencing of DNA in maternal plasma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2008;105(51):20458-63. PubMed PMID: PMC2600580.
- Liao GJW, Chan KCA, Jiang P, Sun H, Leung TY, Chiu RWK, et al. Noninvasive Prenatal Diagnosis of Fetal Trisomy 21 by Allelic Ratio Analysis Using Targeted Massively Parallel Sequencing of Maternal Plasma DNA. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(5):e38154. PubMed PMID: PMC3362548.
- Zimmermann B, Hill M, Gemelos G, Demko Z, Banjevic M, Baner J, et al. Noninvasive prenatal aneuploidy testing of chromosomes 13, 18, 21, X, and Y, using targeted sequencing of polymorphic loci. Prenatal Diagnosis. 2012;32(13):1233-41.
- Lo YMD, Lun FMF, Chan KCA, Tsui NBY, Chong KC, Lau TK, et al. Digital PCR for the molecular detection of fetal chromosomal aneuploidy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2007;104(32):13116-21. PubMed PMID: PMC1934923.
- Fan HC, Quake SR. Detection of Aneuploidy with Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction. Analytical Chemistry. 2007 2007/10/01;79(19):7576-9.
- Sparks AB, Wang ET, Struble CA, Barrett W, Stokowski R, McBride C, et al. Selective analysis of cell-free DNA in maternal blood for evaluation of fetal trisomy. Prenatal Diagnosis. 2012;32(1):3-9.

